Data engineering has evolved from a specialized technical role into the foundational infrastructure powering modern enterprises in 2026. As organizations navigate the complexities of artificial intelligence, real-time analytics, and cloud transformation, data engineering has become indispensable for turning raw data into actionable intelligence. Every AI model, business dashboard, and predictive system depends on robust data pipelines designed and maintained by data engineers.
The numbers tell a compelling story of explosive growth and increasing strategic importance. The global data engineering market is projected to reach USD 105.40 billion, driven by cloud adoption, AI workloads, and the shift toward real-time data processing. Organizations allocate 60 to 70 percent of their total data budgets to data engineering activities, reflecting the critical nature of reliable data infrastructure. With 90 percent of AI and machine learning projects depending directly on data engineering pipelines, the profession has moved from operational support to strategic enablement.
This comprehensive report examines the latest data engineering statistics across market trends, technology adoption, salary benchmarks, cloud migration patterns, performance metrics, and emerging challenges. Whether you are planning organizational data strategy, evaluating career opportunities, or assessing technology investments, these insights provide the foundation for informed decision-making in 2026 and beyond.
Key Data Engineering Statistics (Editor’s Pick)
- The global data engineering market is projected to reach USD 105.40 billion in 2026.
- 90% of AI and machine learning projects depend directly on data engineering pipelines.
- Big data and data engineering services market reached USD 91.54 billion in 2025, projected to reach USD 187.19 billion by 2030 (15.38% CAGR).
- About 82% of organizations use real‑time streaming in their pipeline architectures.
- 30–40% of data pipelines experience failures every week.
- Average data engineer salary in the United States is USD 131,000 per year, with senior positions exceeding USD 170,000.
- 94%+ of enterprises use cloud services, with 92% adopting multi-cloud strategies.
- Data quality issues affect nearly one-third (over 30%) of organizational revenue.
- Organizations experience 67 monthly data incidents requiring an average 15-hour resolution time.
Data Engineering Market Insights and Industry Stats
The data engineering market represents one of the fastest-growing technology sectors globally, fueled by digital transformation initiatives, cloud migration, and the exponential growth of data-driven applications. Market projections consistently indicate sustained expansion through 2030, with multiple research firms documenting unprecedented investment levels.
Global Market Growth and Projections
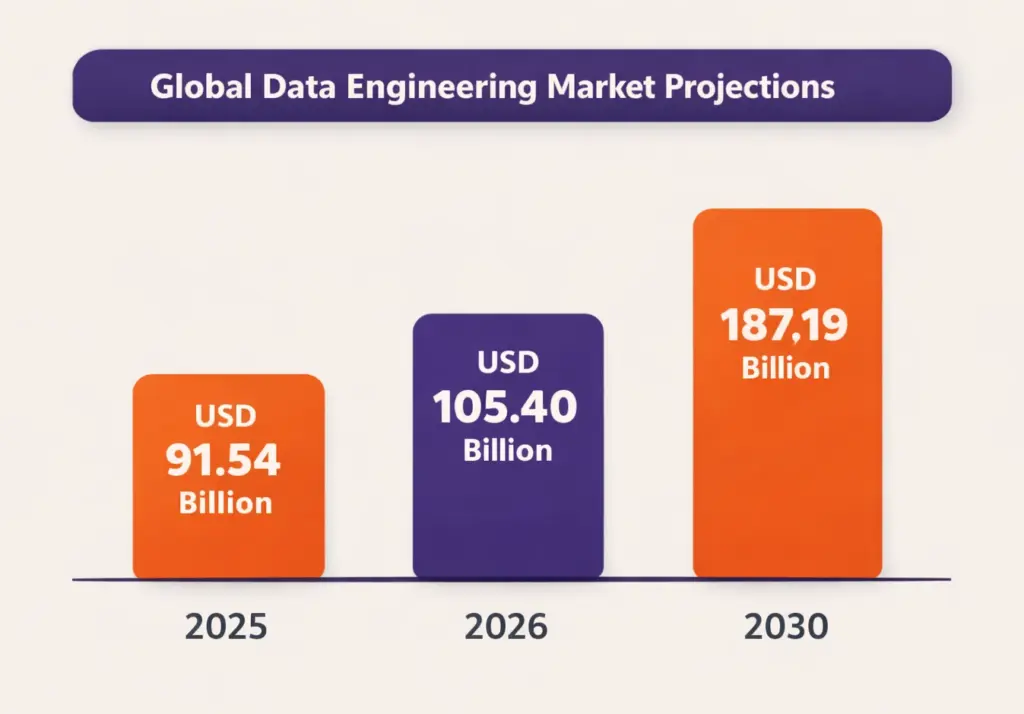
The global data engineering market is projected to reach USD 105.40 billion in 2026, driven by cloud adoption, AI-powered workloads, real-time data processing, and enterprise modernization initiatives. Organizations typically allocate 60–70% of their total data budgets to data engineering activities, including data ingestion, transformation, orchestration, pipeline reliability, and underlying infrastructure costs.
