Big data has moved from being a technical buzzword to becoming the backbone of how modern businesses operate. Today, organizations process more information in a day than entire industries did in a year just a decade ago. According to Statista’s global data volume forecast, the total amount of data created, captured, copied, and consumed globally is projected to exceed 180 zettabytes by 2025 and reach approximately 200 zettabytes by 2027, with continued exponential growth expected through the decade. This explosion isn’t just about volume anymore.
Big data trends now focus on how quickly we can extract value, how intelligently systems can learn from information, and how securely we can handle sensitive data across global operations. Companies leveraging these trends report 5-6% higher productivity compared to competitors who lag behind. The stakes are clear: organizations that adapt to emerging patterns in data collection, processing, and analysis gain significant competitive advantages, while those that don’t risk falling behind in their markets.
This guide breaks down the most important big data trends reshaping how businesses make decisions, deploy artificial intelligence, and transform their digital operations in 2026 and beyond.
Top Big Data Trends Shaping the Future in 2026
The big data space is experiencing its most dynamic period yet, with new approaches emerging that fundamentally change how organizations handle information. Each trend represents not just technological advancement but a shift in business strategy and operational thinking.
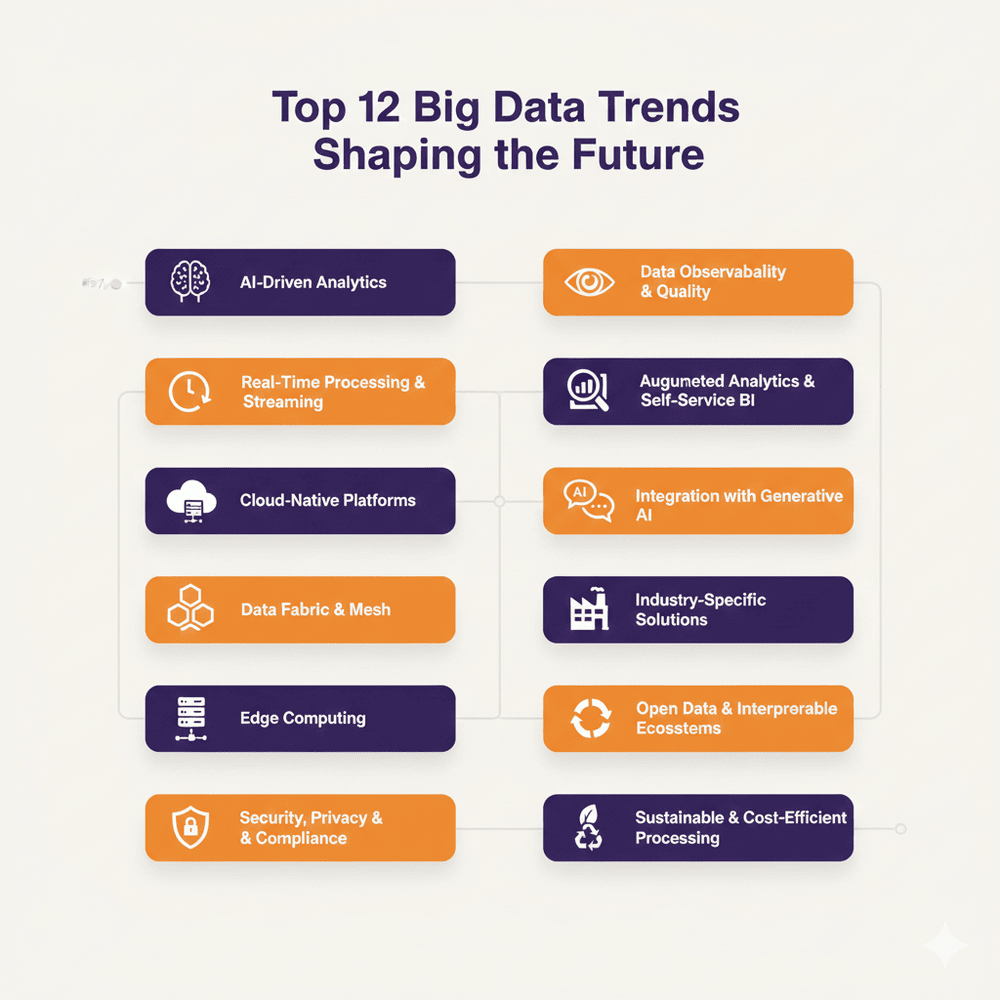
Trend 1: AI-Driven Big Data Analytics
Artificial intelligence has become the primary engine driving value from massive datasets. In 2026, AI doesn’t just analyze data after humans define the questions. Modern systems combine big data and predictive analytics to identify patterns, suggest investigations, and generate insights autonomously. Technologies like Apache Spark MLlib, TensorFlow Extended, and cloud-native ML platforms now process petabytes of information to uncover opportunities human analysts might miss entirely.
