Healthcare supply chain analytics represents the systematic use of data analysis tools and techniques to improve procurement, inventory management, and distribution processes within medical organizations. This discipline combines statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and real-time monitoring to create more efficient supply networks.
The stakes couldn’t be higher in today’s healthcare environment. Medical facilities face unprecedented pressure to reduce costs while maintaining quality care standards. Supply chain disruptions have cost the industry billions, with some hospitals experiencing 20-40% increases in procurement expenses over the past three years.
Healthcare supply chain analytics delivers measurable results: cost reductions of 15-25%, inventory carrying cost decreases of 30%, and improved patient care through better resource availability. Organizations using advanced analytics report fewer stockouts, reduced waste, and stronger supplier relationships.
Yet many healthcare systems still operate with fragmented data, manual processes, and reactive decision-making. These inefficiencies create vulnerabilities that analytics can address, transforming supply chains from cost centers into strategic advantages.
This guide explores how healthcare supply chain analytics can help decision-makers overcome these inefficiencies, transform operations, and turn the supply chain into a true strategic advantage.
What is Healthcare Supply Chain Analytics and Why It Matters
Healthcare organizations generate massive amounts of supply chain data daily. Every purchase order, inventory transaction, and supplier interaction creates information that can drive better decisions. Healthcare supply chain analytics converts this raw data into actionable insights.
The discipline encompasses several key areas: demand forecasting, inventory optimization, supplier performance monitoring, cost analysis, and risk management. Modern analytics platforms integrate data from multiple sources, such as electronic health records, procurement systems, warehouse management tools, and supplier portals, to create comprehensive visibility.
Supply chain analytics in healthcare differs from other industries due to unique regulatory requirements, the life-critical nature of many products, and complex stakeholder relationships. Medical supplies often have strict expiration dates, specialized storage requirements, and regulatory tracking needs that standard analytics approaches can’t address.
Today’s healthcare leaders recognize that supply chain performance directly impacts patient outcomes. When critical medications are unavailable, procedures get delayed. When equipment fails unexpectedly, patient safety suffers. Analytics helps prevent these scenarios by providing early warning systems and predictive insights.
How Do Key Challenges Affect Healthcare Supply Chains?
Healthcare supply chains face distinct challenges that traditional business approaches struggle to solve. Understanding these pain points reveals why analytics becomes essential for modern medical organizations.
Inventory Shortages
Medical facilities regularly experience critical shortages that compromise patient care. The American Hospital Association reports that 99% of hospitals have experienced supply shortages, with 74% citing direct patient care impacts. These shortages often result from poor demand forecasting, supplier disruptions, or inadequate safety stock calculations.
Traditional ordering patterns rely on historical usage data without considering external factors like seasonal disease patterns, demographic changes, or emerging health trends. This reactive approach leaves organizations vulnerable to unexpected demand spikes. Analytics in your healthcare supply chain enables proactive inventory management by incorporating multiple data sources into demand predictions.
Rising Costs & Waste
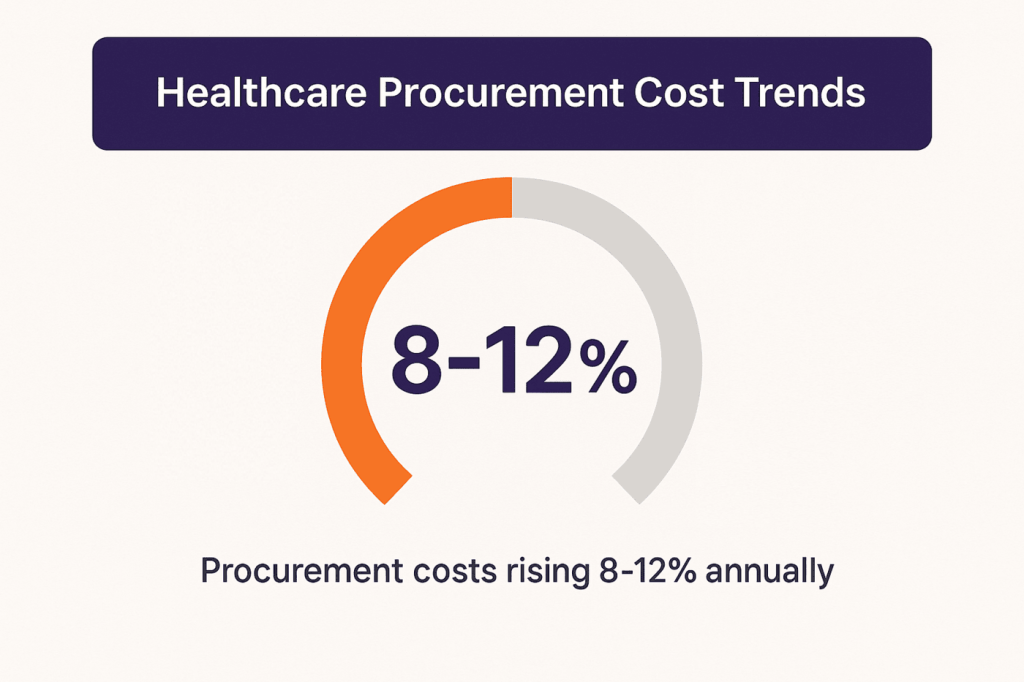