The big data and data engineering services market reached USD 91.54 billion in 2025 and, with a 15.38% CAGR, is forecast to attain USD 187.19 billion by 2030. This growth is propelled by continued adoption of AI-driven decision making, expansion of IoT endpoints, and the necessity to convert raw, unstructured information into reliable intelligence. Enterprises migrate workloads to elastic platforms that slash processing latency, while outcome-based service contracts accelerate time-to-value.
Alternative market projections show the global big data and data engineering services market was worth USD 75.55 billion in 2024, with projections reaching USD 325.01 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 17.6% during the forecast period. The variance in market size estimates reflects different methodological approaches and segment definitions, but all indicators point to sustained double-digit growth rates.
| Market Segment | 2026 Value | 2030 Projection |
| Overall Data Engineering Market | $105B+ | $187-325B |
| Big Data Services | $88-91B | $187B (15.4% CAGR) |
| Cloud Computing Market | $943B | $1T+ by early 2026 |
Regional Market Distribution
1. North America
North America continues to dominate the global data engineering and related services market, accounting for approximately 39.1 % of the worldwide market share in 2024, driven by early technology adoption, strong enterprise demand for advanced analytics, and substantial venture capital investment in data infrastructure and digital transformation initiatives.
Key Stats:
- North America holds the largest regional share in the big data and data engineering services market, with technology innovation hubs and major cloud/data platform vendors concentrated in the U.S. and Canada.
- Over 71 % of enterprises in the North American region use AI-driven analytics platforms, highlighting adoption of data engineering services for advanced insights and automation.
- In autonomous and AI-augmented data engineering market segments, North America accounts for roughly 40–41 % of global market share, supported by strong venture capital flows and rapid enterprise digital adoption.
2. Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing regional market, with projections showing a CAGR of approximately 15.99% through 2030. Factors driving this exceptional growth include digital infrastructure expansion, smart city programs, rapid cloud adoption in countries like China, India, Japan, and Singapore, and aggressive AI investment by governments and enterprises. The region’s growing technology workforce and expanding middle class create substantial demand for data-driven services.
3. European markets

European markets demonstrate steady growth with adoption driven primarily by compliance requirements including GDPR and sector-specific regulations. European organizations invest heavily in data governance frameworks, privacy-preserving analytics technologies, and sovereign cloud infrastructure. The focus on data sovereignty has accelerated adoption of European cloud providers alongside global hyperscalers.
Key Stats:
- Europe holds 28% of the global data governance market (2024), with GDPR as a primary adoption driver.
- 69% of European enterprises have implemented data governance frameworks to meet GDPR requirements.
- Europe leads the sovereign cloud market with 42% global market share, driven by data residency and sovereignty mandates.
Industry-Specific Adoption Patterns
1. Financial
Financial services organizations lead data engineering adoption, driven by regulatory requirements, real-time fraud detection needs, and algorithmic trading systems. These institutions operate some of the most sophisticated data infrastructures globally, processing millions of transactions daily while maintaining strict compliance and audit trails.
2. Healthcare
Healthcare providers rapidly expand their data engineering footprint, accelerated by telemedicine requirements, electronic health records systems, and genomics research.
The sector faces unique challenges balancing HIPAA compliance with the need for data accessibility. Healthcare experienced 725 major data breaches affecting 275 million patient records in 2026, highlighting critical security imperatives.
3. Retail and e-Commerce
Retail and e-commerce companies invest heavily in data engineering in retail, building real-time data pipelines to support personalization engines, inventory optimization, and supply chain visibility. Manufacturing organizations adopt Industry 4.0 initiatives requiring sophisticated data engineering for IoT sensor integration, predictive maintenance, and quality control systems. The manufacturing data pipeline tools market was valued at USD 3.23 billion in 2026, projected to reach USD 21.38 billion by 2032 at a 23.2% CAGR.
4. Tech
Technology companies pioneered cloud-native data architectures and continue driving innovation in data engineering practices. These organizations often develop proprietary data engineering tools and contribute significantly to open-source data infrastructure projects.
Data Engineering Tool & Technology Statistics
The modern data engineering technology landscape has consolidated around a core set of proven platforms while simultaneously diversifying to address specialized use cases. Cloud-native managed services increasingly replace on-premises infrastructure, and organizations balance between proprietary platforms and open-source frameworks based on specific requirements.