What makes this trend revolutionary is the feedback loop. AI models train on historical data, make predictions, observe outcomes, and refine their algorithms continuously. Financial institutions use this approach to detect fraud patterns that evolve daily. Retailers predict customer behavior with accuracy that seemed impossible just three years ago.
The business impact extends beyond efficiency. Companies using AI-driven analytics make faster decisions with greater confidence. Marketing teams optimize campaigns in real-time based on customer response patterns. Supply chain managers anticipate disruptions before they occur. Manufacturing plants predict equipment failures weeks in advance, preventing costly downtime.
Trend 2: Real-Time Data Processing & Streaming Analytics
Batch processing no longer meets business needs when customer expectations and market conditions change by the minute. Real-time data processing has shifted from nice-to-have to business-critical infrastructure. Streaming analytics platforms now handle billions of events per day, processing information the moment it’s generated rather than hours or days later. Organizations adopting designing big data architecture for real-time insights ensure that pipelines and event-driven systems are optimized for low-latency operations.
Apache Kafka has become the backbone of real-time data architectures, with organizations using it to build event-driven systems that respond instantly to changing conditions. Combined with processing frameworks like Apache Flink and Apache Beam, businesses create pipelines that analyze data in motion, not just data at rest.
The business value is immediate and measurable. E-commerce platforms adjust pricing dynamically based on demand, inventory, and competitor actions. Ride-sharing services balance supply and demand across cities in real-time. Financial trading systems execute transactions in milliseconds based on market movements and risk calculations.
Trend 3: Cloud-Native Big Data Platforms
The migration to cloud-native architectures represents more than just moving data from on-premises servers to cloud storage. Modern cloud-native platforms fundamentally reimagine how data systems work. They separate storage from compute, allowing organizations to scale each independently based on actual needs rather than worst-case scenarios.
Platforms like Snowflake, Databricks Lakehouse, and Google BigQuery exemplify this new approach. They eliminate much of the complexity that plagued earlier big data systems. Data teams no longer spend weeks configuring clusters or optimizing storage layouts. The platforms handle these technical details automatically while exposing simple interfaces for analysis and application development.
Cost efficiency has improved dramatically. Organizations pay only for the compute and storage they actually use, not for idle capacity sitting unused most of the time. Automatic scaling means systems handle peak loads without manual intervention, then scale down during quiet periods to minimize expenses.
The business impact extends beyond cost savings. Cloud-native platforms enable collaboration across global teams. Analysts in different countries work with the same data simultaneously without dealing with complex replication or synchronization. Development cycles shrink from months to weeks as teams iterate quickly on new analytics applications.
Trend 4: Data Fabric and Data Mesh Adoption
Traditional centralized data warehouses struggle as organizations grow more complex. Data fabric and data mesh architectures represent fundamentally different approaches to solving this challenge. Rather than forcing all data into a single system, these patterns embrace distributed data ownership while maintaining consistent access and governance. Many organizations adopt these approaches when implementing big data solutions at scale, as they allow growth without creating bottlenecks.
Data fabric uses intelligent automation and metadata to connect data across different systems, locations, and formats. It creates a virtual layer that provides unified access without physically moving or duplicating information. Organizations query data wherever it lives, whether in cloud warehouses, on-premises databases, or external partner systems.
Data mesh takes a different approach, treating data as a product owned by domain teams. Marketing owns marketing data, sales owns sales data, and engineering owns product telemetry. Each team provides clean, documented datasets that others can consume. This distributes responsibility and scales better as organizations grow.
Both patterns address the same core problem: data silos that prevent organizations from seeing complete pictures. Traditional integration approaches broke down as data volumes and variety increased. These new architectures provide sustainable alternatives that work at scale.
Trend 5: Edge Computing and Big Data at the Source
Processing data where it’s generated rather than transmitting everything to central locations represents a significant shift. Edge computing brings analytics capabilities to factories, retail stores, vehicles, and mobile devices. This reduces latency, minimizes bandwidth costs, and enables operations that can’t tolerate delays from round-trips to distant data centers. In many cases, edge systems now act as the first stage of a big data pipeline, filtering and preparing data before it moves downstream.
