A retail data warehouse represents a centralized repository that consolidates data from multiple sources across retail operations, including point-of-sale systems, e-commerce platforms, customer relationship management tools, and supply chain networks. This specialized infrastructure transforms raw transactional data into structured, analytical formats that support business intelligence, reporting, and strategic decision-making processes.
The distinction between general data warehouses and retail-specific implementations lies in the unique requirements of retail operations. While general data warehouses handle various business functions, retail data warehouses focus specifically on customer behavior patterns, inventory cycles, seasonal trends, and omnichannel integration challenges that define modern commerce environments.
Retail warehouses incorporate specialized data models that accommodate product catalogs, pricing structures, promotional campaigns, and customer journey analytics. Modern retailers operate in increasingly data-driven environments where competitive advantage depends on the ability to process vast amounts of information quickly and accurately.
Customer expectations for personalized experiences, inventory availability, and smooth omnichannel interactions require sophisticated data infrastructure that can handle millions of transactions while providing real-time insights for operational optimization and strategic planning.
This blog explores why many retailers are turning to data lakehouse architectures, how they overcome warehouse limitations, and the advantages they bring in driving personalization, operational efficiency, and future-ready retail innovation.
Why Data Warehouses Are Essential for Retailers?
Retail businesses generate enormous volumes of data from diverse sources that require centralized management to extract meaningful insights and drive strategic decisions. Without proper data warehouse infrastructure, retailers struggle to connect customer interactions across channels, optimize inventory levels, and respond quickly to market changes.
Traditional database systems cannot handle the analytical workloads required for retail operations, which often involve complex queries across historical data, seasonal pattern analysis, and retail demand forecasting to support accurate inventory planning and customer segmentation. Data warehouses provide the performance, scalability, and analytical capabilities needed to transform transactional data into actionable business intelligence.
The competitive nature of retail markets demands immediate access to accurate information about customer preferences, product performance, and operational efficiency. Data warehouses enable retailers to consolidate fragmented data sources into unified views that support personalized marketing campaigns, inventory optimization, and strategic planning initiatives that drive revenue growth and operational excellence.
Business Use Cases of Data Warehousing in Retail
Retail data warehouses enable specific business capabilities that directly impact customer experience, operational efficiency, and financial performance across multiple organizational functions.
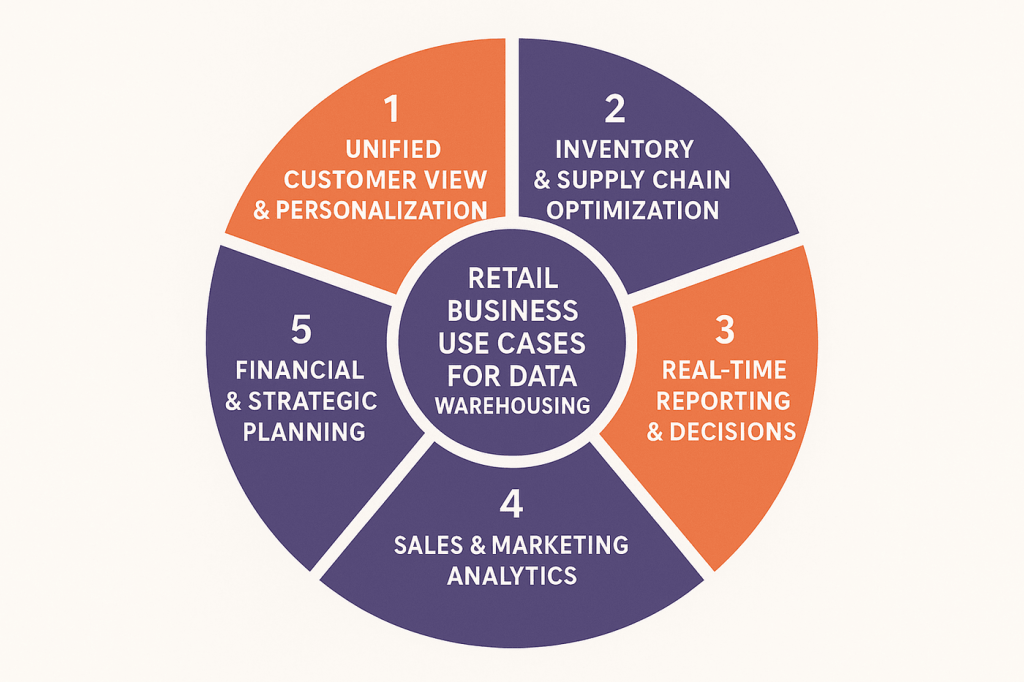
1. Unified Customer View & Personalization
Data warehouses consolidate customer information from online purchases, in-store transactions, loyalty programs, and customer service interactions to create comprehensive profiles that enable personalized experiences. This unified retail customer data allows retailers to track customer journeys across channels, identify preferences and behaviors, and deliver targeted marketing messages that increase engagement and conversion rates.
