Healthcare organizations experienced 1,426 data breaches in 2023, exposing more than 133 million patient records, a stark reminder of the growing vulnerabilities in the industry. These breaches underscore the importance of data security in healthcare, where sensitive information like medical histories, insurance details, and personal identifiers remain high-value targets for cybercriminals.
At its core, healthcare data security refers to the strategies, technologies, and governance practices that safeguard patient information throughout its lifecycle from collection and storage to sharing and disposal. Beyond meeting regulatory obligations, adequate data privacy and security in healthcare is essential for maintaining patient trust, ensuring uninterrupted care delivery, and defending against financial and reputational losses.
The digital transformation of healthcare, driven by electronic health records (EHRs), connected medical devices, and cloud adoption, has unlocked new opportunities for improving patient outcomes. However, it has also introduced complex healthcare data security challenges, including ransomware attacks, insider threats, and third-party risks.
With stricter compliance standards like HIPAA and GDPR and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, healthcare data protection is no longer just an IT concern. Still, it is a strategic necessity for the entire organization. So, keep reading this blog to understand the role of data security in healthcare.
What is Healthcare Data Security?
Healthcare data security refers to the comprehensive protection of all patient health information, whether stored electronically, transmitted digitally, or maintained in physical formats. This includes everything from electronic health records (EHRs) and medical imaging to billing information and research data.
The scope extends beyond just technical safeguards. Effective healthcare data protection integrates physical security measures, administrative controls, and technical safeguards to create a multi-layered defense system. This approach recognizes that patient data flows through multiple touchpoints from initial collection during patient visits to storage in cloud systems, sharing with specialists, and eventual archiving or deletion.
Modern healthcare data security also addresses the unique challenges of mobile health applications, Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices, and telemedicine platforms. Each of these technologies introduces new vulnerabilities that traditional security frameworks weren’t designed to handle.
What Are the Critical Threats Facing Healthcare Data Security?
Healthcare organizations face a rapidly evolving landscape of risks that put healthcare data security under constant pressure. From ransomware and phishing to insider misuse and regulatory pitfalls, each of these threats highlights the importance of data security in healthcare for safeguarding patient trust and ensuring compliance.
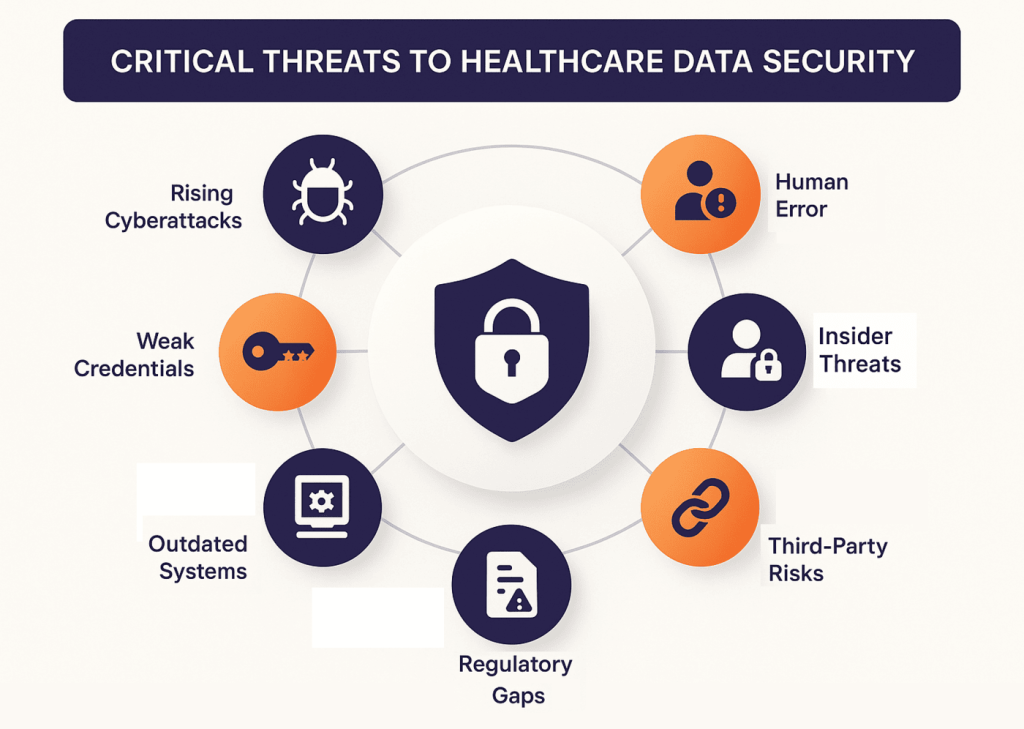
1. Cyberattacks Dominate the Threat Landscape
Ransomware remains one of the most devastating healthcare data security challenges, capable of paralyzing hospitals for weeks by encrypting medical systems. The Universal Health Services ransomware attack (2020) showed how a single incident can disrupt care across hundreds of facilities.