1. Cloud Data Warehouse and Lakehouse Adoption

Over 90 percent of mid-to-large organizations use a cloud data warehouse in 2026, marking near-universal adoption. The three dominant platforms are Snowflake, Databricks, and Google BigQuery, collectively capturing the majority of enterprise data warehouse workloads. Snowflake’s market capitalization hovers around USD 50 billion as of June 2026, reflecting continued growth in cloud data warehousing market share despite increasing competition.
Lakehouse architectures combining data warehouse performance with data lake flexibility see rapid adoption, with over 50 percent of data teams implementing lakehouse patterns. Databricks, founded in 2013 by the creators of Apache Spark, pioneered the lakehouse concept with Delta Lake technology. The platform reported USD 4.8 billion in revenue with 55% growth, though market observers note potential deceleration as the company approaches larger scale.
Many enterprises operate multiple storage layers for different workloads rather than standardizing on a single platform. This multi-platform approach balances performance optimization, cost management, and specialized capability requirements. Organizations increasingly combine Snowflake for business intelligence and reporting with Databricks for machine learning and data science workloads.
2. ETL, Orchestration, and Transformation Tools
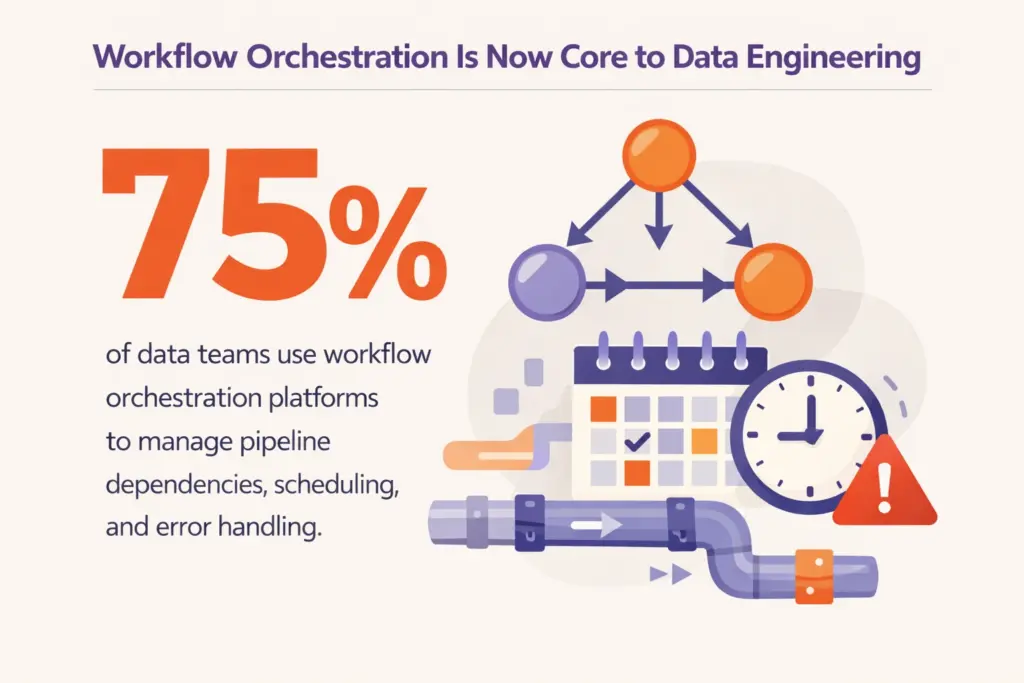
Approximately 75 percent of data teams use workflow orchestration platforms to manage pipeline dependencies, scheduling, and error handling. Apache Airflow remains the most widely adopted open-source orchestration framework, though managed alternatives including Databricks Workflows, AWS Step Functions, and Google Cloud Composer gain traction for organizations prioritizing reduced operational overhead.
Transformation frameworks show strong adoption with over 70 percent of data engineers relying on dedicated tools. dbt (data build tool) has become the de facto standard for SQL-based transformation logic, with widespread adoption across cloud data warehouses. The tool’s focus on version control, testing, and documentation aligns with data engineering and data analytics best practices increasingly applied to modern pipelines.
Managed ETL services gain market share as organizations seek to reduce engineering overhead. Fivetran, Matillion, AWS Glue, Azure Data Factory, and similar managed services attract teams prioritizing time-to-value over customization. The shift toward managed services reflects broader industry maturation and recognition that commodity integration tasks offer limited competitive differentiation.