Healthcare spending on supplies and equipment continues to climb, with many organizations seeing 8-12% annual increases in procurement costs. Simultaneously, waste rates remain high, and studies indicate that 10-15% of medical supplies expire unused, representing millions in lost value for larger health systems, according to NIH.
Price volatility affects everything from basic consumables to specialized equipment. Without proper analytics, procurement teams lack visibility into spending patterns, contract performance, and market trends. This blind spot prevents strategic sourcing decisions and contract negotiations based on actual usage data.
Supplier Disruptions & Risks
Single-source suppliers create significant vulnerabilities in healthcare supply chains. When disruptions occur, whether from natural disasters, quality issues, or business failures, patient care suffers immediately. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted these risks when global supply chains collapsed, leaving hospitals scrambling for essential protective equipment.
Healthcare supply chain analytics helps identify supplier concentration risks before they become critical. By monitoring supplier financial health, quality metrics, and delivery performance, organizations can develop contingency plans and diversify their supplier base strategically.
Regulatory Compliance Issues
Medical supplies face strict regulatory oversight from agencies like the FDA, requiring detailed tracking and documentation throughout the supply chain. Lot tracking, recall management, and audit trails create administrative burdens that manual systems can’t handle efficiently.
Compliance failures result in financial penalties, operational disruptions, and potential patient safety issues. Partnering with healthcare data analytics consulting services can help automate much of this tracking, ensuring accurate documentation while reducing administrative overhead.
Lack of Visibility & Real-Time Data
Most healthcare organizations operate with limited supply chain visibility. Inventory levels, supplier performance, and cost trends are hidden in separate systems that fail to communicate effectively. This fragmentation prevents proactive decision-making and strategic planning.
Real-time visibility becomes crucial during emergencies or rapid demand changes. Without current data, supply chain teams can’t respond quickly to shortages, price changes, or quality issues. Manual reporting processes delay critical decisions when time matters most.
How Healthcare Supply Chain Analytics Solves These Challenges
Advanced analytics transforms these persistent challenges into manageable processes through data-driven approaches that improve accuracy and reduce costs.
Data-Driven Demand Forecasting
Supply chain data analytics in healthcare uses multiple data sources to predict future demand more accurately than traditional methods. These systems analyze historical usage patterns, patient census trends, seasonal variations, and external factors like disease outbreaks or demographic changes.
Machine learning algorithms continuously improve forecast accuracy by incorporating new data and adjusting for changing conditions through predictive analytics techniques. Some healthcare systems report improvements in forecast accuracy after implementing advanced analytics, leading to better inventory availability and reduced carrying costs.
Inventory Optimization
Healthcare supply chain data analytics balances the competing goals of maintaining adequate stock while minimizing carrying costs. Advanced algorithms consider factors like demand variability, lead times, storage costs, and criticality levels to calculate optimal stock levels for each item.
Dynamic safety stock calculations adjust automatically based on supplier performance, demand patterns, and service level requirements. This approach reduces both stockouts and excess inventory, freeing up capital for other priorities while maintaining patient care quality.