Personalization engines powered by data warehouses analyze purchase history, browsing patterns, and demographic information to recommend relevant products, customize pricing offers, and optimize communication timing. Companies like Amazon and Netflix demonstrate how unified customer data drives recommendation systems that generate significant portions of their revenue through personalized experiences.
2. Inventory and Supply Chain Optimization
Retail data warehouses integrate inventory data from multiple locations, suppliers, and channels to provide real-time visibility into stock levels, demand patterns, and supply chain performance. This comprehensive view enables predictive analytics that forecast demand, optimize reorder points, and reduce inventory carrying costs while maintaining service levels.
Advanced analytics identify seasonal trends, regional preferences, and product lifecycle patterns that inform procurement decisions and inventory allocation strategies. Retailers using data warehouse-powered inventory optimization typically achieve 15-30% reductions in inventory costs while improving product availability and customer satisfaction.
3. Real-Time Reporting & Decision-Making
Data warehouses provide the foundation for real-time dashboards and reporting systems that enable managers and executives to monitor business performance, identify trends, and respond quickly to operational issues or market opportunities. These systems rely on real-time data collection to process millions of transactions and deliver current insights about sales performance, customer behavior, and operational metrics.
Self-service analytics capabilities empower business users to explore data and generate insights without technical assistance, accelerating decision-making processes while reducing the burden on IT teams. Real-time reporting enables retailers to adjust pricing strategies, modify marketing campaigns, and optimize operations based on current performance data.
4. Sales & Marketing Analytics
Comprehensive sales analytics powered by real-time data warehouses reveal product performance patterns, customer segment behaviors, and campaign effectiveness metrics that inform marketing strategies and merchandising decisions. These systems analyze conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and lifetime value calculations to optimize marketing spend and improve ROI.
Marketing attribution analysis tracks customer interactions across multiple touchpoints to identify the most effective channels, messages, and timing strategies for different customer segments. This insight enables retailers to allocate marketing budgets more effectively while improving campaign performance and customer engagement.
5. Financial and Strategic Planning
Data warehouses support financial planning and analysis by providing accurate, timely information about revenue trends, cost structures, and profitability metrics across products, channels, and customer segments.
Implementing a well-defined data warehouse strategy ensures that these insights are reliable and accessible, enabling strategic planning processes that align operational activities with business objectives.
Budget forecasting and variance analysis use historical data patterns to predict future performance while identifying factors that influence financial outcomes. Strategic planning processes leverage data warehouse insights to evaluate new market opportunities, assess competitive positioning, and guide investment decisions.
Retail Data Warehouse Architecture & Components
Modern retail data warehouse architecture incorporates multiple layers and components that work together to collect, process, and deliver business insights efficiently and reliably, leveraging best practices in retail data engineering to ensure accurate, timely, and actionable data.
Data Sources: POS, ERP, CRM
- POS: Point-of-sale systems generate transactional data including product sales, payment methods, customer information, and promotional redemptions that provide detailed insights into customer purchasing behavior and product performance. These systems capture real-time transaction data from physical stores, online platforms, and mobile applications.
- ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning systems contribute operational data about inventory levels, supplier relationships, financial transactions, and human resources that support comprehensive business analysis. ERP integration enables retailers to analyze operational efficiency, cost structures, and resource utilization patterns, especially when paired with an AI enterprise search to quickly surface relevant insights across large datasets.
- CRM: Customer Relationship Management systems provide customer interaction data, communication preferences, service history, and engagement metrics that enhance customer analytics and personalization capabilities. CRM integration ensures that customer data remains consistent across all touchpoints and business functions.
ETL/ELT Pipelines
ETL and ELT processes collect data from source systems, apply business rules and data quality checks, and then load clean, structured data into the warehouse for analysis. ETL pipelines ensure data consistency, handle complex transformations, and maintain data quality standards throughout the integration process.
Extract, Load, Transform (ELT) processes leverage the processing power of modern cloud data warehouses to perform transformations after data loading, providing flexibility for exploratory analytics and changing business requirements. ELT approaches enable faster data ingestion while supporting diverse analytical use cases.