The Internet of Things has accelerated edge adoption. Billions of sensors and devices generate data continuously. Sending all this information to the cloud for processing isn’t practical or cost-effective. Edge systems filter, aggregate, and analyze locally, transmitting only meaningful insights or anomalies to central systems.
Industrial applications show clear benefits. Manufacturing equipment with edge processors detects quality issues immediately, adjusting production parameters in real-time rather than discovering problems hours later. Autonomous vehicles must process sensor data instantly to make driving decisions. Even milliseconds of latency could cause accidents.
Retail stores use edge computing to enhance customer experiences. Smart shelves track inventory in real-time. Video analytics identify shopping patterns and optimize store layouts. Payment systems process transactions locally even when internet connections fail, ensuring continuous operations.
Trend 6: Big Data Security, Privacy, and Compliance
Data breaches and privacy regulations have made security a primary concern rather than an afterthought. Organizations now build security into data architectures from the beginning, not adding it later as a separate layer. This shift reflects both regulatory pressure and business reality: customers and partners demand strong data protection.
Compliance requirements have multiplied. GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, LGPD in Brazil, and dozens of other regulations create complex requirements for how organizations collect, store, and use personal information. Big data systems must enforce these rules automatically across petabytes of information in multiple jurisdictions.
Modern platforms provide security features that once required custom development. Encryption protects data at rest and in transit. Fine-grained access controls ensure individuals see only information relevant to their roles. Audit logs track every access and modification for compliance reporting. Data masking and tokenization protect sensitive fields while preserving analytical value.
Trend 7: Data Observability and Quality Management
As data systems grow more complex, understanding what’s actually happening inside them becomes challenging. Data observability applies principles from software engineering to data pipelines. Organizations monitor data health continuously, detecting issues before they cause problems in downstream applications or reports.
Quality problems with big data can be subtle and expensive. A single corrupted field in a dataset with billions of records might go unnoticed for weeks, affecting countless business decisions. Pipeline failures that stop processing data entirely are obvious. Silent failures that produce wrong results are much more dangerous.
Modern observability platforms track multiple dimensions. They monitor data freshness, alerting teams when expected updates don’t arrive. They profile data distributions, detecting unexpected changes that might indicate upstream problems. They measure completeness, identifying missing records or fields. They validate business rules, ensuring data maintains expected relationships and constraints.
Trend 8: Augmented Analytics and Self-Service BI
Business intelligence has traditionally required specialized skills in SQL, data modeling, and statistical analysis. Augmented analytics changes this by embedding AI capabilities into analytics tools themselves. Business users ask questions in natural language and receive answers without writing code or understanding technical details, making visualizing big data more accessible to non-technical teams.
Modern BI platforms like Tableau, Power BI, and ThoughtSpot use natural language processing to interpret questions. Users type “What were sales by region last quarter?” and receive visualizations showing the answer. The system handles the technical work: identifying relevant data sources, joining tables, performing calculations, and creating appropriate charts.
Automated insight generation goes further. These tools analyze data proactively, surfacing interesting patterns and anomalies without waiting for users to ask. Marketing teams receive alerts when campaign performance deviates from expected patterns. Finance teams get notifications about unexpected spending trends. Sales managers see which territories are outperforming or underperforming targets.
Trend 9: Big Data Integration with Generative AI
Generative AI applications like ChatGPT have captured public attention, but their real business value emerges when integrated with enterprise big data. Organizations are building systems where generative models access proprietary data to answer questions, generate reports, and create content specific to their business contexts.
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has become the standard pattern. When users ask questions, systems retrieve relevant information from data warehouses, documents, and knowledge bases. They provide this context to large language models, which generate responses grounded in actual company data rather than generic training knowledge.
Vector databases like Pinecone, Weaviate, and capabilities in Snowflake enable semantic search across unstructured content. Organizations convert documents, emails, support tickets, and other text into embeddings that capture meaning. This allows finding relevant information based on concepts rather than just keyword matching.
Trend 10: Industry-Specific Big Data Solutions
While general-purpose platforms remain important, pre-built solutions for specific industries have gained traction. These solutions combine relevant data models, analytics templates, and domain-specific AI models. Organizations get faster time-to-value by starting with frameworks designed for their industry rather than building everything from scratch.
Healthcare solutions include clinical data models, patient journey analytics, and predictive models for readmission risk and treatment effectiveness, forming the foundation of modern Healthcare analytics solutions. Financial services platforms provide anti-money laundering detection, credit risk scoring, and regulatory reporting templates. Retail solutions offer customer segmentation, demand forecasting, and personalization engines.