Supplier Performance Analysis
Comprehensive supplier scorecards track multiple performance dimensions: delivery reliability, quality metrics, pricing competitiveness, and financial stability. Healthcare contract analytics identifies which suppliers consistently meet expectations and which create risks for the organization.
Organizations are increasingly integrating customer service analytics to understand how supplier performance impacts patient-facing operations and overall service quality.
Automated alerts notify procurement teams when supplier performance degrades, enabling proactive intervention before problems affect patient care. This visibility supports better contract negotiations and helps identify opportunities for supplier development or replacement.
Predictive Risk Management
Advanced analytics identifies potential supply chain risks before they materialize. By monitoring supplier financial health, geopolitical factors, weather patterns, and market conditions, healthcare organizations can prepare contingency plans for likely disruptions.
Risk scoring models evaluate the probability and potential impact of various scenarios, helping leaders prioritize mitigation efforts. Some health systems use predictive models to maintain strategic stockpiles of critical items based on risk assessments rather than arbitrary buffer levels.
Regulatory Compliance Tracking
Automated tracking systems maintain detailed records of product lots, expiration dates, and supplier certifications without manual intervention. When recalls occur, these systems can instantly identify affected inventory and track its distribution throughout the organization.
Compliance dashboards provide real-time visibility into potential issues like expiring products, missing documentation, or supplier certification lapses. This proactive approach prevents compliance failures while reducing administrative burden on supply chain staff.
Folios3 delivers real-time healthcare supply chain analytics for smarter inventory, supplier monitoring, demand forecasting, and compliance.
What Benefits Can Healthcare Supply Chain Analytics Deliver?
Organizations implementing comprehensive analytics programs report significant improvements across multiple dimensions of supply chain performance.
Cost Reduction & Waste Minimization
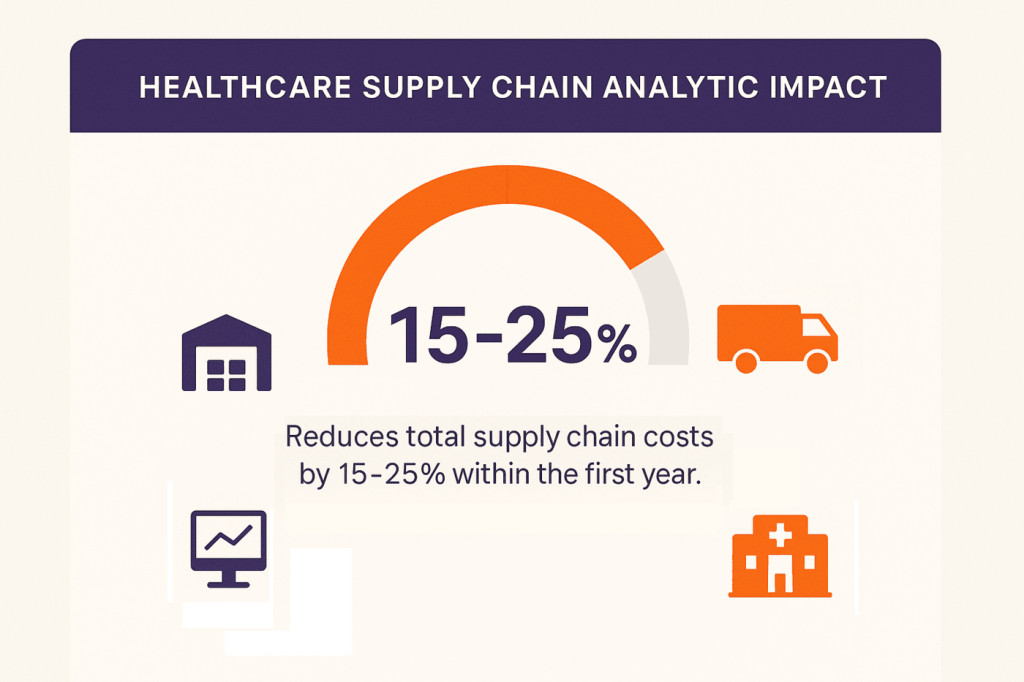
Healthcare organizations typically see 15-25% reductions in total supply chain costs within the first year of implementing advanced analytics. These savings come from better contract negotiations, reduced waste, improved inventory turns, and the elimination of rush orders.