Data Lake vs Warehouse
Data lakes and data warehouses serve complementary roles in modern data architectures. Data lakes store raw, unstructured data in its native format, providing flexibility for future analysis and machine learning applications while supporting diverse data types including text, images, and streaming data. Lakes complement warehouses by preserving complete data history and enabling exploratory analytics.
Data warehouses organize structured data using predefined schemas optimized for analytical queries and reporting, ensuring consistent performance for business intelligence applications. Warehouses excel at handling formatted retail data with established business rules and reporting requirements.
Data Marts: Sales, Inventory, Finance
- Sales: Sales data marts contain product performance data, customer analytics, and revenue metrics organized for sales team analysis and reporting needs. These specialized repositories provide fast access to sales-specific data while maintaining detailed transaction histories.
- Inventory: Inventory data marts focus on stock levels, demand patterns, supplier performance, and logistics data that support supply chain optimization and inventory management decisions. These marts enable real-time inventory visibility across multiple locations and channels.
- Finance: Finance data marts consolidate financial data, profitability analysis, and cost accounting information that support financial planning, budgeting, and performance management processes. Financial marts ensure accurate, timely reporting while maintaining audit trails and compliance requirements.
7 Clear Signs Your Retail Business Needs a Data Warehouse
Retailers can identify specific indicators that signal the need for data warehouse implementation to address growing analytical requirements and business complexity.
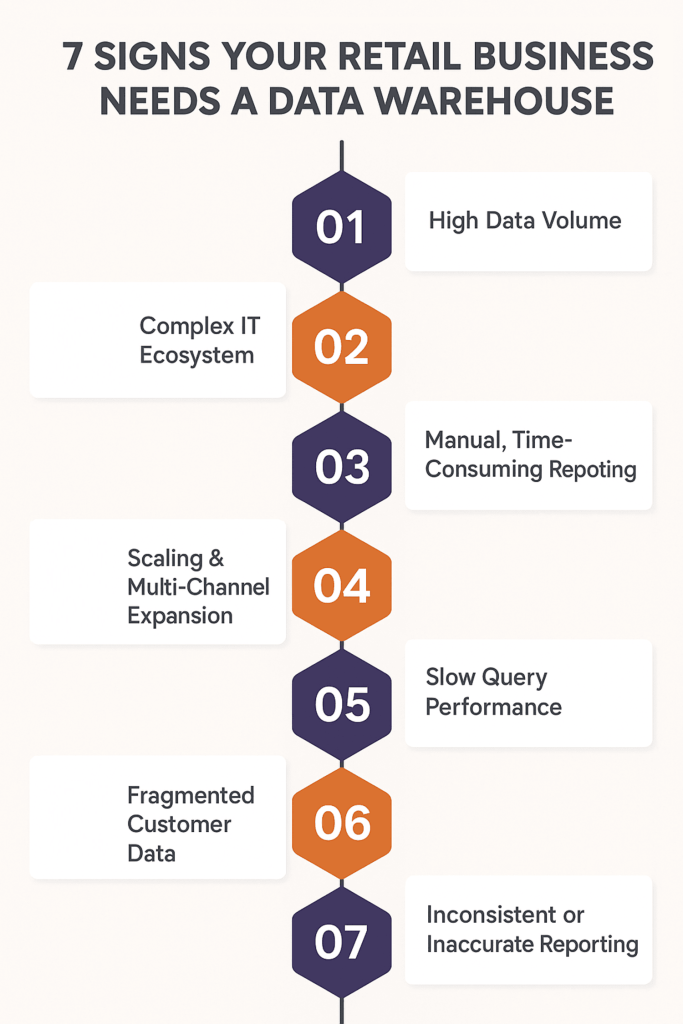
Sign 1: High Data Volume
When retail businesses process millions of transactions monthly across multiple channels, traditional database systems struggle to maintain performance while supporting analytical queries. High data volumes require scalable infrastructure that can handle both transactional processing and analytical workloads efficiently.
Sign 2: Complex IT Ecosystem
Retailers operating multiple systems for e-commerce, POS, inventory management, and customer service create data silos that prevent comprehensive business analysis. Complex IT ecosystems require data warehouses to integrate information and provide unified views of business performance, helping overcome common data lake challenges such as unstructured data management and inconsistent reporting.
Sign 3: Time-Consuming Manual Reporting
Manual report generation processes that require hours or days to compile business insights indicate the need for automated data warehouse capabilities. Time-consuming reporting prevents timely decision-making and reduces operational agility in competitive markets, limiting opportunities for retail data monetization through actionable insights.