3. Open-Source vs. Managed Services
Organizations typically adopt hybrid approaches combining open-source tools with managed services rather than exclusively choosing one model. Open-source frameworks including Apache Spark, Apache Kafka, and Apache Flink remain foundational for data-intensive workloads requiring customization and fine-grained control. However, managed variants including Databricks, Confluent Cloud, and Amazon Kinesis reduce operational burden.
Cloud-managed data engineering tools are used by over 80 percent of startups, reflecting preferences for rapid deployment and predictable costs over infrastructure management. Larger enterprises balance between managed services for standardized workloads and self-managed infrastructure for specialized or cost-sensitive applications.
4. Emerging Technology Adoption
Apache Iceberg adoption accelerates as the open table format standard enabling multi-engine data access. The format allows different compute engines to work on the same data without duplication or transformation, addressing a decade of interoperability challenges in the data ecosystem. Major cloud providers and data platforms increasingly standardize on Iceberg for lakehouse implementations.
Vector databases transition from specialized machine learning tools to core data infrastructure components. In 2026, understanding how to design, optimize, and operate vector storage becomes as fundamental as relational database management. This shift reflects the proliferation of AI applications requiring similarity search and semantic retrieval capabilities.
Real-time streaming infrastructure becomes baseline capability rather than specialized tooling. Approximately 60 percent of new data pipelines incorporate real-time or near-real-time requirements, with streaming workloads representing over 45 percent of total data engineering activity. Organizations implement change data capture, event streaming, and real-time aggregation to support operational analytics and AI-driven applications.
Data Engineering Salary & Workforce Stats
Data engineering compensation reflects exceptional demand for specialized skills combined with persistent talent shortages. Salary levels vary significantly based on experience, geographic location, industry sector, and specific technical capabilities, but consistently rank among the highest-paid technology roles.
1. United States Salary Benchmarks

The average salary for a data engineer in the United States reaches USD 131,000 per year in 2026, including base salary and additional compensation such as bonuses and profit sharing. Entry-level data engineers with less than one year of experience earn average total compensation of USD 80,000 to USD 90,000. Early career professionals with one to four years of experience command USD 93,000 to USD 110,000.
Mid-career data engineers with five to nine years of experience see average compensation ranging from USD 118,000 to USD 149,000 nationally, with substantial geographic variation. In major technology hubs, salaries significantly exceed national averages. San Francisco data engineers earn USD 148,000 to USD 186,000, New York professionals command USD 130,000 to USD 170,000, and Seattle ranges from USD 135,000 to USD 165,000.
Senior data engineers with over ten years of experience and demonstrated expertise in distributed systems, cloud architecture, and machine learning infrastructure earn USD 170,000 to USD 220,000 or more. Top-tier technology companies including Airbnb, Meta, Google, and Amazon offer compensation packages exceeding USD 200,000 for principal-level data engineering positions.
Cloud data engineers specializing in AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform command premium compensation due to high demand and specialized certification requirements. These professionals focus on cloud-native architectures, infrastructure as code, and cost optimization strategies.
| Experience Level | Average Salary (US) | Top Markets Range |
| Entry-Level (<1 year) | $80,000-$90,000 | $90,000-$110,000 |
| Early Career (1-4 years) | $93,000-$110,000 | $110,000-$140,000 |
| Mid-Career (5-9 years) | $118,000-$149,000 | $148,000-$186,000 |
| Senior (10+ years) | $170,000-$220,000 | $200,000-$280,000+ |
2. Global Salary Comparisons
Data engineering compensation varies significantly across global markets, shaped by local economic conditions, industry maturity, talent supply, and cost of living. While the United States, Switzerland, and Singapore lead in absolute salary figures, tax-free markets like the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia offer compelling net compensation packages.
In Singapore, data engineers typically earn between SGD 95,000 for entry-level positions and SGD 160,000 for senior professionals in finance and technology sectors. The nation’s position as a regional digital hub, hosting global headquarters for major financial institutions and technology companies, drives sustained demand. Bonuses average 15 to 30 percent, with multinational employers offering housing and relocation benefits.
The United Arab Emirates, particularly Dubai and Abu Dhabi, offers competitive compensation augmented by zero income tax. Entry-level salaries start at AED 250,000, while senior professionals exceed AED 420,000, especially within sovereign wealth entities and multinational corporations. Housing, education, and relocation allowances are common perks for expatriate talent.
European markets show substantial variation. United Kingdom data engineers earn between GBP 48,000 and GBP 65,000 depending on location and experience, with London commanding premium salaries. German data engineers typically earn EUR 55,000 to EUR 85,000, while Netherlands professionals command EUR 60,000 to EUR 90,000. Scandinavian markets including Sweden offer EUR 50,000 to EUR 75,000, often supplemented by strong benefits packages and work-life balance.
