Financial institutions process massive amounts of data every single day, but turning that data into actionable insights remains a challenge. Predictive analytics in finance uses historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning to forecast future outcomes and trends.
According to a McKinsey report, financial services leads all industries in AI adoption, with 56% of organizations reporting AI use in at least one business function.
The global economy generates approximately 402.74 million terabytes of data every day, creating unprecedented opportunities for predictive modeling. Banks and financial institutions now rely on predictive analytics to detect fraud, assess credit risk, personalize customer experiences, and optimize investment portfolios. This technology helps finance teams move from reactive problem-solving to proactive strategy development, reducing losses while identifying new revenue opportunities.
What Is Predictive Analytics In Finance?
Predictive analytics in finance applies statistical methods and machine learning algorithms to historical financial data to predict future events, behaviors, and trends. This approach helps financial institutions make informed decisions based on data patterns rather than intuition alone.
The process involves collecting data from multiple sources, including transaction records, market feeds, customer interactions, and economic indicators. Analysts then clean and organize this information to identify meaningful patterns. Machine learning models learn from historical outcomes to predict future scenarios with measurable accuracy levels.
Financial predictive analytics differs from traditional analysis by focusing on what will happen rather than what has happened. Banks use these models to anticipate customer needs, market movements, and potential risks before they materialize. The technology processes complex datasets faster than human analysts, revealing insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Modern predictive systems continuously improve their accuracy by learning from new data. When predictions prove incorrect, algorithms adjust their parameters to perform better next time. This self-improving capability makes predictive analytics increasingly valuable as more data becomes available.
Financial institutions implement these systems across departments, from retail banking to investment management. The technology scales to handle everything from individual customer predictions to market-wide forecasts, making it accessible to organizations of all sizes.
Applications Of Predictive Analytics In Financial Services
Financial services organizations apply predictive analytics across numerous operational areas to improve efficiency, reduce risk, and enhance customer satisfaction. These applications demonstrate how data-driven forecasting transforms traditional financial processes into intelligent, automated systems.
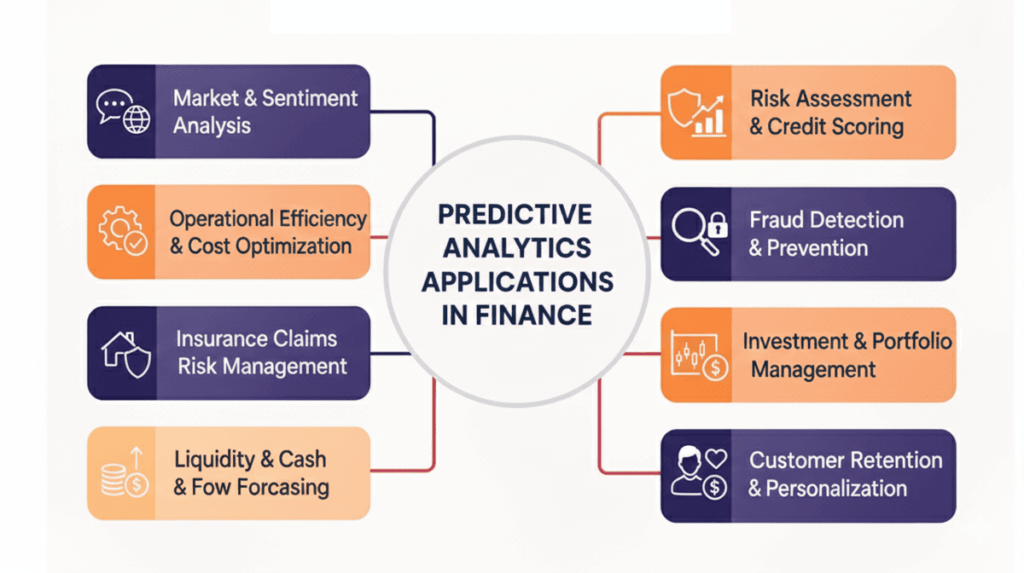
Risk Assessment and Credit Scoring
Banks use predictive models to evaluate creditworthiness more accurately than traditional scoring methods. These systems analyze hundreds of variables, including payment history, income stability, debt ratios, and behavioral patterns to predict default probability. Machine learning algorithms identify non-obvious risk indicators that human underwriters might miss.
Alternative data sources like utility payments, rental history, and even social media activity now supplement traditional credit bureau information. This expansion helps lenders assess applicants with limited credit history while reducing bias. Predictive models also enable dynamic risk pricing, adjusting interest rates based on real-time risk assessments.
Financial institutions continuously validate their credit models against actual outcomes. When economic conditions change, algorithms adapt their risk thresholds accordingly. This flexibility helps maintain lending standards during both stable and volatile market periods while protecting profitability.
Fraud Detection and Prevention
Real-time fraud detection systems analyze transaction patterns to identify suspicious activities instantly. These models learn normal behavior for each customer, flagging deviations that suggest fraudulent activity. Machine learning algorithms detect complex fraud schemes that rule-based systems miss.
Predictive fraud models examine multiple data points simultaneously, including transaction location, amount, timing, merchant category, and device information. When patterns match known fraud signatures, systems can block transactions before completion. This proactive approach saves millions in potential losses while reducing false positives that inconvenience legitimate customers.
Banks also use predictive analytics to identify accounts at high risk for future fraud attempts. These insights enable targeted security measures and customer education. As fraudsters develop new tactics, machine learning models adapt their detection methods, maintaining effectiveness against evolving threats.
Investment and Portfolio Management
Investment firms apply predictive analytics to forecast market movements, optimize portfolio allocation, and identify trading opportunities. These models process vast amounts of market data, news sentiment, economic indicators, and historical patterns to generate trading signals. Algorithmic trading systems execute strategies based on these predictions with minimal human intervention.