Cloud providers and independent software vendors both offer industry solutions. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud have vertical-specific offerings. Specialized vendors focus on particular industries, providing deeper functionality and domain expertise. Organizations choose based on their needs for customization versus rapid deployment.
Trend 11: Open Data and Interoperable Ecosystems
Vendor lock-in has long concerned organizations adopting big data platforms. Open data formats and interoperable systems address this by ensuring big data storage remains accessible regardless of which tools process it. Apache Parquet, Apache Iceberg, and Delta Lake provide open standards for storing data that any tool can read.
The lakehouse architecture exemplifies this trend. It stores data in open formats on object storage like S3 or Azure Blob Storage. Multiple processing engines then access the same data: Spark for batch processing, Presto for interactive queries, TensorFlow for machine learning. Organizations aren’t forced to choose a single platform or duplicate data across systems.
Data sharing initiatives extend this openness beyond organization boundaries. Healthcare providers share anonymized patient data to improve research. Supply chain partners exchange inventory and logistics information to optimize operations. Government agencies publish datasets for public benefit and transparency.
Standards organizations and industry consortiums drive interoperability. The Open Data Initiative from Microsoft, Adobe, and SAP promotes common data models. The Cloud Data Management Capabilities framework provides guidance for data governance across hybrid environments. These efforts reduce friction in data exchange and collaboration.
Business benefits include flexibility and reduced risk. Organizations adopt new technologies without abandoning existing investments. They negotiate better pricing with vendors knowing they can switch if necessary. They collaborate with partners more easily when data sharing doesn’t require complex integrations.
Trend 12: Sustainable and Cost-Efficient Data Processing
Environmental concerns and cost pressures have made efficiency a priority. Data centers consume enormous amounts of electricity, and wasteful data processing directly impacts both expenses and carbon footprints. Organizations now optimize for sustainability alongside performance and cost.
Cloud providers have made major investments in renewable energy and efficient infrastructure. According to Google Cloud’s sustainability report, their data centers use 1.5x more energy-efficient equipment than typical enterprise data centers. Organizations moving to cloud-native platforms automatically benefit from these improvements.
Data lifecycle management reduces storage costs and environmental impact. Not all data needs to be kept forever or accessed instantly. Modern architectures automatically move infrequently accessed data to cheaper, slower storage tiers. They delete data that’s no longer needed based on retention policies. These practices dramatically reduce costs while maintaining access to valuable information.
Query optimization and workload management prevent waste. Platforms like Snowflake and BigQuery charge based on data processed, creating direct incentives to write efficient queries. Automated optimization can rewrite queries to reduce compute needs. Workload management ensures analytical queries don’t interfere with operational systems.
Organizations are measuring and reporting on data sustainability. They track compute hours, storage consumed, and estimated carbon emissions. Some include these metrics in sustainability reports alongside manufacturing and transportation impacts. This visibility drives continuous improvement and demonstrates corporate responsibility.
Partner with Folio3 to integrate AI, cloud-native platforms, and data mesh architectures into your operations, ensuring faster, smarter, and cost-efficient analytics.
Industry-Specific Big Data Trends
Different industries face unique data challenges and opportunities. Understanding how big data evolves in specific sectors helps organizations apply relevant approaches to their own situations.
1. Big Data Trends in Healthcare
Healthcare generates enormous amounts of data from electronic health records, medical imaging, genomic sequencing, wearables, and research studies. Organizations analyze this information to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and accelerate medical discoveries. The industry faces strict privacy regulations and requires high reliability, making technology choices especially critical.
Predictive diagnostics use machine learning models trained on millions of patient records to identify disease risk early. Healthcare predictive analytics combines genetic markers, lifestyle factors, and clinical history to predict which patients will likely develop specific conditions. This enables preventive interventions before diseases become severe and expensive to treat.
Personalized medicine tailors treatments to individual patients based on their unique characteristics. Genomic data combined with clinical outcomes shows which cancer treatments work best for patients with specific genetic profiles. Pharmaceutical companies use big data to identify patient populations most likely to benefit from new drugs, making clinical trials more efficient and effective.
2. Big Data Trends in Finance & Banking
Financial institutions have always been data-driven, but the volume, velocity, and variety of information they process continues growing. Real-time fraud detection, algorithmic trading, personalized banking experiences, and regulatory compliance all depend on sophisticated big data capabilities, making them a core data analytics application in finance. The industry invests heavily in infrastructure that processes millions of transactions daily while maintaining security and accuracy.