Sign 4: Scaling & Multi-Channel Expansion
Business growth through new locations, channels, or product lines creates additional data sources and analytical complexity that overwhelm existing systems. Scaling operations require data warehouse infrastructure that can accommodate growth without performance degradation.
Sign 5: Slow Query Performance
Database queries that take hours to complete or fail due to resource constraints prevent real-time business analysis and decision-making. Slow performance indicates the need for analytical infrastructure optimized for complex queries and large datasets.
Sign 6: Fragmented Customer Data
Customer information scattered across multiple systems prevents comprehensive customer analysis and personalization initiatives. Implementing customer data integration through a data warehouse creates unified customer views that support experience optimization.
Sign 7: Inconsistent or Inaccurate Reporting
Reports that show different results from various systems create confusion and reduce confidence in data-driven decisions. Inconsistent reporting indicates the need for centralized data warehouse infrastructure that ensures data quality and consistency.
Don’t let slow queries and scattered systems hold you back. Build a modern data warehouse that scales with your business.
Retail Data Warehouses vs. Traditional Databases – Key Differences
Here are some of the factors that differentiate retail data warehouses from traditional databases:
| Feature | Retail Data Warehouse | Traditional Database |
| Purpose | Analytics and reporting | Transactional processing |
| Data Structure | Denormalized, dimensional | Normalized, relational |
| Query Performance | Optimized for complex analytical queries | Optimized for simple transactional operations |
| Data Volume | Handles petabytes of historical data | Limited to current operational data |
| Update Frequency | Batch updates, typically daily | Real-time transactional updates |
| Schema Design | Star/snowflake schemas for analysis | Entity-relationship models |
| Data Sources | Multiple systems integration | Single application focus |
| Historical Data | Maintains years of historical trends | Limited historical data retention |
| Scalability | Designed for analytical workload scaling | Optimized for transaction throughput |
| Cost Structure | Higher storage costs, lower query costs | Lower storage costs, higher processing costs |
Key Considerations for Building a Retail Data Warehouse
Successful data warehouse implementation requires careful planning and consideration of technical, organizational, and business factors that influence project success and long-term value.
1. Assess Current Infrastructure
Evaluate existing systems, data sources, and technical capabilities to understand integration requirements and identify potential challenges. Infrastructure assessment includes network capacity, security requirements, compatibility with modern data warehouse technologies, and selection of appropriate data integration techniques to ensure seamless data flow.
2. Define Resource Requirements
Determine staffing needs, budget allocation, and technical expertise required for successful implementation and ongoing operations. Resource planning includes training requirements, vendor support needs, and internal capability development strategies, as well as leveraging data integration consulting to ensure best practices and smooth system integration.
3. Set Realistic Timelines
Establish implementation phases that deliver incremental value while managing complexity and risk. Realistic timelines account for data migration strategy, testing, and user training requirements to ensure successful deployment.
4. Plan for Scalability
Design architecture that can accommodate business growth, additional data sources, and evolving analytical requirements without major rebuilds. Scalability planning includes cloud platform selection, storage optimization, and performance monitoring capabilities, all aligned with a robust data integration architecture to ensure seamless flow of information across systems.
5. Address Common Challenges
Identify potential obstacles including data quality issues, system integration complexity, and change management requirements that could impact project success. Proactive challenge mitigation ensures smooth implementation and user adoption.
Common Challenges in Retail Data Warehouse Deployment
Data warehouse implementation encounters predictable obstacles that require strategic planning and systematic approaches to overcome while maintaining business operations.
1. Data Silos Across Channels
Legacy systems designed for specific functions create isolated data repositories that complicate integration efforts and prevent comprehensive business analysis. Channel integration requires careful planning to maintain data consistency while connecting diverse systems, especially when scaling for big data implementation.
2. Data Quality & Governance
Inconsistent data formats, missing values, and duplicate records across source systems create accuracy issues that compromise analytical reliability. Quality management requires automated validation processes and governance policies that maintain standards throughout the data lifecycle, especially when integrating with modern data lake architecture to manage large volumes of unstructured data.
3. High Infrastructure Costs
Traditional on-premise data warehouse infrastructure requires significant upfront investments in hardware, software, and maintenance resources that strain IT budgets. Modern cloud-based solutions provide cost-effective alternatives with usage-based pricing models and support advanced technologies such as generative AI for retail to enhance predictive analytics and customer insights.
4. Legacy System Integration
Connecting outdated systems with modern data warehouse platforms requires specialized expertise and careful migration planning to avoid business disruption.
Many retailers engage retail analytics consulting to design custom integration strategies, build necessary connectors, and oversee extensive testing to ensure smooth communication between legacy and cloud environments.