3. Workforce Demand and Job Market Trends
Data engineers rank among the most sought-after technology professionals in 2026. The data engineering sector employs over 150,000 professionals globally, adding more than 20,000 new jobs in the past year with continued growth projected. Organizations are closely tracking data engineering trends, as demand significantly outpaces supply and nearly every industry requires pipeline expertise to support digital operations.
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 36 percent growth in data-related positions between 2023 and 2033, far exceeding average occupation growth rates. This translates to approximately 20,800 job openings annually during that timeframe. However, these projections may understate actual demand given the accelerating adoption of AI and machine learning applications.
Talent shortages remain acute, particularly for professionals combining deep technical skills with business acumen. The UK Government Data Skills Report identifies severe shortages across data engineering positions, driving salary inflation and retention challenges. Organizations increasingly invest in training programs to develop internal talent pipelines rather than relying exclusively on external hiring.
4. In-Demand Skills and Certifications
SQL remains the most universally required skill, appearing in virtually all data engineering job postings. Proficiency in Python follows closely, valued for data processing, automation, and integration with machine learning frameworks. Java and Scala maintain relevance for big data processing with Apache Spark, though Python increasingly dominates new development.
Cloud platform expertise commands premium compensation, with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud certifications validating specialized knowledge. Multi-cloud experience grows increasingly valuable as organizations adopt distributed cloud strategies. Understanding of infrastructure as code using Terraform or similar tools becomes standard expectation rather than differentiator.
Experience with modern data stack components including dbt, Airflow, Kafka, and Spark appears frequently in job requirements. Knowledge of data warehousing concepts, dimensional modeling, and ETL design patterns remains foundational. Emerging skills in vector databases, real-time streaming, and DataOps practices increasingly appear in senior-level positions.
Soft skills including communication, collaboration, and business context understanding differentiate high-performing data engineers. The ability to translate technical concepts for non-technical stakeholders and understand business requirements becomes increasingly important as data engineering teams assume more strategic roles.
Data Engineering Performance & Pipeline Statistics
Data pipeline reliability and performance directly impact business operations, with downtime and quality issues translating immediately to revenue loss and compliance risk. Organizations increasingly treat data infrastructure with the same rigor as production application systems, implementing comprehensive monitoring, testing, and incident response protocols.
1. Pipeline Reliability and Failure Rates
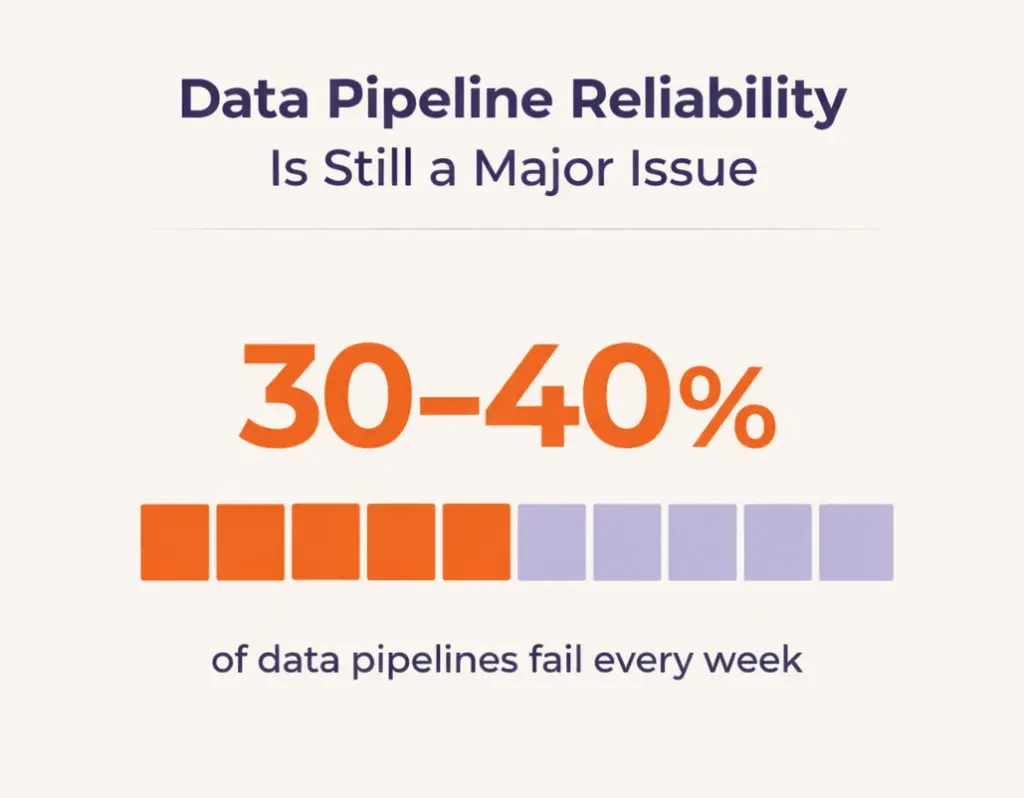
30 to 40 percent of data pipelines experience failures every week, representing a persistent operational challenge across organizations. Organizations experience an average of 67 monthly data incidents requiring approximately 15-hour resolution time. This represents a 166 percent increase in resolution time compared to 2020’s average of 5.5 hours, reflecting growing pipeline complexity and inadequate monitoring infrastructure.