Risk modeling has evolved from periodic portfolio reviews to continuous real-time assessment. Banks analyze credit applications using hundreds of variables including traditional credit scores, transaction history, social data, and behavioral patterns. This improves approval accuracy while reducing losses from defaults. Investment firms model market risk across complex portfolios, running thousands of scenarios to understand potential exposures.
Fraud detection systems analyze transaction patterns in milliseconds, blocking suspicious activity before it completes. Machine learning models trained on historical fraud cases identify new attack patterns as they emerge. The systems adapt continuously as criminals change tactics, providing protection that rule-based systems can’t match. According to Juniper Research, this prevents billions in fraudulent losses annually while minimizing false positives that frustrate legitimate customers.
3. Big Data Trends in Retail & E-commerce
Retail has transformed completely through data-driven personalization and operational optimization, showcasing some of the most impactful big data in retail use cases today. Online retailers track every click, view, and purchase to understand customer preferences. Physical stores use sensors, cameras, and transaction data to optimize layouts and inventory. The combination of online and offline data creates comprehensive views of customer journeys across channels.
Customer personalization engines recommend products, customize marketing messages, and adjust pricing based on individual preferences and behaviors. These systems analyze purchase history, browsing patterns, demographic information, and responses to past offers. The result is experiences that feel tailored to each customer, increasing conversion rates and average order values significantly.
Demand forecasting has moved from seasonal patterns to real-time prediction incorporating weather, social media trends, competitor actions, and inventory levels. Retailers optimize stock across distribution centers and stores to minimize both stockouts and excess inventory. This improves margins while ensuring popular items remain available when customers want them.
4. Big Data Trends in Manufacturing & Supply Chain
Manufacturing and supply chain operations generate continuous streams of data from sensors, production equipment, logistics systems, and quality control processes. Organizations analyze this information to optimize efficiency, prevent failures, and respond quickly to changing conditions. The industry increasingly adopts real-time analytics and edge computing to make decisions at the point of operation.
Predictive maintenance uses sensor data from equipment to forecast failures before they occur. Machine learning models learn normal operating patterns for motors, conveyor belts, and production machines. When sensors detect deviations from these patterns, systems alert maintenance teams to inspect and repair equipment during planned downtime rather than facing unexpected failures during production runs. This improves equipment availability while reducing maintenance costs.
Big Data Analytics Market & Adoption Trends
The big data analytics market continues maturing from early adoption phases into mainstream use across industries. Understanding current market direction helps organizations position themselves appropriately and learn from others’ experiences.
Market growth has shifted from initial infrastructure buildout to expanding applications and use cases. Organizations have established basic data warehouses and lakes. Now they’re extending these platforms with real-time capabilities, AI integration, and industry-specific applications. Cloud adoption accelerates this trend by reducing infrastructure barriers that once limited smaller organizations.
Enterprise adoption patterns differ significantly from small and medium business approaches. The following comparison highlights key differences:
| Aspect | Small & Medium Businesses | Large Enterprises |
| Platform Preference | Managed cloud services | Hybrid cloud and multi-cloud |
| Implementation | Rapid deployment of SaaS tools | Custom development with flexibility |
| Data Volume | Gigabytes to low terabytes | Petabytes to exabytes |
| Team Structure | Small teams with broad skills | Specialized roles and large teams |
| Use Cases | Operational reporting and basic analytics | Advanced AI, real-time processing, complex modeling |
| Budget Focus | Minimize upfront costs | Optimize total cost of ownership |
| Vendor Relationships | Single primary vendor | Multiple vendors and integration |
The shift toward lakehouse architectures and unified platforms represents a significant market trend. Organizations are consolidating data infrastructure that previously required separate systems for data warehouses, data lakes, streaming, and machine learning. Platforms like Databricks Lakehouse and Snowflake unify these capabilities, reducing complexity and cost while improving flexibility.
Demand for architectures that support both real-time processing and AI-ready data is driving platform evolution. Organizations want systems that handle streaming data for operational decisions while also supporting the batch processing and feature engineering required for machine learning. Modern platforms are designed for these dual requirements from the ground up rather than bolting on capabilities after the fact.
Key Benefits of Adopting Modern Big Data Trends
Organizations implementing current big data approaches see tangible advantages across multiple dimensions of their business. These benefits explain why investment continues growing despite economic uncertainty.