Waste reduction programs identify products nearing expiration before they become unusable, enabling redistribution or return programs. Some health systems have reduced expired inventory by 60-80% through better demand forecasting and automated alerts.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Automated processes reduce manual work while improving accuracy. Staff can focus on strategic activities rather than routine data entry, ordering, and tracking tasks. Many organizations report 30-50% reductions in time spent on routine supply chain activities.
Exception-based management allows supply chain teams to focus attention where it’s needed most. Instead of reviewing every transaction, analytics systems highlight unusual patterns, performance issues, and opportunities for improvement.
Enhanced Patient Care & Safety
Better inventory availability ensures that clinical staff have the necessary supplies when patients need them. Reduced stockouts mean fewer delayed procedures and better patient satisfaction scores. Some hospitals report 65% reductions in stockout incidents after implementing analytics programs.
Quality tracking systems identify potential safety issues before they affect patients. By monitoring supplier quality metrics and product performance data, healthcare organizations can proactively address problems and prevent adverse events.
Real-Time Visibility & Agility
Modern analytics platforms provide dashboard views of key supply chain metrics, updating continuously as conditions change. This visibility enables rapid response to emergencies, market changes, or operational issues.
Mobile access allows key personnel to monitor supply chain performance from anywhere, supporting faster decision-making during critical situations. Real-time alerts ensure that important issues receive immediate attention regardless of staff location.
Better Data-Driven Decision Making
Analytics platforms provide the information foundation for strategic supply chain decisions. Instead of relying on intuition or limited historical data, leaders can evaluate options based on a comprehensive analysis of costs, risks, and performance implications.
Scenario modeling capabilities allow organizations to evaluate potential changes before implementation. This analysis reduces the risk of unintended consequences while identifying opportunities for improvement that might not be obvious otherwise.
How Can Healthcare Organizations Implement Analytics in Supply Chains?
Successful implementation requires a systematic approach that addresses technology, processes, and organizational change management.
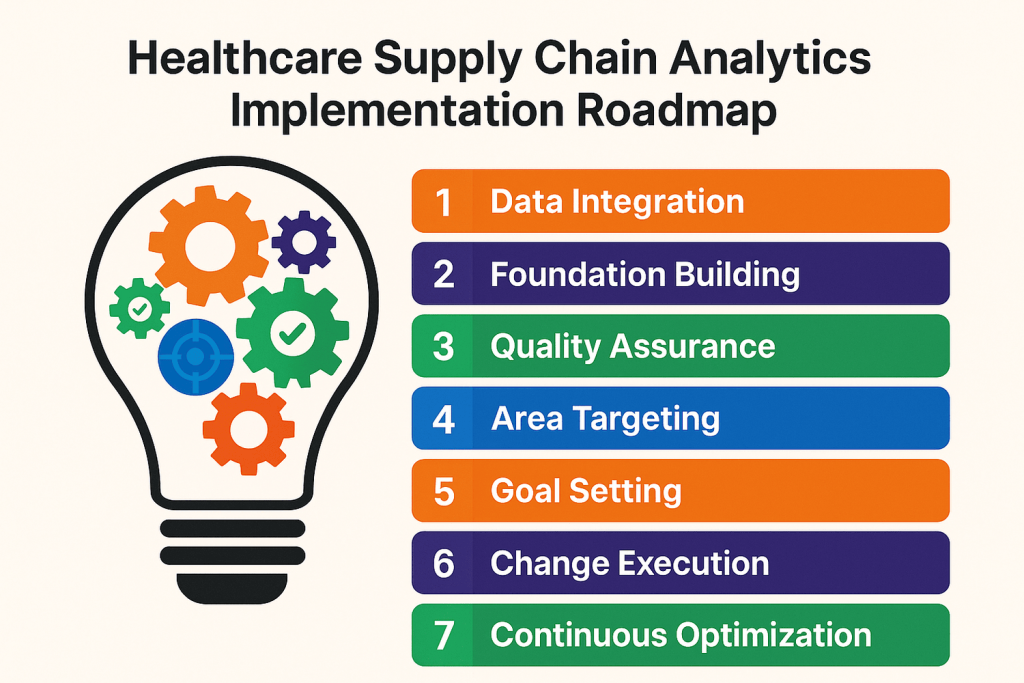
Step 1: Identify & Integrate Data Sources
Most healthcare organizations have supply chain data scattered across multiple systems: ERP platforms, procurement tools, warehouse management systems, and supplier portals. The first step involves cataloging these data sources and understanding what information each system contains.