Detection lag remains critical, with 68 percent of organizations requiring four or more hours to identify data quality problems. Over two-thirds of companies cannot identify issues within acceptable timeframes, allowing corrupted or incomplete data to propagate downstream to analytics, dashboards, and machine learning models.
Data downtime costs large organizations millions of dollars annually through lost productivity, incorrect decisions, compliance failures, and customer impact. Undetected data issues persist for days or weeks without proper observability tooling. Most enterprises experience multiple significant data incidents per quarter, with 80 percent struggling with inconsistent or incomplete data.
Orchestration failures constitute a common cause of data downtime, highlighting the importance of robust workflow management. Teams prioritize tools with retry logic, dependency management, and comprehensive observability. Manual scheduling becomes increasingly rare in mature data environments as automation reduces human error.
2. Real-Time and Batch Processing Patterns
Real-time data processing transitions from specialized capability to baseline expectation. Over 60 percent of new data pipelines incorporate real-time or near-real-time requirements to support operational analytics, personalization systems, fraud detection, and AI-driven applications. Streaming workloads now represent over 45 percent of total data engineering activity.
Ultra-low latency use cases target sub-10 millisecond response times for applications including financial trading, fraud prevention, and real-time bidding systems. These demanding requirements drive adoption of specialized streaming infrastructure and edge computing architectures.
Batch processing remains essential for historical analysis, complex transformations, and cost-sensitive workloads where immediate results are unnecessary. Organizations increasingly implement hybrid architectures combining batch and streaming patterns, selecting appropriate processing models based on specific use case requirements rather than standardizing on single approaches.
3. Data Quality and Testing Practices
Poor data quality affects nearly one-third of organizational revenue through incorrect decisions, compliance failures, and operational inefficiencies. Organizations lose an average of USD 9.7 to 15 million yearly from quality issues, while 77 percent rate their data quality as average or worse. Implementing data engineering best strategies, such as automated monitoring, schema validation, and clear ownership assignments, helps prevent downstream errors, improves AI model effectiveness, and reduces project failure rates.
Data contracts emerge as a key practice for preventing quality issues, defining schema expectations, freshness guarantees, and semantic meaning. Producers validate data against contracts before delivery, with violations failing immediately rather than propagating downstream. Schema checks, freshness guarantees, and distribution constraints integrate into continuous integration pipelines.
Automated data quality monitoring gains widespread adoption, with platforms providing continuous validation, anomaly detection, and lineage tracking. These systems identify issues proactively rather than waiting for downstream consumers to report problems. However, monitoring alone proves insufficient without clear ownership and escalation processes.
4. AI and Machine Learning Pipeline Integration
About 90 percent of AI and machine learning projects depend directly on data engineering pipelines for training data delivery, feature engineering, and real-time inference. Data engineers play central roles in feature versioning, reuse, and governance, with automated feature pipelines reducing model deployment time significantly.
Fifty-five percent of AI-powered applications require near-real-time data ingestion, with streaming data critical for personalization engines, fraud detection systems, and recommendation platforms. Pipeline latency directly impacts user experience quality in AI-driven applications, making performance optimization essential.
Machine learning operations (MLOps) practices increasingly integrate with data engineering workflows. Data version control, experiment tracking, and model registry capabilities become standard components of production data platforms. The convergence of DataOps and MLOps reflects recognition that AI success depends fundamentally on data infrastructure quality.
Data Engineering Cloud vs On-Premise Stats
Cloud adoption for data engineering workloads reached near-universal levels in 2026, with hybrid and multi-cloud architectures becoming standard patterns. Organizations balance between cloud agility and on-premises control based on regulatory requirements, cost considerations, and specific workload characteristics.