Portfolio optimization tools use predictive models to balance risk and return based on individual investor goals. These systems simulate thousands of potential market scenarios to recommend asset allocations that maximize expected returns within acceptable risk parameters. Rebalancing recommendations adjust automatically as market conditions change.
Quantitative hedge funds build entire investment strategies around predictive models. Their algorithms identify pricing inefficiencies, predict earnings surprises, and forecast volatility across global markets. Machine learning approaches have proven particularly effective at detecting subtle patterns in high-frequency trading data.
Customer Retention and Personalization
Financial institutions predict which customers are likely to close accounts or switch to competitors. Churn prediction models analyze account activity, service usage, customer service interactions, and demographic factors to calculate retention risk scores. Banks then deploy targeted retention campaigns before customers actually leave.
Modern financial data analytics applications also enable personalized product recommendations by identifying which customers would benefit from specific services based on their financial behavior and life stage. This approach increases cross-selling success rates while improving customer satisfaction by offering relevant solutions.
Personalization extends to communication preferences and timing. Predictive systems determine the best channels, messages, and moments to engage each customer. Banks report higher response rates and deeper relationships when leveraging these data-driven personalization strategies.
Liquidity and Cash Flow Forecasting
Treasury departments use predictive models to forecast cash positions and liquidity needs with greater accuracy. By staying informed on emerging data analytics trends, these systems analyze historical cash flow patterns, upcoming obligations, seasonal trends, and market conditions to predict future liquidity requirements. Accurate forecasts enable better working capital management and reduce the need for expensive short-term borrowing.
Banks apply similar techniques to predict deposit flows and loan demand. These insights inform funding strategies and help maintain regulatory liquidity ratios. Predictive analytics also supports stress testing by simulating cash flow impacts under various adverse scenarios.
Corporate finance teams leverage cash flow predictions for budgeting and strategic planning. When models forecast cash shortfalls, organizations can arrange financing in advance on favorable terms. Conversely, surplus predictions enable opportunistic investments or debt reduction.
Insurance Claim Prediction and Risk Management
Insurance companies use predictive analytics to estimate claim frequency and severity when underwriting new policies. Models analyze policyholder characteristics, historical claims data, and external factors like weather patterns to price premiums accurately. This data-driven approach improves profitability while ensuring competitive pricing.
Claims processing benefits from predictive models that identify potentially fraudulent submissions. Systems flag claims with characteristics similar to known fraud cases for detailed investigation. Automated triage also routes straightforward claims for fast approval while directing complex cases to experienced adjusters.
Risk management teams use predictive analytics to anticipate catastrophic events and their financial impacts. Insurers model hurricane damage, earthquake losses, and other major risks to ensure adequate reserves and reinsurance coverage. These simulations help companies survive major claim events without jeopardizing solvency.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Optimization
Banks apply predictive analytics to optimize staffing levels based on forecasted transaction volumes. Branch and call center managers use these predictions to schedule employees efficiently, reducing overtime costs while maintaining service quality. Predictive maintenance models also forecast when ATMs and other equipment need servicing before failures occur.
Process automation leverages predictive models to identify which transactions require human review versus automated processing. This intelligent routing reduces manual work while maintaining accuracy and compliance. Document processing systems predict information location within forms, accelerating data extraction.
Cost optimization models help financial institutions identify opportunities to reduce expenses without impacting service delivery. These systems analyze spending patterns across departments to highlight inefficiencies and suggest improvements. Predictive analytics also supports procurement decisions by forecasting price trends for purchased services and supplies.
Market and Customer Sentiment Analysis
Financial institutions analyze social media, news articles, earnings call transcripts, and other text sources to gauge market sentiment. Natural language processing models extract sentiment signals that predict stock movements, market volatility, and economic trends. Traders incorporate these insights into their decision-making processes.
Customer sentiment analysis helps banks understand how clients perceive their services and brand. Predictive models process customer service transcripts, survey responses, and online reviews to identify satisfaction trends before they impact retention. Early warning signals enable proactive service improvements.
Sentiment analysis also supports regulatory compliance by detecting employee communications that suggest misconduct risk. Banks monitor internal messages for language patterns associated with past compliance violations. This predictive approach helps prevent problems before they result in regulatory penalties.
Benefits Of Predictive Analytics In Finance
Implementing predictive analytics delivers measurable advantages across financial operations, from improved accuracy in forecasting to substantial cost savings and enhanced customer relationships. These benefits compound over time as models improve and organizations develop deeper analytical capabilities.
1. Enhanced Decision-Making Accuracy
Predictive models reduce human bias and emotional factors in financial decisions. Algorithms process information objectively, applying consistent logic across thousands of scenarios. This data-driven approach leads to more accurate forecasts and better strategic choices.
Financial leaders gain confidence in their decisions when backed by statistical evidence. Predictive analytics quantifies uncertainty, showing not just the most likely outcome but also the range of possibilities. This transparency helps executives balance risk and opportunity more effectively.
Organizations that adopt predictive analytics report significant improvements in forecast accuracy. Better predictions translate directly to better outcomes, whether in investment returns, loan performance, or operational efficiency. The technology essentially upgrades institutional decision-making capabilities across the board.
2. Proactive Risk Management
Traditional risk management responds to problems after they emerge. Predictive analytics enables proactive identification of risks before they materialize. Banks can adjust lending criteria, increase reserves, or hedge positions based on predicted risk scenarios.
Early warning systems detect deteriorating credit quality in loan portfolios, allowing timely intervention. Financial institutions can restructure troubled loans or set aside provisions before defaults occur. This forward-looking approach reduces losses compared to reactive management.
Market risk models predict volatility and potential drawdowns, informing position sizing and hedging strategies. Investment managers use these insights to protect capital during turbulent periods while maintaining upside participation. Predictive risk management essentially provides an early warning system for the entire organization.
3. Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Automation powered by predictive analytics eliminates manual processes and reduces headcount needs. Systems handle routine decisions faster and more accurately than human workers. Financial institutions redirect employee time toward higher-value activities that require judgment and creativity.
Predictive maintenance prevents costly equipment failures and service disruptions. Forecasting models optimize inventory levels for branches and ATMs, reducing waste while ensuring availability. These operational improvements accumulate into substantial cost savings over time.
Resource allocation becomes more efficient when driven by accurate predictions. Banks staff branches based on forecasted traffic, purchase technology based on predicted demand, and invest in expansion where models show growth potential. Better allocation reduces wasted spending while improving service delivery.
4. Improved Customer Engagement
Personalization based on predictive insights creates more relevant customer experiences. Predictive customer analytics enables banks to anticipate client needs and preferences, allowing them to deliver offers and communications aligned with each individual rather than generic marketing. This relevance increases engagement rates and strengthens customer relationships.
Predictive analytics helps financial institutions anticipate customer needs before customers themselves recognize them. Banks can proactively offer solutions at important life moments, like home purchases or business expansion. This consultative approach positions the bank as a trusted advisor rather than a transactional service provider.
Customer satisfaction improves when banks resolve issues before customers complain. Predictive monitoring identifies potential problems, triggering preemptive outreach. These positive experiences build loyalty and reduce churn, increasing customer lifetime value substantially.
Why Finance Teams Use Predictive Analytics
Finance departments implement predictive analytics to solve specific business challenges and capitalize on opportunities that traditional methods cannot address. Understanding these motivations helps organizations prioritize their analytics investments and measure success appropriately.
Improve Decision-Making Accuracy
Finance teams face constant pressure to make accurate forecasts that guide strategic planning and resource allocation. Predictive analytics removes guesswork by providing data-backed insights. By applying big data strategies, teams can analyze patterns across millions of data points from diverse sources that humans cannot process manually.
Budget forecasts become more reliable when based on predictive models rather than historical trends alone. These systems account for changing market conditions, seasonal patterns, and business cycle effects. Better accuracy reduces the need for mid-year budget revisions and enables more confident strategic commitments.
Investment decisions benefit from predictive models that evaluate potential returns across multiple scenarios. Finance teams can compare options objectively, selecting projects with the highest expected value. This disciplined approach improves capital allocation and ultimately drives better financial performance.
Enhance Risk Management
Financial risk managers use predictive analytics to quantify and monitor various risk exposures. Credit risk models predict default probabilities across loan portfolios, enabling proactive management. Market risk systems forecast volatility and potential losses under stress scenarios.
Regulatory compliance requires sophisticated risk monitoring capabilities. Predictive models help institutions meet capital adequacy requirements by accurately forecasting losses under adverse conditions. These systems also identify emerging risks that require management attention before regulators raise concerns.
Operational risk analytics predict potential failures in processes and systems. Finance teams use these insights to strengthen controls and prevent costly disruptions. Fraud prediction specifically protects institutions from financial crimes that erode profitability and damage reputation.
Optimize Resource Allocation
Limited resources require careful allocation to maximize returns. Predictive analytics identifies where investments will generate the highest returns. Finance teams model different allocation scenarios to find optimal strategies.
Staffing decisions benefit from workforce demand forecasting. Organizations hire and schedule employees based on predicted workload rather than historical patterns. This precision reduces labor costs while maintaining service levels during peak periods.
Technology investments increasingly rely on predictive models showing expected returns. Finance teams evaluate software, hardware, and infrastructure purchases using data-driven projections. This analytical approach ensures technology spending delivers measurable business value rather than following trends.
Increase Revenue Opportunities
Predictive analytics uncovers revenue opportunities that traditional analysis misses. Customer propensity models identify which clients are most likely to purchase additional products. Sales teams focus efforts on high-probability prospects rather than pursuing everyone equally.
Pricing optimization uses predictive models to find the sweet spot between volume and margin. Financial institutions can adjust pricing dynamically based on demand forecasts, competitor actions, and customer price sensitivity. This sophisticated approach maximizes revenue without sacrificing market share.
Market expansion decisions rely on predictions about growth potential in different segments and geographies. Finance teams model expected returns before committing resources to new initiatives. Better predictions lead to more successful expansions and fewer costly mistakes.
Boost Operational Efficiency
Process automation guided by predictive analytics reduces costs while improving speed and accuracy. Finance teams identify which tasks machines can handle and which require human expertise. This optimization reduces manual work and accelerates transaction processing.
Exception handling becomes more efficient when predictive models route only complex cases to specialists. Routine transactions process automatically, freeing staff for higher-value work. This intelligent workflow management improves productivity without increasing headcount.
Performance monitoring leverages predictive analytics to identify declining efficiency before it impacts results. Finance teams receive early warnings about process bottlenecks or quality issues. Proactive intervention prevents small problems from becoming major disruptions.
Implementing Predictive Analytics In Finance
Successful implementation requires careful planning, appropriate technology choices, and organizational commitment. Financial institutions must follow a structured approach to realize the full benefits of predictive analytics while avoiding common pitfalls.