Malware and phishing attacks also threaten medical data security. Malware infiltrates networks through compromised emails or infected websites, silently stealing credentials or patient data. Phishing, often disguised as urgent messages from colleagues or regulators, continues to trick healthcare staff into exposing sensitive information or downloading malicious software.
2. Error as a Hidden Vulnerability
Even with strong controls, data privacy in healthcare often suffers from simple mistakes. Staff may send patient files to the wrong recipient, leave records unsecured, or misconfigure EHR settings. These errors underscore the necessity for healthcare data security solutions, including automated privacy controls, access confirmations, and continuous auditing, to mitigate risks associated with human error.
3. Insider Threats and Misuse of Privileged Access
Not all threats come from outsiders. Employees, contractors, or business associates may misuse legitimate access, intentionally compromising healthcare data privacy for financial gain or personal motives. Detecting insider threats requires advanced behavior monitoring tools that balance data protection in healthcare with employee trust and workplace transparency.
Incorporating strong data integration techniques can also help by unifying logs and security events from multiple systems, making it easier to spot unusual access patterns across disparate data sources.
4. Weak Credentials and Account Mismanagement
Weak or reused passwords continue to undermine data security in healthcare. When stolen credentials provide entry into multiple systems, attackers can escalate privileges and access vast amounts of patient information. Organizations must enforce strong authentication methods, regularly audit user accounts, and revoke access promptly when employees leave.
5. Legacy Systems and Unpatched Vulnerabilities
Many healthcare providers rely on outdated medical devices and software that were never built for modern healthcare data protection. These legacy systems often cannot be patched easily due to cost, integration complexity, or regulatory barriers, leaving organizations exposed to attacks that exploit known vulnerabilities.
6. Third-Party and Vendor Risks
Partnerships with external vendors increase the attack surface. From billing providers to cloud services, every connection introduces potential gaps in data privacy and security in healthcare. While business associate agreements define obligations, organizations often lack visibility into vendors’ actual practices, making vendor risk management critical for safeguarding patient data.
Engaging experts in healthcare data analytics consulting can help assess these third-party relationships more effectively, using detailed analytics to identify weak points and track vendor compliance metrics.
7. Regulatory Non-Compliance Intensifies Risk
Failure to comply with standards like HIPAA, GDPR, or other national frameworks not only creates legal exposure but also reflects weaknesses in core healthcare data security practices. Overlapping regulations can confuse, and gaps in compliance often translate into exploitable vulnerabilities.
How Can Healthcare Organizations Address Their Biggest Data Protection Challenges?
Protecting patient information goes far beyond basic IT measures. Healthcare data security requires balancing clinical workflows, regulatory mandates, and rapidly advancing technology, all while keeping costs under control. These challenges make data protection in healthcare uniquely complex compared to other industries.
Regulatory Complexity Demands Specialized Expertise
Healthcare organizations operate under some of the most stringent rules for data privacy and security in healthcare. HIPAA, GDPR, state-specific privacy laws, and FDA regulations all impose overlapping requirements that often conflict with one another. For organizations operating across multiple regions, this creates significant healthcare data security challenges.
Many providers are adopting modern cloud platforms such as the Snowflake healthcare data cloud to centralize sensitive patient data while meeting strict compliance controls and simplifying cross-border data management.
Without dedicated compliance expertise, interpreting these frameworks can be overwhelming. Regular updates further complicate compliance, requiring organizations to adjust their policies and systems continuously. A proactive regulatory strategy is essential to maintain healthcare data protection while avoiding costly penalties.