1. Cloud Adoption Rates
Over 94 percent of enterprises use cloud services in some capacity, with cloud computing adoption nearly universal across organizations of all sizes. Among large enterprises with over 1,000 employees, more than 94 percent have significant portions of their workloads in cloud environments. Only approximately three percent of enterprises report no plans to migrate any workloads to cloud infrastructure.
Companies currently run about 50 percent of their workloads in public clouds, representing steady growth from 39 percent in 2022. Small and medium businesses host roughly 63 percent of workloads and 62 percent of data in cloud environments. Fewer than five percent of organizations plan to migrate workloads back to on-premises infrastructure, indicating sustained cloud commitment.
By deployment mode, cloud captured 65.61% of big data engineering services market share in 2024, with hybrid deployment projected to expand at 16.36% CAGR through 2030. This growth reflects organizations balancing cloud benefits with data sovereignty, regulatory compliance, and performance requirements driving hybrid architecture adoption.
2. Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Strategies
Ninety-two percent of organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies, combining different public and private cloud service providers. Over 78 percent utilize two or more cloud providers simultaneously, reflecting desires to avoid vendor lock-in while leveraging best-of-breed services from multiple platforms.
Hybrid cloud models, combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, represent preferred approaches for many enterprises. Gartner predicts 90 percent of organizations will adopt hybrid cloud approaches through 2027, driven by needs to balance scalability, security, and regulatory compliance requirements.
Amazon Web Services maintains market leadership with approximately 30 percent global market share, followed by Microsoft Azure at 20 percent and Google Cloud at 13 percent. Despite AWS’s dominant position, Azure and Google Cloud post higher quarterly growth rates, driven by AI service integration and enterprise hybrid cloud adoption.
Regional cloud providers gain traction, particularly in markets with data sovereignty requirements. European providers including OVHcloud, Scaleway, and Hetzner see increased adoption driven by GDPR compliance and trade considerations. OVHcloud surpassed EUR 1 billion in annual revenue in fiscal year 2025, representing a significant milestone for European cloud infrastructure.
3. Cost Management and Optimization

Cloud cost management emerges as the primary challenge, with 82 percent of decision-makers citing managing cloud spend as their top concern. Companies waste as much as 32 percent of their cloud spending on unused or over-provisioned resources, highlighting critical need for improved financial governance and resource optimization strategies.
Cost visibility remains the fundamental obstacle to effective cloud financial management. Organizations struggle to monitor shared and untagged cloud costs, with 30 percent reporting this as a significant challenge. Companies waste over USD 135,000 on average due to unused SaaS software licenses, indicating broader issues with resource tracking and accountability.
FinOps practices gain widespread adoption as organizations implement dedicated cloud financial operations teams and tools. These initiatives focus on cost attribution, budget forecasting, resource right-sizing, and eliminating waste. Cloud cost optimization tools enable real-time visibility into spending patterns and automated recommendations for efficiency improvements.
Data engineering workloads represent some of the most expensive cloud consumption patterns, particularly for compute-intensive processing and high-volume storage. Engineers increasingly receive visibility into cost impacts of architectural decisions, changing behavior patterns. Storage tiering, query optimization, and compute scheduling become standard practices for cost-conscious teams.
4. Security and Compliance Considerations
Ninety-four percent of businesses report improved security posture after migrating to cloud environments, benefiting from hyperscaler investments in security infrastructure and expertise. However, 98 percent of organizations experienced at least one cloud security breach in the past two years, with misconfiguration representing the top threat at 68 percent, followed by unauthorized access at 58 percent.
Data breach costs continue escalating, reaching an average of USD 4.88 million in 2024. Healthcare sector breaches significantly exceed this average at USD 10.9 million per incident, reflecting sensitive nature of patient data and stringent regulatory requirements. These financial impacts drive continued investment in cloud security and compliance tools.
Regulatory compliance adds complexity to cloud data engineering, particularly for organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions. GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and industry-specific regulations require sophisticated data governance capabilities. Organizations with mature governance programs demonstrate 40 percent higher analytics ROI through improved data quality and stakeholder trust.
Data Engineering Challenges & Pain Points Statistics
Despite widespread adoption and substantial investment, organizations continue facing significant challenges in maximizing data engineering effectiveness. These obstacles range from technical complexity to organizational dynamics, with many transcending individual companies to represent industry-wide patterns.
1. Talent Shortage and Skills Gaps
Talent acquisition and retention constitute the most frequently cited challenge across organizations. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics notes a 40 percent shortage of qualified data engineers in 2024, limiting rapid deployment of data solutions. This supply-demand imbalance drives salary inflation and forces organizations to compete aggressively for experienced professionals.