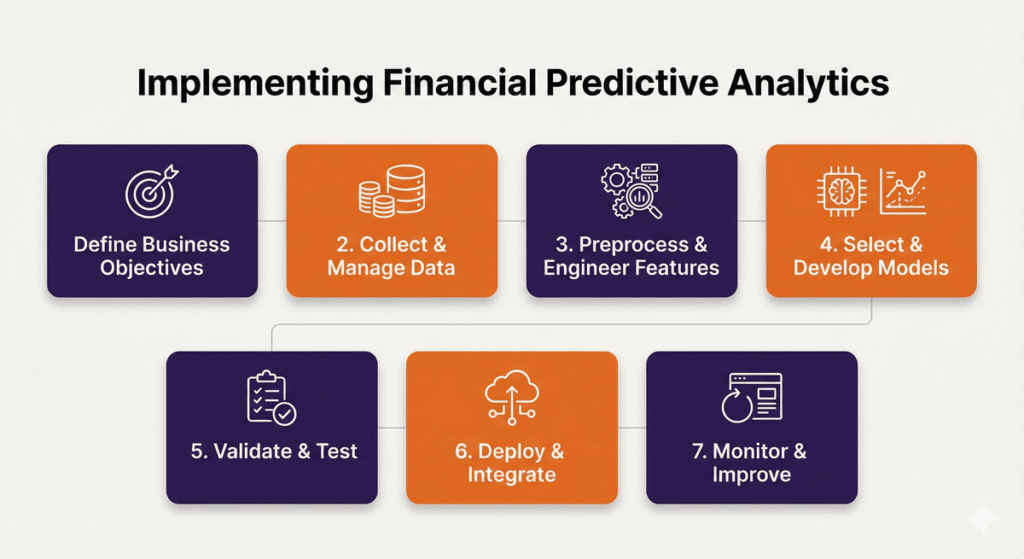
1. Define Business Objectives
Implementation begins with clear objectives tied to specific business outcomes. Organizations must identify which problems they want to solve or which opportunities to pursue. Vague goals like “use more data” lead to unfocused efforts without measurable returns.
Stakeholder alignment ensures analytics initiatives address real business needs. Finance leaders, risk managers, and operations teams should jointly define priorities. This collaboration prevents building sophisticated models that nobody actually uses.
Success metrics must be established before development begins. Organizations should specify how they will measure whether predictive analytics delivers value. These metrics guide project scope decisions and provide accountability throughout implementation.
2. Data Collection and Management
Predictive models require clean, comprehensive data from relevant sources. Organizations must audit existing data assets and identify gaps. Data collection processes should capture all information needed for accurate predictions while respecting privacy regulations.
Effective implementation often depends on data processing and engineering expertise to design pipelines, integrate disparate systems, and ensure data is reliable, consistent, and accessible across the organization.
Data governance establishes standards for quality, security, and accessibility. Finance teams need confidence that their data is accurate and reliable. Governance frameworks define ownership, update frequencies, and validation procedures for each data source.
Integration challenges arise when data resides in multiple systems with different formats. Organizations must invest in data pipelines that consolidate information into accessible repositories. Modern data platforms simplify this integration while providing scalability for growing data volumes.
3. Data Preprocessing and Feature Engineering
Raw data rarely works directly in predictive models. Analysts must clean datasets by handling missing values, correcting errors, and removing outliers. This preprocessing ensures models learn from accurate information rather than data quality issues.
Feature engineering transforms raw data into inputs that help models make better predictions. Analysts create calculated fields, aggregate historical patterns, and encode categorical variables appropriately. Thoughtful feature engineering often contributes more to model performance than algorithm selection.
Normalization and scaling ensure different data types work together effectively. Financial data includes various units and scales, from binary flags to millions of dollars. Proper transformation prevents any single feature from dominating model behavior.
4. Model Selection and Development
Algorithm selection depends on the specific prediction task and available data. Classification models predict categorical outcomes like default or no default. Regression models forecast continuous values like stock prices or loan amounts. Time series models specialize in sequential data with temporal patterns.
Model complexity must balance accuracy with interpretability. Complex neural networks may achieve slightly better predictions but operate as black boxes. Simpler models like decision trees provide transparency that regulators and business users value. Finance teams should start with interpretable models before exploring complex alternatives.
Training processes expose models to historical data so they learn predictive patterns. Analysts split datasets into training, validation, and test subsets. This separation prevents overfitting where models memorize training data rather than learning generalizable patterns.
5. Validation and Testing
Model validation ensures predictions perform well on new, unseen data. Testing on held-out datasets reveals whether models generalize beyond their training examples. Poor test performance indicates overfitting or fundamental data quality issues.
Backtesting evaluates model performance across historical periods. This technique particularly matters for financial predictions where market regimes change. Models should maintain accuracy across different economic environments rather than optimizing for a single period.
Sensitivity analysis tests how models respond to extreme inputs or unusual combinations. Financial institutions need confidence that their systems behave reasonably under stress. These tests identify potential failure modes before deployment into production environments.
6. Deployment and Integration
Production deployment requires integrating predictive models into operational systems and workflows. Models must connect to live data sources and deliver predictions when needed. Technical infrastructure must handle required transaction volumes with acceptable latency.
User interfaces should present predictions in actionable formats. Decision makers need clear recommendations with supporting evidence, not just raw model scores. Visualization helps communicate complex predictions to non-technical stakeholders effectively.
Change management helps organizations adopt new predictive tools. Training programs teach employees how to interpret and act on model outputs. Clear policies define when to follow predictions versus applying human judgment.
7. Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Performance monitoring tracks whether deployed models maintain accuracy over time. Model drift occurs when relationships in data change, degrading prediction quality. Automated alerts notify teams when performance falls below acceptable thresholds.
Retraining incorporates new data to keep models current. Financial markets and customer behaviors evolve continuously, requiring periodic model updates. Organizations should establish retraining schedules based on how quickly their data patterns change.
Feedback loops capture actual outcomes and compare them to predictions. This information drives model improvements and reveals blind spots in existing approaches. Continuous learning ensures predictive systems become more accurate and valuable over time.
Move from theory to execution with Folio3’s end-to-end predictive analytics implementation services built for finance teams.
Case Studies: Predictive Analytics In Corporate Finance
Real-world implementations demonstrate how leading financial institutions leverage predictive analytics to achieve measurable business results. These examples illustrate both the opportunities and challenges organizations face when deploying advanced analytics at scale.
JPMorgan Chase: Fraud Detection and Prevention
JPMorgan Chase processes billions of transactions annually, making fraud detection a critical capability. The bank developed machine learning models that analyze transaction patterns in real time to identify fraudulent activities. These systems examine hundreds of variables simultaneously, including merchant information, transaction amounts, locations, and historical customer behavior.