Legacy Infrastructure Resists Modern Security Measures
Outdated systems remain one of the biggest risks to medical data security. Many hospitals still rely on older devices and applications that lack modern safeguards like encryption or multi-factor authentication. Because these systems are critical to patient care, replacing them can be costly and disruptive.
When legacy infrastructure connects with newer tools, vulnerabilities multiply. Organizations must adopt creative healthcare data security solutions such as network segmentation, virtual patching, or isolation protocols to protect older systems until long-term upgrades are possible.
Data Volume Growth Strains Security Resources
The explosion of data from electronic health records and imaging files to genomics and IoMT device outputs has transformed data security in healthcare. Traditional methods often fail to secure this volume and variety of information.
While cloud adoption provides scalability, it also raises questions about data privacy in healthcare, sovereignty, and vendor accountability. Security strategies must adapt to handle both structured and unstructured data, ensuring frontline clinicians can access information quickly for patient care.
Budget Constraints Limit Security Investments
Even with the importance of data security in healthcare well established, many organizations face budgetary pressures that limit investments. Security initiatives often compete with immediate patient care priorities, leaving gaps in protection.
Smaller providers, in particular, struggle to afford enterprise-grade defenses or specialized staff. Demonstrating ROI is difficult because successful healthcare data protection often means preventing breaches that never occur. Still, underinvestment can result in severe financial and reputational damage if incidents happen.
Technological Advancement Outpaces Security Adaptation
Healthcare is quick to embrace new innovations like telemedicine, AI-driven diagnostics, and mobile health apps. Yet, security measures often trail behind adoption, creating healthcare data privacy concerns.
Unvetted tools, rushed deployments, and poor integration with legacy systems can open doors to attackers. To mitigate these risks, organizations must integrate data privacy and security into every stage of healthcare technology evaluation and rollout.
Implementing real-time analytics in healthcare systems requires careful security planning to protect patient data while enabling immediate insights. This ensures innovation improves care without compromising healthcare data security.
Folio3 helps healthcare providers forecast threats, prioritize security investments, & implement cost-effective measures to safeguard patients and reputation.
How to Secure Healthcare Data? – 7 Essential Best Practices
Ensuring healthcare data security requires more than just firewalls and passwords, but it demands a proactive, multi-layered approach that addresses both technical vulnerabilities and human factors. Below are the 7 essential best practices healthcare organizations can adopt to strengthen data privacy and security in healthcare while maintaining compliance and operational efficiency.
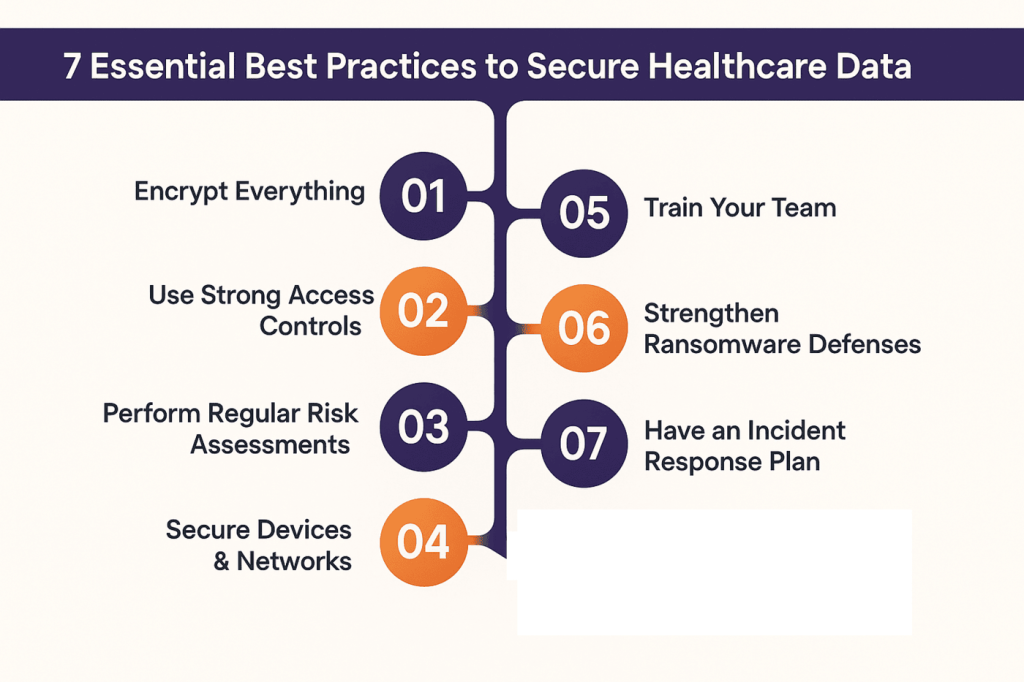
1. Encrypt Data Everywhere
Encryption is the backbone of medical data security, ensuring that sensitive patient records remain protected even if intercepted. Organizations should encrypt data at rest, in transit, and in use:
- At rest: Secure databases, servers, mobile devices, and backups with strong standards like AES-256.