Effective healthcare data processing ensures that information from diverse sources can be consolidated and analyzed accurately for supply chain optimization.
Integration challenges vary depending on system architecture and data formats. Some organizations choose to implement data warehouses that consolidate information from multiple sources, while others use APIs to connect systems directly. Cloud-based platforms often provide faster implementation timelines and lower upfront costs.
Step 2: Establish a Strong Data Foundation
Data quality determines analytics success more than any other factor. Before implementing analytics tools, organizations must clean existing data, establish data governance processes, and create standards for ongoing data management.
Master data management becomes crucial for maintaining consistent item catalogs, supplier information, and location hierarchies across systems. Without clean master data, analytics results will be unreliable and potentially misleading.
Step 3: Maintain Data Integrity & Quality
Ongoing data quality monitoring prevents analytics degradation over time. Automated validation rules identify data entry errors, missing information, and inconsistencies before they affect analysis results.
Data stewardship roles ensure that someone takes responsibility for maintaining data quality in each functional area. These individuals work with IT teams to resolve data issues and improve processes that create data problems.
Step 4: Target Key Areas for Improvement
Rather than trying to implement analytics across all supply chain functions simultaneously, successful organizations focus on high-impact areas first through strategic data analytics framework approaches. Common starting points include inventory optimization, supplier performance management, and spend analysis.
Quick wins build momentum and demonstrate value to skeptical stakeholders. Many organizations begin with automated reporting and dashboards before moving to predictive analytics and advanced optimization models.
Step 5: Benchmark & Set Measurable Goals
Establishing baseline performance metrics provides a foundation for measuring analytics impact. Key performance indicators include inventory turns, stockout rates, cost per case, supplier performance scores, and forecast accuracy.
Realistic goal-setting prevents disappointment and maintains organizational support for analytics initiatives. Most organizations see meaningful results within 6-12 months, with continued improvement over time as processes mature and data quality improves.
Step 6: Implement Data-Driven Changes
Analytics insights only create value when they drive actual process changes. This step often proves most challenging because it requires changing established workflows and decision-making processes through comprehensive data analytics modernization initiatives.
Change management support helps staff adapt to new processes and tools. Training programs ensure that users understand how to interpret analytics results and incorporate them into daily operations.
Step 7: Monitor & Continuously Optimize
Analytics programs require ongoing attention to maintain effectiveness. Regular reviews of model performance, data quality, and business results identify opportunities for improvement and ensure that analytics capabilities evolve with organizational needs.
Continuous improvement processes incorporate user feedback, changing business requirements, and new data sources into analytics programs. This iterative approach ensures that analytics capabilities remain relevant and valuable over time.
What Real-World Applications Demonstrate Supply Chain Analytics Success?
Healthcare organizations across different segments have implemented analytics programs with measurable results that demonstrate the technology’s practical value.
Hospitals
Cleveland Clinic implemented predictive analytics to forecast patient demand and reduce critical drug shortages. Their system analyzes historical usage patterns, patient census trends, and clinical protocols to predict medication needs up to 30 days in advance. The program reduced stockouts while decreasing inventory carrying costs by $2.3 million annually.
Mayo Clinic uses analytics to optimize OR supply inventory based on surgeon preferences and procedure schedules. By analyzing historical usage patterns for each surgeon and procedure type, they reduced OR supply costs while maintaining availability for critical items.
Pharmaceutical Companies
Johnson & Johnson implemented end-to-end supply chain analytics across their pharmaceutical division to optimize manufacturing and distribution through real-time data integration. Their system uses real-time demand signals from hospital customers to adjust production schedules and inventory allocation, reducing delivery delays by 35% and improving customer satisfaction scores.
Pfizer uses predictive analytics to anticipate demand for seasonal medications like flu vaccines. Their models incorporate CDC surveillance data, weather patterns, and historical usage trends to forecast demand by geographic region, enabling better production planning and distribution strategies.