The bank’s predictive fraud models have significantly reduced false positives compared to rule-based systems. This improvement means fewer legitimate transactions get blocked, reducing customer friction while maintaining security. Machine learning algorithms continuously adapt to new fraud tactics, maintaining effectiveness as criminals evolve their methods.
JPMorgan’s approach combines multiple model types, including neural networks for pattern recognition and decision trees for interpretable rules. This hybrid strategy balances accuracy with explainability, an important consideration for regulatory compliance. The system flags suspicious transactions for review while automatically approving clearly legitimate activities.
HSBC: Real-Time Transaction Monitoring
HSBC implemented predictive analytics to enhance its anti-money laundering capabilities across global operations. According to HSBC’s annual report, traditional transaction monitoring generated excessive false positives, overwhelming compliance teams with alerts. The bank deployed machine learning models that learn normal behavior patterns for each customer and account.
These predictive systems reduced false positive rates by over 20% while improving detection of actual suspicious activities. Compliance analysts now focus on higher-risk cases rather than investigating thousands of benign alerts. The efficiency gains allow HSBC to process higher transaction volumes without proportionally increasing compliance staff.
Real-time processing enables HSBC to block suspicious transfers before completion rather than detecting problems after the fact. This proactive approach protects both the bank and its customers from financial crime. The system also provides better documentation for regulatory reporting requirements.
Capital One: Personalized Offers And Churn Prediction
Capital One built one of the financial industry’s most sophisticated customer analytics capabilities. The bank uses predictive models to identify which products each customer would find valuable based on their financial behavior, life stage, and preferences. This personalization dramatically improves marketing campaign response rates.
Churn prediction models help Capital One identify customers at risk of closing accounts or reducing engagement. The bank proactively reaches out with targeted retention offers before customers actually leave. This approach has significantly improved customer retention rates compared to reactive strategies.
Capital One’s data science team continuously experiments with new modeling techniques and features. The bank’s test-and-learn culture drives ongoing improvements in prediction accuracy. Advanced analytics have become a core competitive advantage, enabling better customer experiences and stronger financial performance.
Goldman Sachs: Algorithmic Trading and Market Forecasting
Goldman Sachs employs predictive analytics extensively in its trading operations. The firm’s algorithmic trading systems analyze market data, news sentiment, and order flow patterns to identify trading opportunities. Machine learning models predict short-term price movements with statistical edges that generate consistent profits.
Market forecasting models help Goldman’s investment banking division advise clients on mergers, acquisitions, and capital raising. These systems analyze comparable transactions, market conditions, and company fundamentals to predict valuations and deal outcomes. Better forecasts improve the quality of strategic advice the firm provides.
Goldman also uses predictive analytics for risk management across its trading portfolio. Models simulate thousands of market scenarios to estimate potential losses under various conditions. This comprehensive risk assessment informs position limits and hedging strategies.
The Voleon Group: Quantitative AI-Powered Asset Management
The Voleon Group relies entirely on machine learning for portfolio management. Its custom data and analytics pipelines ingest massive datasets, including price histories, fundamentals, and alternative sources, to uncover predictive patterns undetectable by human analysts. This approach enables Voleon to maintain fully data-driven investment strategies with strong risk-adjusted returns.
Voleon’s approach demonstrates how far predictive analytics can advance beyond traditional finance methods. The firm maintains no traditional research analysts or portfolio managers. Instead, data scientists and machine learning engineers continuously improve the predictive models that drive all investment decisions.
Performance results validate the approach, with Voleon achieving strong risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional asset managers. The firm’s success illustrates how predictive analytics can create entirely new business models in finance rather than simply improving existing processes.
Techniques And Tools For Financial Predictive Analytics
Financial institutions employ various analytical techniques and software platforms to build and deploy predictive models. Selecting the right approach often depends on the organization’s big data predictive analytics framework, which defines how data is ingested, processed, and modeled at scale. Understanding the available options helps organizations align tools, workflows, and technical expertise with their strategic goals.
1. Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning provides powerful techniques for discovering patterns in financial data. Different algorithm families excel at different prediction tasks, so practitioners often try multiple approaches to find the best performer.
Random Forest Models
Random forests combine multiple decision trees to improve prediction accuracy and reduce overfitting. Each tree trains on a random subset of data and features, then predictions get averaged across all trees. This ensemble approach performs well across diverse financial applications from credit scoring to fraud detection.
Neural Networks
Neural networks excel at finding complex nonlinear patterns in large datasets. Deep learning architectures with multiple layers can model sophisticated relationships between inputs and outcomes. Financial applications include algorithmic trading, fraud detection, and customer behavior prediction.
Gradient Boosting Machines
Gradient boosting builds prediction models sequentially, with each new model correcting errors made by previous ones. This iterative process produces highly accurate predictions across many financial tasks. Popular implementations include XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost.
Support Vector Machines
Support vector machines find optimal decision boundaries between different outcome classes. They work well with high-dimensional data where traditional methods struggle. Financial applications include credit default prediction and market direction forecasting.
2. Statistical Forecasting Techniques
Traditional statistical methods remain relevant for many financial predictions, particularly time series forecasting. These techniques offer interpretability and work well when data follows known patterns. Financial institutions often incorporate these methods into their predictive analytics models to improve forecast accuracy and risk assessment.
Time Series Analysis
Time series methods analyze sequential data where past values predict future outcomes. These techniques decompose data into trends, seasonal patterns, and irregular components. Applications include stock price forecasting, economic indicator prediction, and demand planning.
Regression Models
Regression analysis quantifies relationships between independent variables and outcomes. Linear regression provides interpretable coefficients showing how each factor influences predictions. Extensions like logistic regression handle categorical outcomes such as default versus no default.