- In transit: Use TLS 1.3 or higher to protect information flowing across internal and external networks.
- In processing: Use advanced encryption that protects data while it’s actively being used, adding another layer of data protection in healthcare.
2. Strengthen Access Controls with MFA
Unauthorized access remains one of the biggest healthcare data security challenges. Role-based access controls (RBAC) should restrict users to the minimum data necessary for their role. Adding multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly reduces risks from stolen or compromised credentials. Privileged access management further safeguards administrators, who represent prime targets for cyberattacks.
3. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Systematic risk assessments are essential for identifying vulnerabilities before they turn into breaches. Healthcare organizations should:
- Perform annual data security assessments in healthcare, as well as additional assessments after system changes.
- Review compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulations.
- Address both digital risks (network gaps, unpatched systems) and physical risks (facility access and device security).
4. Secure Connected Devices and Networks
The rise of IoMT devices has expanded the attack surface, making data privacy in healthcare harder to maintain. To mitigate risks:
- Segment networks to isolate EHR systems and medical devices.
- Apply strict device management protocols for tablets, smartphones, and clinical equipment.
- Implement wireless security and continuous monitoring to detect suspicious activity early.
Strong security at this level is essential for safeguarding healthcare data processing, since these connected devices continuously collect and transmit patient information that must remain accurate and confidential.
5. Educate and Train Staff
Human error remains a leading cause of breaches. Healthcare data protection depends on well-informed staff who can recognize threats. Effective training includes:
- Regular phishing simulations.
- Incident reporting drills.
- Role-specific sessions for clinicians, nurses, and administrators.
6. Build Ransomware Defenses
Ransomware is one of the most pressing healthcare data security challenges. This builds a culture where healthcare data privacy is everyone’s responsibility. Best practices include:
- Maintaining offline and encrypted backups.
- Deploying Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions.
- Using network behavior analytics to detect early attack patterns.
- Preparing detailed incident response playbooks for swift recovery.
7. Develop and Test an Incident Response Plan
Even the best healthcare data security solutions cannot guarantee 100% prevention. A well-defined incident response plan ensures rapid containment, minimal disruption to patient care, and compliance with breach notification requirements.
Regular testing of these plans helps refine processes and strengthen organizational resilience. Healthcare organizations should also implement comprehensive data governance strategy frameworks to ensure consistent security protocols across all departments and systems.
Major Healthcare Data Security Laws and Standards
Healthcare organizations operate under complex regulatory frameworks designed to safeguard patient information, ensure data privacy in healthcare, and enforce accountability. These laws not only define minimum security standards but also impose significant penalties for noncompliance, making healthcare data protection a top priority worldwide.
Many providers now use real time monitoring tools similar to healthcare dashboard examples that visualize compliance metrics to track adherence to these regulations and quickly identify potential gaps.

1. HIPAA & HITECH Drive U.S. Healthcare Privacy
In the United States, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) laid the foundation for medical data security. HIPAA’s Security Rule requires administrative, technical, and physical safeguards such as access controls, audit logging, and transmission security to protect electronic health records (EHRs).
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act expanded HIPAA by increasing penalties for non-compliance and introducing breach notification requirements. It also extended obligations to business associates, recognizing that third-party vendors often handle sensitive patient data.