5. Real-Time Analytics Bottlenecks
Meeting real-time reporting requirements while maintaining data warehouse performance requires specialized architecture and infrastructure optimization. Real-time capabilities often require additional streaming data platforms and processing resources.
How Folio3 Helps Build Smarter Retail Data Warehouses?
Folio3 Data Services provides comprehensive retail data warehouse solutions that address the unique challenges and requirements of modern commerce operations through proven methodologies, industry expertise, and expert data warehouse consulting to guide businesses from planning to implementation.
1. End-to-End Expertise
Our team manages complete data warehouse implementations from initial assessment through deployment and ongoing optimization. We provide architecture design, data engineering services, migration, and performance tuning that ensure successful project outcomes and long-term value.
2. Retail Industry Knowledge
Deep understanding of retail business processes, data patterns, and analytical requirements enables us to design solutions that address specific industry challenges. Our retail expertise includes omnichannel integration, seasonal analytics, and customer behavior modeling, supported by robust cloud data integration to unify information across platforms.
3. Cloud & Modern Architecture Focus
We specialize in cloud-based data warehouse implementations that provide scalability, cost-effectiveness, and advanced analytical capabilities. Our cloud expertise includes platform selection, migration strategies, and optimization techniques that maximize performance while controlling costs.
4. Data Quality & Governance First
Comprehensive data quality and governance frameworks ensure accurate, reliable information that supports confident business decisions. Our governance approach includes automated quality monitoring, security controls, and compliance management that protect business interests, enhanced by an AI data extraction solution to streamline data collection and improve accuracy.
5. Proven Business Impact
Our implementations deliver measurable improvements in operational efficiency, customer experience, and revenue growth through strategic data infrastructure investments. By leveraging big data in the retail industry, our solutions enable retailers to gain actionable insights, optimize operations, and achieve significant ROI through improved decision-making capabilities and operational optimization.
Partner with Folio3 to design and implement a cloud-based data warehouse that ensures quality, scalability, and measurable ROI.
FAQs
What is the meaning of retail warehouse?
A retail warehouse is a centralized data repository that consolidates information from multiple retail systems to support analytics and business intelligence. It differs from physical warehouses by focusing on data storage and processing rather than physical goods management.
What is the role of a data warehouse in the retail industry?
Data warehouses enable retailers to integrate customer data across channels, optimize inventory management, and support strategic decision-making through comprehensive analytics. They provide the foundation for personalization, forecasting, and operational efficiency improvements.
How does a retail data warehouse differ from a traditional data warehouse?
Retail data warehouses include specialized schemas for customer behavior, product catalogs, and seasonal patterns that address commerce-specific requirements. They incorporate retail-specific data models and analytical capabilities that traditional warehouses may not provide.
How can a data warehouse improve customer experience in retail?
Data warehouses create unified customer views that enable personalization, consistent experiences across channels, and proactive service delivery. They support recommendation engines and targeted marketing that increase satisfaction and loyalty.
How does a retail data warehouse support data-driven retail analytics?
Retail warehouses provide clean, integrated data that feeds analytical applications including demand forecasting, customer segmentation, and performance analysis. They enable complex queries and historical analysis that support strategic planning and operational optimization.
What are the common challenges in implementing a retail data warehouse?
Key challenges include integrating diverse data sources, ensuring data quality across systems, managing implementation costs, and connecting legacy systems. Organizations also face change management and skill development requirements.
How does AI and machine learning enhance retail data warehousing?
AI improves data quality through automated cleansing, enhances customer segmentation accuracy, and enables predictive analytics for demand forecasting. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns and trends that inform business strategies and operational decisions.
Should retailers choose a cloud or on-premise data warehouse?
Cloud solutions typically offer better scalability, lower upfront costs, and advanced analytical capabilities compared to on-premise alternatives. However, the choice depends on security requirements, existing infrastructure, and specific business needs.
What is the future of retail data warehousing?
Future trends include real-time analytics, AI-powered automation, and integration with IoT data sources for enhanced customer insights. Modern architectures will emphasize flexibility, scalability, and support for emerging technologies like augmented analytics.
Conclusion
Retail data warehouses represent essential infrastructure for modern commerce operations that enable competitive advantage through comprehensive data integration and advanced analytics capabilities. Successful implementations require careful planning, appropriate technology selection, and ongoing optimization to deliver maximum business value. Folio3 Data Services provides the expertise and proven methodologies needed to implement retail data warehouses that transform business operations and drive sustainable growth through data-driven decision-making capabilities.