ARIMA and SARIMA Models
Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average models specialize in forecasting time series with trends and seasonality. SARIMA extends ARIMA to explicitly model seasonal patterns. These techniques work well for predicting financial metrics like revenue, expenses, and asset prices.
ARIMA models require stationary data where statistical properties remain constant over time. Analysts must differentiate or transform data appropriately before modeling. Despite these requirements, ARIMA remains popular for financial forecasting due to strong performance and interpretability.
Exponential Smoothing
Exponential smoothing methods weight recent observations more heavily than older data. This approach works well when recent patterns matter more than distant history. Variations handle trends and seasonality in addition to basic smoothing.
3. Software And Platforms
Financial institutions choose analytics platforms based on their technical requirements, existing technology stack, and available expertise. The right tools depend on specific use cases and organizational capabilities.
SAS Analytics
SAS provides enterprise analytics software widely adopted in financial services. The platform offers comprehensive tools for data management, statistical analysis, and predictive modeling. SAS’s strengths include regulatory compliance features and extensive documentation.
Many banks standardized on SAS decades ago, creating substantial institutional knowledge and legacy systems. The platform handles large-scale production deployments reliably. However, SAS requires expensive licensing and uses proprietary programming languages.
Python Libraries
Python has emerged as the preferred language for modern data science. Libraries like pandas, scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch provide powerful analytics capabilities. Python’s open-source ecosystem enables rapid innovation and broad community support.
Financial institutions increasingly adopt Python for new analytics projects. The language integrates well with modern data platforms and cloud services. Python developers are more readily available than specialists in proprietary tools.
R Programming
R remains popular for statistical analysis and academic research. The language provides extensive statistical libraries and visualization capabilities. Many statisticians and quantitative researchers prefer R for exploratory analysis and research projects.
R excels at statistical techniques but can face performance challenges with very large datasets. The language integrates with production systems less smoothly than Python. Financial institutions often use R for research and prototyping before deploying Python versions to production.
Tableau Visualization
Tableau creates interactive visualizations and dashboards that communicate analytical insights effectively. Users can explore predictive model outputs visually without programming knowledge. The platform connects to various data sources and updates dashboards automatically.
Some organizations incorporate outputs from generative AI implementation into Tableau dashboards to simulate “what-if” scenarios or visualize synthetic datasets alongside real financial data.
Financial institutions use Tableau to share model predictions with business stakeholders. Interactive dashboards let users drill down into forecasts and understand drivers. However, Tableau itself does not build predictive models, serving instead as a presentation layer.
Power BI Dashboards
Microsoft Power BI provides business intelligence and visualization capabilities similar to Tableau. The platform integrates tightly with Microsoft’s ecosystem including Excel and Azure services. Power BI offers strong value for organizations already using Microsoft technologies.
Power BI includes some basic predictive analytics features like forecasting and clustering. However, sophisticated modeling typically occurs in other tools with results displayed in Power BI. The platform works well for operational reporting and performance monitoring.
Challenges In Implementing Predictive Analytics In Finance
Despite significant benefits, organizations face obstacles when deploying predictive analytics. Understanding these challenges helps institutions prepare appropriate responses and increase implementation success rates.
1. Data Quality Issues
Predictive models depend entirely on training data quality. Financial institutions often struggle with incomplete records, inconsistent formats, and errors accumulated over decades. Legacy systems store data in proprietary formats that resist integration efforts.
Missing values create particular challenges for modeling. Analysts must decide whether to exclude incomplete records, impute missing values, or use algorithms that handle gaps naturally. Each approach introduces potential biases that affect prediction accuracy.
Data quality improvement requires sustained investment in governance and infrastructure. Organizations must establish data standards, implement validation rules, and clean existing repositories. These foundational efforts consume time and resources before any predictive models launch.
2. Model Accuracy Risks
Predictive models never achieve perfect accuracy. Financial institutions must accept some level of prediction error while managing the resulting risks. For example, models designed to predict demand using AI can help anticipate customer needs or market shifts, but overfitting or outdated data may reduce reliability. Overly confident decisions based on flawed predictions can lead to significant losses.
Overfitting causes models to memorize training data rather than learning generalizable patterns. These models perform well on historical data but fail on new examples. Cross-validation and proper testing help detect overfitting before deployment.
Model drift occurs when relationships in data change over time. A credit model trained on pre-recession data may perform poorly during economic downturns. Continuous monitoring and periodic retraining maintain accuracy as conditions evolve.
3. Regulatory Compliance Challenges
Financial regulators require institutions to explain their decision-making processes. Complex machine learning models that operate as black boxes create compliance difficulties. Banks must balance predictive accuracy with the interpretability that regulators demand.
Fair lending laws prohibit discrimination based on protected characteristics. Models trained on historical data may learn biased patterns from past decisions. Financial institutions must audit their predictions for discriminatory outcomes and implement appropriate safeguards.
Model validation requirements impose additional burdens. Regulators expect independent testing of predictive systems before deployment and ongoing monitoring afterward. These validation processes require specialized expertise and documentation procedures.
4. Legacy System Integration
Many financial institutions run critical operations on decades-old mainframe systems. Integrating modern predictive analytics with legacy infrastructure creates technical challenges. Data extraction alone can require custom development work.
Real-time predictions may not be feasible when older systems process batch transactions overnight. Organizations must either modernize their core platforms or accept limitations on how quickly they can act on predictions.
Legacy systems often lack the APIs and data access capabilities that modern analytics platforms expect. Middleware solutions can bridge these gaps but add complexity and potential points of failure. Some institutions ultimately face decisions about wholesale system replacement.
Our experts help you improve data quality, reduce model risk, and integrate modern analytics with legacy systems – without disrupting operations.
7 Best Practices for Financial Predictive Analytics
Following established best practices increases the likelihood of successful predictive analytics implementations. These guidelines reflect lessons learned across numerous financial institutions and use cases.