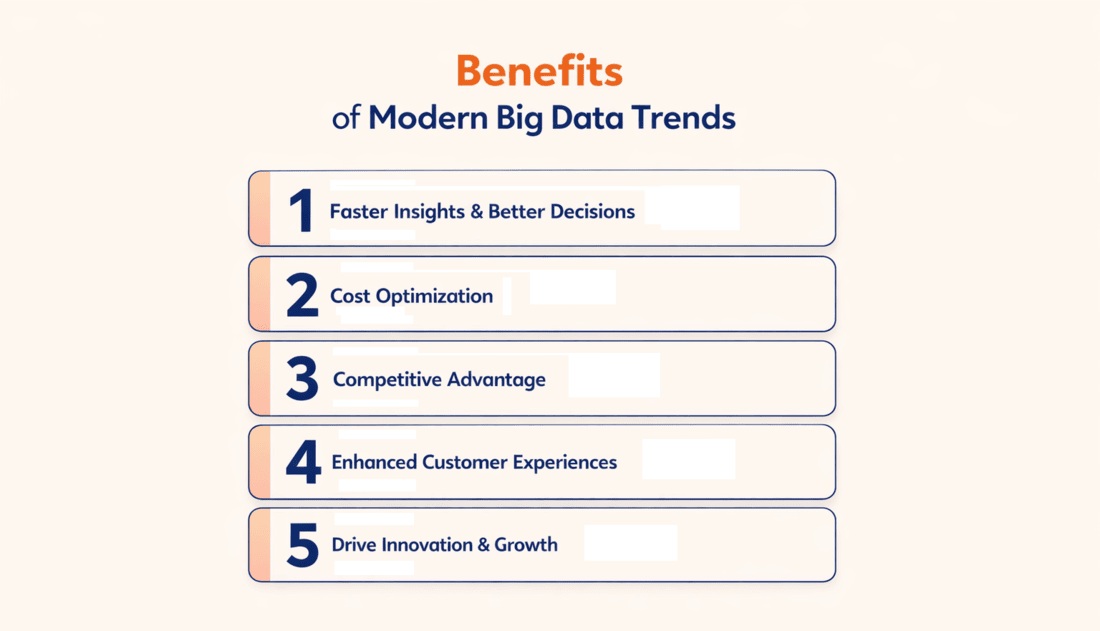
1. Faster Insights, Better Decisions
Speed matters in competitive markets. Modern big data platforms reduce the time from question to answer from days or weeks to minutes or hours. Business users access self-service tools that provide information on demand. Real-time analytics show current conditions rather than yesterday’s state. This acceleration enables organizations to respond quickly to opportunities and threats.
Decision quality improves alongside speed. More complete data, better analytical tools, and AI assistance help people understand complex situations. Decisions are based on evidence rather than intuition alone. Organizations can test different scenarios and understand likely outcomes before committing resources.
2. Optimize Costs Efficiently
Cloud-native platforms with consumption-based pricing convert capital expenses into operational expenses that scale with actual usage. Organizations pay for the compute and storage they need, not for capacity sitting idle. Automation reduces the staff time required for routine tasks like backup, scaling, and optimization.
Better data visibility helps identify waste throughout operations. Supply chain analytics reduce inventory carrying costs. Predictive maintenance prevents expensive emergency repairs. Marketing analytics eliminate spending on ineffective campaigns. These operational improvements often exceed the cost of the data platforms themselves.
3. Gain Competitive Advantage
Organizations that use data more effectively than competitors gain sustainable advantages. They understand customers better, deliver more personalized experiences, and spot market trends earlier. Building big data strategies thoughtfully allows them to optimize operations, reduce costs while maintaining quality, and respond faster to changing conditions. These advantages compound over time as data capabilities mature.
First-mover advantages matter in data-driven competition. Organizations that implement effective analytics earlier accumulate more historical data and refined models. They attract and retain talent with strong data skills. They build organizational cultures around data-driven decision-making that become difficult for competitors to replicate.
4. Enhance Customer Experiences
Modern big data enables personalization at scale. Organizations remember customer preferences, anticipate needs, and provide relevant recommendations. They resolve issues faster by giving support teams complete context. They communicate through preferred channels at appropriate times. These improvements increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and lifetime value.
Real-time capabilities enable responsive experiences. E-commerce sites adjust to customer behavior within the same session. Mobile apps provide location-aware services. Contact centers route customers to appropriate agents based on their history and current situation. These interactions feel natural rather than generic.
5. Drive Innovation and Growth
Big data analytics reveals opportunities that might otherwise remain hidden. Organizations discover underserved customer segments, identify new product features that resonate with users, and spot market trends before they become obvious. These insights fuel innovation and growth strategies.
Data-driven experimentation accelerates learning. Organizations test new approaches quickly, measure results accurately, and scale what works. This disciplined innovation reduces risk while increasing the pace of improvement. Companies iterate products and services based on actual customer feedback rather than internal assumptions.