Medical Device Suppliers
Medtronic implemented IoT-enabled analytics to track equipment usage and lifecycle management at customer sites through real-time data collection. Their connected devices transmit usage data that enables predictive maintenance, optimizes replacement scheduling, and improves customer relationships through proactive service.
Stryker uses analytics to optimize surgical instrument sets based on actual usage patterns at each hospital customer. By analyzing which instruments are used together frequently, they can configure custom sets that reduce costs for hospitals while improving operational efficiency.
Health Systems Leveraging Predictive Models
Kaiser Permanente developed predictive models to plan for emergencies, including pandemic responses. Their analytics platform integrates patient census data, supplier capacity information, and external threat assessments using advanced data integration techniques to maintain strategic stockpiles and ensure continued operations during disruptions.
Intermountain Healthcare uses analytics to predict seasonal demand patterns for respiratory medications and equipment. Their models incorporate local weather data, disease surveillance information, and demographic trends to prepare for conditions like RSV outbreaks or severe flu seasons.
Payers & Insurers Analyzing Supply Chain
UnitedHealthcare analyzes pharmaceutical supply chain data to identify generic substitution opportunities and optimize formulary designs. Their analytics platform evaluates clinical outcomes, cost differentials, and market dynamics to make evidence-based formulary decisions.
What Tools & Technologies Power Healthcare Supply Chain Analytics?
The technology landscape for healthcare supply chain analytics continues to evolve rapidly, with new capabilities emerging regularly.
AI & Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence enables healthcare supply chain analytics to identify complex patterns in large datasets that humans might miss through AI in data engineering. Machine learning algorithms continuously improve their accuracy as they process more data, making predictions more reliable over time.
Natural language processing, combined with an AI data extraction solution, helps extract insights from unstructured data sources like supplier communications, quality reports, and contract documents. This capability expands the information available for analysis beyond traditional transaction data.
Predictive Analytics & Big Data
Big data platforms handle the volume and variety of information generated by modern healthcare supply chains. These systems can process data from internal sources like ERP systems alongside external data feeds, including weather, demographic, and market information.
Healthcare predictive analytics leverages these platforms to forecast future events based on historical patterns and current conditions. Applications include demand forecasting, risk assessment, and performance prediction across suppliers and internal operations.
IoT & RFID Tracking
Internet of Things sensors provide real-time visibility into inventory locations, environmental conditions, and equipment status. RFID tags enable automatic tracking of high-value items and critical supplies throughout healthcare facilities.
Smart shelves and automated inventory systems reduce manual counting while improving accuracy. Some organizations use IoT-enabled cabinets that automatically reorder supplies when stock levels reach predetermined thresholds.
Cloud-Based Supply Chain Platforms
Cloud platforms offer faster implementation timelines and lower upfront costs compared to traditional on-premise solutions. These systems provide scalability to handle growing data volumes and new analytics capabilities without significant infrastructure investments.
Integration capabilities allow cloud platforms to connect with existing healthcare systems through APIs and standard data formats. This cloud data integration enables comprehensive analytics without replacing established operational systems.
Integration with EHR & Procurement Systems
Electronic health record integration provides a clinical context for supply chain decisions. Understanding patient conditions, treatment protocols, and clinical outcomes helps optimize inventory levels and product selections.
Procurement system integration automates many routine analytics processes, from contract compliance monitoring to supplier performance tracking. This automation reduces manual work while improving data accuracy and timeliness.
Future of Healthcare Supply Chain Analytics
Emerging technologies and changing healthcare delivery models will continue to reshape supply chain analytics capabilities and applications.
AI-Driven Forecasting
Artificial intelligence will make demand forecasting significantly more accurate by incorporating broader data sources and identifying subtle patterns that traditional statistical methods miss through AI demand forecasting. Future systems will automatically adjust for external factors like disease outbreaks, weather events, and demographic changes.
Autonomous supply chain systems will make routine decisions without human intervention, freeing staff to focus on strategic activities and exception management. These systems will continuously learn from outcomes and adjust their decision-making processes to improve performance.