Effective compliance often depends on a strong data strategy and data governance framework to maintain accurate records, manage access, and monitor how data moves across complex healthcare ecosystems.
Recent enforcement actions highlight the importance of robust healthcare data security solutions, with regulators imposing multimillion-dollar fines on organizations that failed to maintain adequate safeguards.
2. GDPR Sets Global Privacy Standards
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies to any healthcare entity handling personal data of EU residents, regardless of its physical location. For U.S. healthcare providers serving European patients, GDPR creates additional data privacy and security obligations in healthcare.
Organizations building a modern data stack—with cloud-based storage, real-time analytics, and automated compliance tools—can more easily meet these stringent requirements while keeping patient information secure.
Key principles include “privacy by design,” which requires data protection in healthcare systems to be considered from the outset, and the “right to be forgotten,” which challenges organizations to balance patient rights with record retention and public health needs.
3. PIPEDA Governs Canadian Healthcare Privacy
Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) governs how healthcare organizations collect, use, and share patient information across provincial and national boundaries.
PIPEDA emphasizes meaningful patient consent, which can complicate data sharing for treatment or operational purposes. It also mandates strict breach notification requirements, compelling organizations to report incidents to regulators and affected individuals when risks of significant harm are present.
4. Toolkit Standardizes U.K. Healthcare Security
In the United Kingdom, the NHS Data Security and Protection Toolkit provides a standardized framework for ensuring data protection in healthcare organizations. The toolkit outlines mandatory requirements for security training, network management, and incident response.
Healthcare providers must complete annual assessments and supply evidence of compliance. Non-compliance may result in contract penalties and restricted access to national healthcare networks, underscoring the importance of data security in healthcare operations.
The Impact of Emerging Tech on Healthcare Data Protection
As healthcare systems evolve, new technologies are reshaping the landscape of healthcare data security. While these innovations bring advanced defenses against cyber threats, they also introduce new healthcare data security challenges that organizations must address to safeguard patient trust and comply with strict regulatory standards.
Partnering with a data analytics services company can help healthcare providers monitor compliance more effectively, using advanced analytics to track security metrics, detect anomalies, and maintain adherence to frameworks like HIPAA and GDPR.
AI and Machine Learning Strengthen Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming healthcare data protection by enabling real-time analysis of vast datasets. These technologies can detect anomalies, suspicious login patterns, or subtle indicators of compromise that traditional systems often overlook.
Advanced techniques such as AI data extraction help security teams pull critical details from unstructured logs and patient records, making it easier to identify threats hidden in complex data sources. Their adaptive nature allows ML models to evolve with emerging attack vectors, making them invaluable in managing data privacy and security in healthcare.
Healthcare organizations are increasingly adopting AI in data engineering approaches to automate threat detection and response. However, AI also poses risks such as data poisoning or biased algorithms that attackers may exploit.
To mitigate these risks, organizations must validate AI models regularly and maintain human oversight over automated decisions.
Blockchain Ensures Data Integrity and Transparency
Blockchain technology offers powerful solutions for medical data security by creating tamper-proof, immutable records of all data access and modifications. This ensures transparency and strengthens healthcare data privacy by making unauthorized changes easily detectable.
Additionally, blockchain’s distributed ledger can enable secure data sharing between healthcare providers without centralized control, enhancing collaboration while maintaining data protection in healthcare. Still, challenges like scalability, energy consumption, and integration with legacy healthcare systems can slow adoption. Organizations must carefully weigh benefits against implementation costs.
Zero-Trust Architecture Redefines Security Boundaries
Traditional perimeter-based security is no longer sufficient in modern healthcare environments. A zero-trust architecture assumes no inherent trust, requiring verification for every access request, whether internal or external.
By combining identity verification, multi-factor authentication, and micro-segmentation, zero-trust models prevent attackers from moving laterally across systems. This proactive approach strengthens healthcare data security solutions, helping organizations reduce risks tied to insider threats and credential theft.
Partnering with data integration consulting experts can further ensure that identity systems, access logs, and monitoring tools work seamlessly together, creating a unified framework that supports zero-trust principles.
Cloud Solutions Deliver Scalable Healthcare Data Security
Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern healthcare data privacy and security strategies. Leading providers offer enterprise-grade healthcare data security solutions, including encryption, continuous monitoring, and automated compliance frameworks that many organizations struggle to replicate in-house.