Challenges of Adopting Big Data Trends
Despite clear benefits, organizations face significant obstacles implementing modern big data approaches. Understanding these challenges helps teams prepare appropriate responses and set realistic expectations.
1. Data Silos & Integration
Most organizations have data scattered across numerous systems that don’t communicate well. Customer information lives in CRM tools, transaction data in ERP systems, web activity in analytics platforms, and documents in content management systems. Breaking down these silos requires strong data integration expertise, ensuring that technical connections and workflows function reliably across all systems.
Legacy systems often lack modern APIs or use proprietary formats that complicate integration. Organizations must decide whether to replace old systems, build custom connectors, or accept limitations. Each approach involves tradeoffs between cost, time, and functionality. Data quality problems compound integration challenges as inconsistent formats and definitions slow progress.
2. Talent and Skill Gaps
Demand for data engineering, data science, and analytics skills significantly exceeds supply. Organizations struggle to hire qualified professionals and retain them against competitive offers. Building internal capabilities through training requires time and investment while operational needs create pressure for immediate results.
The skills required span technical domains that rarely exist in single individuals. Data engineers understand distributed systems and software development. Data scientists know statistics and machine learning. Analytics translators bridge business and technical teams. Building teams with complementary skills and effective collaboration takes deliberate effort beyond just hiring credentials.
3. Security and Governance Issues
Protecting sensitive data while making it accessible for analysis creates tension. Overly restrictive security prevents legitimate use. Insufficient protection risks breaches with severe consequences. Organizations need frameworks that balance security, privacy, compliance, and usability. These frameworks require coordination between security teams, legal departments, and business units.
Governance becomes more complex as data volumes and use cases grow. Organizations must catalog data assets, track lineage, enforce access policies, and ensure quality. Manual governance doesn’t scale. Automated tools help but require configuration and maintenance. Many organizations lack clear data ownership models, leaving governance responsibilities unclear.
Folio3 helps organizations tackle integration, talent, and governance obstacles to successfully implement modern big data strategies. Partner with us to turn challenges into actionable solutions.
How Can Your Business Prepare for Future Big Data Trends?
Success with big data requires deliberate preparation across technology, people, and processes. Organizations that take systematic approaches position themselves to capitalize on emerging opportunities while avoiding common pitfalls. Thoughtful data and analytics implementation ensures that infrastructure, tools, and culture work together seamlessly to deliver measurable business value.
1. Modernize Data Infrastructure
Assess current infrastructure honestly. Identify systems that limit scalability, flexibility, or cost efficiency. Develop a migration plan that balances risk and reward. Many organizations adopt a phased approach, moving workloads to modern platforms incrementally rather than attempting a big-bang migration.
Cloud-native platforms provide compelling advantages for most organizations. Evaluate options from AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and specialized vendors like Databricks and Snowflake. Consider factors beyond features: pricing models, integration with existing tools, vendor stability, and ecosystem strength. Choose platforms that align with your technical skills and business requirements.
2. Choose Right Analytics Tools
Select tools that match your users’ skills and needs. Business analysts need different capabilities than data scientists. Self-service BI tools democratize access but require good data governance to work effectively. Specialized analytics platforms provide depth for technical users who need full control.
Build toward a coherent ecosystem rather than accumulating disconnected tools. Ensure platforms integrate well and share common security models. Consolidation often provides better value than best-of-breed approaches that require extensive custom integration. Evaluate the total cost of ownership including training, support, and maintenance, not just licensing fees.
3. Build Data-Driven Culture
Technology alone doesn’t create data-driven organizations. Leadership must model data-informed decision-making and reward evidence-based approaches. Encourage questions and experimentation. Accept that data sometimes challenges assumptions and comfortable beliefs. Create environments where people feel safe admitting uncertainty rather than pretending confidence.
Invest in data literacy across the organization. Basic training helps everyone understand how to interpret charts, assess data quality, and ask good questions. Specialized training develops deeper skills in analytics, statistics, and machine learning for those who need them. Communities of practice help people learn from each other and establish consistent standards.
4. Invest in Data Governance
Establish clear data ownership. Assign responsibility for quality, documentation, and access decisions. Owners should be domain experts who understand business context, not just technical administrators. Support owners with tools and processes that make governance manageable rather than burdensome.
Implement data catalogs that help people discover and understand available data. Good catalogs include business definitions, quality metrics, usage examples, and contact information for questions. Automate governance tasks where possible: classification of sensitive data, lineage tracking, policy enforcement, and compliance reporting. Manual governance doesn’t scale and creates bottlenecks.