Blockchain for Transparency
Blockchain technology promises to create immutable records of supply chain transactions, improving traceability and reducing fraud. This capability becomes particularly valuable for high-value items, controlled substances, and products with complex regulatory requirements.
Smart contracts could automate many routine supply chain processes, from order placement to payment processing, while maintaining detailed audit trails for compliance purposes. This automation reduces administrative costs while improving accuracy and security.
Predictive & Proactive Supply Chains
Future supply chains will anticipate problems before they occur and automatically implement solutions. Predictive maintenance IoT solutions will prevent equipment failures by monitoring the condition of critical devices in real time, while proactive supplier management will identify and resolve performance issues before they affect patient care.
Real-time optimization will continuously adjust inventory levels, supplier selections, and distribution patterns based on changing conditions. These dynamic systems will respond to disruptions faster than human decision-makers while considering complex trade-offs between cost, quality, and service levels.
IoT & Real-Time Tracking
Expanded IoT deployment will provide unprecedented visibility into supply chain operations. Innovative packaging will monitor product conditions during transit, while embedded sensors will track usage patterns and provide automatic reordering signals. When integrated with real-time data warehouses, this continuous data flow ensures analytics and operational dashboards are always up to date.
Digital twins of supply chain networks will enable sophisticated scenario planning and optimization. These virtual models will help organizations evaluate potential changes and disruptions before implementing them in real operations.
FAQs
What is healthcare supply chain analytics?
Healthcare supply chain analytics uses data analysis tools and techniques to improve procurement, inventory management, and distribution processes within medical organizations. It combines statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and real-time monitoring to create more efficient and effective supply networks.
What types of data are used in healthcare supply chain analytics?
Healthcare supply chain analytics incorporates multiple data types: transactional data from procurement systems, inventory levels from warehouse management systems, clinical data from electronic health records, supplier performance metrics, financial information, and external data like weather patterns and disease surveillance reports.
How do hospitals get started with supply chain analytics?
Hospitals should begin by identifying and cataloging existing data sources, establishing data quality standards, and selecting high-impact areas for initial implementation. Most successful programs start with basic reporting and dashboards before advancing to predictive analytics and optimization models.
What are the common challenges in healthcare supply chain management?
Key challenges include inventory shortages affecting patient care, rising costs and waste, supplier disruptions and risks, regulatory compliance requirements, and a lack of real-time visibility into supply chain operations.
What challenges can analytics help solve in healthcare supply chains?
Analytics addresses most major supply chain challenges through data-driven demand forecasting, inventory optimization, supplier performance monitoring, predictive risk management, and automated compliance tracking.
What are the main benefits for healthcare businesses?
Organizations typically see 15-25% cost reductions, improved operational efficiency, enhanced patient care and safety, real-time visibility and agility, and better data-driven decision making.
Which tools are used in supply chain analytics?
Standard tools include AI and machine learning platforms, predictive analytics software, IoT and RFID tracking systems, cloud-based supply chain platforms, and integrated systems that connect with EHR and procurement platforms.
What are some real-world examples of healthcare supply chain analytics?
Examples include Cleveland Clinic’s predictive medication forecasting system, Johnson & Johnson’s end-to-end supply chain optimization, Medtronic’s IoT-enabled equipment tracking, and Kaiser Permanente’s emergency preparedness modeling.
What role does predictive analytics play in healthcare supply chains?
Predictive analytics enables proactive decision-making by forecasting future demand, identifying potential risks, predicting supplier performance issues, and anticipating compliance problems before they affect operations or patient care.
Conclusion
Healthcare supply chain analytics represents more than just a technological upgrade; it’s a fundamental shift toward proactive, data-driven supply chain management that directly impacts patient outcomes. Organizations that use this transformation position themselves to thrive in an increasingly complex healthcare environment.
However, success depends on more than deploying the right tools. Strong data quality, seamless integration, and ongoing improvement are essential to unlocking long-term value.
This is where Folio3 can help. With deep expertise in healthcare data services, advanced analytics solutions, and secure, scalable platforms, Folio3 supports and helps healthcare organizations to build resilient supply chains that cut costs, minimize disruptions, and improve patient care.
Partnering with Folio3 ensures your supply chain analytics initiatives deliver sustainable impact and position your organization for future-ready healthcare.