However, healthcare organizations must understand shared responsibility models. While cloud vendors secure infrastructure, it remains the healthcare provider’s responsibility to configure, monitor, and manage data correctly. Misconfigurations are among the most common healthcare data security challenges, making proper governance and cloud expertise essential.
Multi-cloud and hybrid strategies further enhance resilience but demand robust management tools to ensure consistent data protection in healthcare environments.
Real-World Healthcare Data Breaches & Lessons Learned
High-profile breaches highlight both the importance of data security in healthcare and the costly consequences of weak defenses. These cases illustrate how healthcare data security challenges demand proactive monitoring, stronger authentication, and comprehensive healthcare data protection strategies:
- Anthem Inc. (2015): Nearly 80 million records were compromised after attackers stole employee credentials through spear-phishing. The absence of multi-factor authentication and insufficient monitoring allowed undetected access for months. This breach demonstrated how lapses in medical data security can result in over $115 million in costs and stricter regulations.
- Universal Health Services (2020): A ransomware attack forced more than 400 facilities offline, disrupting patient care for weeks. The attack revealed how interconnected systems amplify risk and highlighted the value of segmentation, reliable backups, and incident response planning. It remains a cautionary tale of ransomware’s impact on data protection in healthcare.
- SingHealth (2018): Hackers accessed data from 1.5 million patients, including sensitive prescription details. Weak monitoring and compromised credentials enabled long-term unauthorized access. The breach spurred regulatory reforms, showing how data privacy and security in healthcare require continuous assessments and rapid patching.
Partner with Folio3 to implement multi-factor authentication, monitoring, and incident response plans that safeguard patient data.
FAQs
How Can Healthcare Organizations Prevent Data Breaches?
Healthcare organizations can prevent data breaches by encrypting patient data, enforcing multi-factor authentication, and training staff to spot threats. Strong healthcare data security solutions, like regular risk assessments and vendor vetting, reduce vulnerabilities.
What Are the Most Common Cybersecurity Threats in Healthcare?
Ransomware, phishing, insider threats, and unpatched systems are the most common healthcare data security challenges. Legacy devices and third-party vendors further expand risks to medical data security.
How Does HIPAA Compliance Improve Data Protection?
HIPAA enforces data privacy and security in healthcare through safeguards like encryption, audit logs, and breach notifications. These requirements strengthen healthcare data protection and help organizations meet compliance.
What Role Do Emerging Technologies Play in Healthcare Data Security?
AI, blockchain, and zero-trust models enhance data security in healthcare by improving threat detection and ensuring data integrity. Cloud platforms also provide scalable healthcare data security solutions.
What Is the Difference Between Data Privacy and Data Security in Healthcare?
Data privacy in healthcare ensures patients control how their information is used, while data security in healthcare protects it from breaches. Both are critical for patient trust and compliance.
How Often Should Healthcare Facilities Conduct Security Risk Assessments?
Healthcare organizations should conduct annual risk assessments, with more frequent checks for critical systems or after incidents. This proactive approach addresses ongoing healthcare data security challenges.
What Steps Should Be in a Healthcare Incident Response Plan?
An incident response plan should define detection, containment, investigation, and recovery procedures. Clear communication ensures healthcare data privacy and compliance with regulatory reporting.
What is Zero-Trust Security and How Does It Benefit Healthcare IT?
Zero-trust requires verifying every access request, strengthening healthcare data security against insider threats and compromised credentials. It minimizes risks that traditional perimeter defenses often miss.
How Do Regular Backups Help with Ransomware Protection?
Regular, tested backups protect healthcare data security by enabling recovery without paying ransom. Offline backups ensure reliable data protection in healthcare against modern ransomware.
Conclusion
Healthcare data security is a strategic necessity for protecting patient trust, ensuring compliance, and enabling digital transformation. With rising threats and complex regulations, organizations need proactive, multi-layered defenses that balance innovation with protection.
Partnering with experts like Folio3 Data Services ensures access to customised healthcare data security solutions, regulatory expertise, and advanced technologies that help healthcare providers safeguard sensitive data while driving operational excellence and improved patient outcomes.