1. Ensure Data Quality
Invest in data governance before building predictive models. Establish clear ownership for each data source and implement validation rules that catch errors at entry points. Regular audits identify quality issues before they contaminate model training.
Document data lineage so analysts understand where information originates and how it transforms. This transparency helps troubleshoot prediction problems and satisfies regulatory requirements. Automated data quality monitoring catches degradation promptly.
2. Select Appropriate Models
Match model complexity to available data and business needs. Simple models work well when data is limited or interpretability matters. Complex algorithms make sense only when sufficient data exists and accuracy improvements justify reduced transparency.
Test multiple modeling approaches rather than committing to a single technique. Different algorithms excel on different problems, and empirical testing reveals which performs best. This experimental mindset leads to better outcomes than theoretical arguments about model superiority.
3. Validate and Test Models
Split data into separate training, validation, and test sets before beginning model development. Reserve the test set until final evaluation to get unbiased performance estimates. Cross-validation provides additional confidence in model stability.
Test models under various scenarios including historical stress periods. Financial models must perform adequately across different market conditions rather than optimizing for average circumstances. Scenario testing reveals potential failure modes.
4. Monitor Model Performance
Implement automated monitoring that tracks prediction accuracy on new data. Set thresholds that trigger alerts when performance degrades beyond acceptable levels. Regular review meetings discuss monitoring results and prioritize improvement efforts. Using generative AI for data analytics, institutions can simulate stress scenarios or rare events to test model robustness more efficiently.
Compare predictions to actual outcomes systematically. This analysis identifies where models work well and where they struggle. Pattern recognition in prediction errors often suggests specific model enhancements.
5. Maintain Regulatory Compliance
Build compliance considerations into model development from the start rather than treating them as afterthoughts. Involve legal and compliance teams early to understand requirements. Documentation standards should capture development decisions and validation results.
Audit models for potential discriminatory outcomes even when protected characteristics are excluded from inputs. Proxy variables can introduce bias indirectly. Fairness testing should become standard practice for customer-facing predictions.
6. Integrate With Systems
Plan for production deployment during model development. Technical requirements like latency, throughput, and reliability influence design choices. Building production-ready systems from the start avoids costly rework later.
Design user interfaces that present predictions in actionable formats. Decision makers need clear recommendations with supporting context. Visualization helps communicate complex information effectively to non-technical audiences.
7. Foster Domain Expertise
Combine data science skills with deep financial domain knowledge. Models built without business understanding often miss important nuances or make unrealistic predictions. Cross-functional teams produce better results than isolated technical efforts.
Encourage ongoing learning and skill development in both analytics and finance. The field evolves rapidly with new techniques emerging regularly. Organizations that invest in their people maintain competitive advantages in predictive capabilities.
Measuring ROI Of Predictive Analytics In Finance
Organizations need systematic approaches to quantify the value delivered by predictive analytics investments. Clear measurement frameworks demonstrate business impact and inform future investment decisions.
1. Track Cost Savings
Automation powered by predictive analytics reduces manual work and associated labor costs. Organizations often rely on predictive analytics experts to design and implement these systems effectively. Measure headcount savings or productivity improvements in processes like fraud review, credit underwriting, and customer service. Calculate annual savings against implementation and maintenance costs.
Error reduction delivers cost savings by preventing losses. Fraud prevention systems save amounts that would otherwise be stolen. Credit models reduce defaults by identifying risky borrowers earlier. Quantify these avoided losses as tangible returns.
2. Measure Revenue Impact
Improved customer targeting increases marketing campaign response rates and conversion. Track revenue generated from predictive model recommendations compared to baseline approaches. Calculate lift from personalization and propensity scoring.
Pricing optimization enables institutions to capture more value without losing volume. Measure revenue changes after implementing dynamic pricing models. Compare results to previous pricing strategies while controlling for market conditions.
3. Monitor Risk Reduction
Predictive risk models reduce losses from defaults, fraud, and operational failures. Calculate the dollar value of prevented losses attributed to early warning systems. Compare risk-adjusted returns before and after analytics deployment.
Regulatory capital requirements decrease when institutions demonstrate better risk management. Calculate capital savings from improved risk models approved by regulators. These savings free up resources for lending and investment.
4. Evaluate Operational Efficiency
Process automation speeds up transaction processing and reduces turnaround times. Measure cycle time improvements for loan approvals, account openings, and other key processes. Faster processing improves customer satisfaction while reducing costs.
Resource utilization improves when predictive models optimize staffing and technology deployment. Track utilization rates and idle time before and after implementation. Better allocation delivers services more efficiently without adding resources.
5. Assess Customer Outcomes
Customer satisfaction scores often improve after implementing predictive personalization. Survey results and net promoter scores provide feedback on customer experience. Link satisfaction improvements to retention and lifetime value.
Churn reduction directly impacts revenue through retained accounts and relationships. Measure retention rate improvements attributable to predictive intervention programs. Calculate the present value of saved customer relationships.
6. Use Analytics KPIs
Model performance metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall quantify technical effectiveness. Track these metrics over time to ensure maintained performance. Degradation signals the need for model updates.
Business impact metrics connect predictions to outcomes. If credit models aim to reduce defaults, track actual default rates. If fraud systems target false positive reduction, measure alert accuracy. Align technical metrics with business objectives.
The Future Of Financial Predictive Analytics
Emerging technologies and evolving business needs will shape how financial institutions leverage predictive analytics in coming years. Several trends appear likely to influence the field substantially.
AI-Driven Analytics and Automation
Artificial intelligence capabilities continue advancing rapidly. Large language models now assist with ai powered data extraction, model building, and insight generation. Financial institutions will increasingly adopt AI assistants that accelerate analytics workflows.