FAQs
What Are the Latest Big Data Trends?
The latest big data trends include AI-driven analytics, real-time streaming, cloud-native platforms, data mesh architectures, edge computing, enhanced security, data observability, augmented analytics, generative AI integration, industry-specific solutions, open standards, and sustainable processing focused on faster insights and cost optimization.
How Is AI Changing Big Data Analytics?
AI automates insight discovery, enables natural language queries, improves predictions, and processes unstructured data like text and images. Machine learning identifies hidden patterns while generative AI creates summaries, making analytics accessible to non-technical users and accelerating decisions.
What Industries Benefit Most from Big Data?
Healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, telecommunications, and logistics gain substantial benefits. Healthcare improves outcomes, finance detects fraud, retail personalizes experiences, and manufacturing prevents failures. Industries with large customer bases, complex operations, or rapid change see the greatest advantages.
What Is the Future of Big Data Analytics?
The future brings tighter AI integration, more real-time processing, improved accessibility for non-technical users, stronger security, and greater automation. Organizations will treat data as products with clear ownership. Edge computing will process more locally while platforms become simpler yet more powerful.
How Are Cloud-Native Platforms Transforming Big Data Management?
Cloud-native platforms eliminate infrastructure overhead, enable independent scaling of storage and compute, provide automatic optimization, and offer pay-per-use pricing. They democratize capabilities that previously required significant capital investment, allowing faster deployment and easier scaling as needs change.
What Role Does Edge Computing Play in Modern Data Analytics?
Edge computing processes data at its source, reducing latency for real-time decisions, minimizing bandwidth costs, and enabling operations during network outages. It addresses privacy concerns by keeping sensitive data local, benefiting industrial IoT, autonomous vehicles, retail, and telecommunications networks.
How Can Businesses Ensure Data Quality and Observability in Big Data Pipelines?
Businesses monitor data freshness, completeness, accuracy, and consistency continuously. Automated profiling detects unexpected changes. Data contracts define expectations between teams. Observability platforms alert teams to issues before impacting applications, treating quality as continuous practice rather than one-time validation.
What Are the Key Challenges in Implementing Next-Generation Big Data Strategies?
Major challenges include breaking data silos, integrating legacy systems, finding qualified talent, balancing security with accessibility, establishing governance, managing costs, and changing culture. Technical complexity and skill gaps slow implementations. Success requires realistic timelines, executive support, and learning from failures.
How Is Augmented Analytics Improving Decision-Making for Enterprises?
Augmented analytics embeds AI into business intelligence tools, enabling natural language queries, automated insight discovery, and smart recommendations. Business users get answers without technical skills, reducing dependence on analysts. It proactively identifies anomalies and patterns, helping organizations spot opportunities faster.
What Impact Do Data Mesh and Data Fabric Architectures Have on Organizational Data?
Data mesh and fabric architectures distribute data ownership to domain teams while maintaining consistent access and governance. This scales better than centralized approaches as organizations grow. Domain experts ensure quality and relevance of their data products. Users access information they need without understanding physical locations or technical details. These patterns reduce bottlenecks and improve data usability.
How Can Businesses Secure Big Data While Maintaining Privacy and Compliance?
Businesses use encryption, access controls, audit logging, data masking, and automated compliance monitoring. Privacy-preserving techniques like differential privacy enable analysis while protecting individuals. Modern platforms provide built-in security features. Organizations must implement governance processes, train staff, and conduct regular assessments.
What Emerging Technologies Will Shape Big Data Trends in the Next 5 Years?
Advanced AI models will improve in capability and efficiency. Spatial computing and augmented reality will create new data sources. Improved networking enables faster data movement. Quantum computing may eventually transform analysis. However, the biggest changes will come from better applying existing technologies.
Conclusion
Big data has moved from experimental technology to business necessity. Organizations using current trends effectively make better decisions, operate more efficiently, and compete more successfully. The pace of change shows no signs of slowing. Cloud-native platforms, AI integration, real-time processing, and improved accessibility continue reshaping how businesses work with information. Success requires ongoing investment in technology, skills, and culture. Organizations that treat data as a strategic asset rather than a technical concern position themselves for long-term advantage.
Folio3 Data Services helps organizations navigate the complexity of modern big data trends. Our team specializes in data engineering, cloud migration, analytics implementation, and AI integration across healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing sectors. We work with platforms like Snowflake, Databricks, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to build solutions that deliver measurable business value. Whether you’re starting your data journey or optimizing existing capabilities, Folio3 brings deep expertise in turning data challenges into competitive advantages.