Automated machine learning platforms reduce the technical expertise needed to build predictive models. These tools automatically select algorithms, tune parameters, and generate production-ready code. Democratization of analytics enables broader adoption across organizations.
Explainable AI techniques address the black box problem in complex models. New methods provide insights into why models make specific predictions. This transparency helps financial institutions satisfy regulatory requirements while using sophisticated algorithms.
Blockchain Integration
Blockchain technology creates immutable records of transactions and agreements. Integrating blockchain data with predictive analytics could improve fraud detection and credit assessment. Decentralized finance applications may generate entirely new data sources for modeling.
Smart contracts on blockchain platforms could automatically execute based on predictive model outputs. For example, insurance claims might settle automatically when models validate legitimacy. This automation reduces costs while accelerating processes.
Advanced Personalization
Predictive personalization will become more sophisticated and granular. Financial institutions will use real-time data to customize every customer interaction. Products, pricing, and communications will adapt dynamically to individual circumstances.
Privacy-preserving machine learning techniques enable personalization without compromising data security. Federated learning trains models on decentralized data without exposing sensitive information. These approaches balance personalization with growing privacy regulations.
Sustainable Finance and ESG
Environmental, social, and governance factors increasingly influence investment decisions. Predictive models will incorporate ESG data to forecast sustainable investment performance. Analytics will help institutions identify climate risks in lending portfolios.
According to Bloomberg Intelligence, ESG assets could exceed $50 trillion by 2025. Predictive analytics will play a central role in managing these investments. Models will forecast which companies meet ESG criteria and predict long-term sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Predictive Analytics In Finance?
Predictive analytics in finance uses historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning to forecast future financial outcomes. It helps institutions anticipate risks, identify opportunities, and make data-driven decisions across operations from lending to investment management.
How Does Predictive Analytics Improve Financial Decision-Making?
Predictive analytics removes guesswork by providing objective, data-backed insights. It processes patterns across millions of data points that humans cannot analyze manually, leading to more accurate forecasts and better strategic choices with quantified uncertainty levels.
Which Financial Processes Benefit Most From Predictive Analytics?
Fraud detection, credit risk assessment, customer churn prediction, portfolio management, and cash flow forecasting benefit significantly. These processes involve large datasets with identifiable patterns where predictive models substantially outperform traditional rule-based approaches.
Can Predictive Analytics Detect Financial Fraud In Real-Time?
Yes, modern systems analyze transactions instantly to identify suspicious patterns. They learn normal behavior for each customer and flag deviations suggesting fraud. This real-time detection enables blocking fraudulent transactions before completion rather than discovering problems afterward.
What Types Of Models Are Used In Financial Predictive Analytics?
Common models include random forests, neural networks, gradient boosting machines, logistic regression, and time series forecasting methods like ARIMA. The choice depends on the specific prediction task, available data, and requirements for model interpretability.
How Can Predictive Analytics Reduce Operational Costs In Banking?
Automation powered by predictive models eliminates manual processes and reduces labor costs. Systems handle routine decisions faster than humans while fraud prevention and credit models reduce losses. Resource optimization based on accurate forecasts prevents waste.
How Do Banks Use Predictive Analytics For Risk Management?
Banks predict default probabilities across loan portfolios, forecast market volatility, and identify emerging operational risks. Early warning systems enable proactive intervention before problems materialize. Stress testing simulates adverse scenarios to ensure adequate capital reserves.
What Tools and Software Are Best For Predictive Analytics In Finance?
Popular options include Python with scikit-learn for machine learning, R for statistical analysis, SAS for enterprise deployments, and Tableau or Power BI for visualization. The best choice depends on existing infrastructure, available expertise, and specific requirements.
What Are the Challenges of Implementing Financial Predictive Analytics?
Key challenges include data quality issues, model accuracy risks, regulatory compliance requirements, and legacy system integration difficulties. Organizations must invest in data governance, continuous monitoring, and appropriate documentation to overcome these obstacles.
How Can Predictive Analytics Enhance Customer Experience In Finance?
Predictive models enable personalized product recommendations, proactive service improvements, and relevant communications. Banks anticipate customer needs before they arise and resolve potential issues before complaints occur. This attentive approach strengthens relationships and increases satisfaction.
What Are The Best Practices For Financial Predictive Analytics?
Essential practices include ensuring data quality, selecting appropriate models, thorough validation and testing, continuous performance monitoring, maintaining regulatory compliance, integrating with existing systems, and combining data science with financial domain expertise.
What Is The Future Of Predictive Analytics In Finance?
The future includes AI-driven automation making analytics more accessible, blockchain integration creating new data sources, advanced real-time personalization, and sustainable finance analytics incorporating ESG factors. Explainable AI will address transparency concerns while maintaining sophisticated capabilities.
Conclusion
Predictive analytics has transformed from an experimental technology into a fundamental capability for modern financial institutions. Banks, investment firms, and insurance companies now depend on data-driven forecasting to compete effectively in dynamic markets. The technology delivers measurable benefits including improved decision accuracy, proactive risk management, operational efficiency, and enhanced customer experiences.
While implementation challenges exist around data quality, regulatory compliance, and system integration, established best practices help organizations navigate these obstacles successfully. As artificial intelligence capabilities advance and new data sources emerge, predictive analytics will only grow in importance. Financial institutions that build strong analytical foundations today position themselves for sustained competitive advantage.
Folio3 Data Services helps financial institutions implement predictive analytics solutions that drive measurable business results. Our team combines deep expertise in data engineering, machine learning, and financial services to design systems that integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure. We specialize in building compliant, production-ready models for risk assessment, fraud detection, customer analytics, and operational optimization. Our approach emphasizes not just technical excellence but also practical business value, with clear ROI measurement frameworks.
Whether modernizing legacy analytics capabilities or launching new initiatives, Folio3 provides the strategic guidance and technical execution that financial organizations need to succeed with predictive analytics.