Sixty-five percent of data teams identify data engineering as their biggest scalability bottleneck, not analytics or data science capabilities. This reflects the specialized nature of data engineering skills and the time required to develop expertise across cloud platforms, distributed systems, and modern data stack components.
Organizations increasingly invest in upskilling existing technical staff rather than relying exclusively on external hiring. Training programs focus on cloud certifications, modern data tools, and DataOps practices. However, developing proficiency requires substantial time investment, creating interim capacity constraints.
2. Data Governance and Quality Management

Sixty-four percent of organizations cite poor data quality as their top data integrity challenge. Poor quality data undermines AI initiatives, analytics accuracy, and operational efficiency across all business functions. Organizations lose an average of 25 percent of revenue annually due to quality-related inefficiencies and incorrect decisions.
Seventy-seven percent of organizations rate their data quality as average or worse, representing an 11-point decline from 2020 levels. This deterioration despite increased investment reveals growing complexity overwhelming traditional quality management approaches. Data volumes doubling every two years outpace quality management capabilities, creating expanding technical debt.
Sixty-two percent of organizations identify data governance as the greatest impediment to AI advancement. Unclear data ownership, inconsistent policies, and privacy concerns paralyze AI initiatives. Companies successfully addressing governance challenges deploy AI three times faster with 60 percent higher success rates than organizations with governance deficiencies.
Only 31 percent of firms report their data is AI-ready, highlighting fundamental data quality and structure issues restraining AI adoption. This represents a major constraint preventing organizations from capitalizing on AI investment despite substantial spending on machine learning platforms and talent.
3. Technical Complexity and Integration Challenges
Enterprises manage an average of 400 or more data sources across systems, creating substantial integration complexity. Legacy systems, cloud platforms, SaaS applications, and IoT devices generate data in diverse formats requiring sophisticated transformation and harmonization processes.
Seventy-three percent of organizations report cloud adoption has increased operational complexity, requiring new skills and processes. Multi-cloud environments compound this challenge, forcing teams to maintain expertise across multiple cloud platforms with different service models, pricing structures, and operational paradigms.
Data silos and interoperability issues persist despite data lake and warehouse implementations. Different business units often maintain separate data infrastructure, creating redundancy and inconsistency. Breaking down these silos requires organizational change management as much as technical solutions.
4. Economic Pressures and Budget Constraints
Forty-one percent of data teams report negative budget impacts from economic pressures, forcing teams to deliver more capabilities with reduced resources and headcount. Organizations must prioritize high-ROI pipeline projects and eliminate lower-value activities.
Thirty-three percent of organizations reduced data team headcount in 2024, creating additional workload pressure on remaining staff. This contraction occurred despite continued growth in data volumes and business demands for data-driven capabilities, forcing greater automation and efficiency.
High implementation and maintenance costs represent barriers for smaller organizations lacking economies of scale. While cloud services reduce entry barriers through pay-as-you-go models, sustained usage costs accumulate quickly for data-intensive workloads. Organizations without dedicated cost optimization expertise frequently encounter unexpectedly high bills.
5. Organizational and Cultural Barriers
Cultural and organizational barriers dominate transformation challenges, exceeding technology obstacles. Data initiatives fail more frequently due to organizational resistance, unclear ownership, and misaligned incentives than technical limitations. Successful transformations require executive sponsorship, cross-functional collaboration, and sustained change management.
Communication failures between data engineering teams and business stakeholders create misaligned priorities and expectations. Engineers build technically sophisticated solutions addressing wrong problems, while business users struggle to articulate requirements in technically actionable terms. Bridging this gap requires data engineers with strong communication skills and business acumen.
Data literacy gaps across organizations limit effectiveness of data investments. Business users lack skills to effectively consume data products, while executives struggle to evaluate data strategy proposals. Investments in data literacy training programs yield substantial returns by enabling broader organizational data utilization.
Data Engineering Emerging Trends & Predictions
The data engineering landscape continues rapid evolution, with several emerging trends poised to reshape practices and priorities through 2027 and beyond. These developments reflect technological advancement, changing business requirements, and maturation of data engineering as a discipline.
1. AI-Enabled Automation and Autonomous Operations
Eighty-eight percent of organizations investigate AI in data engineering for data processing applications, representing near-universal interest in AI-powered pipeline automation. Generative AI transforms data preparation, quality checking, and anomaly detection processes. However, automation augments rather than replaces data engineers, shifting responsibilities from routine tasks to high-level system design and supervision.
AI copilots for data engineers provide intelligent assistance for code generation, query optimization, and troubleshooting. These tools reduce time spent on repetitive implementation tasks while maintaining human oversight for critical decisions. Prompt engineering emerges as valuable skill, with engineers orchestrating AI capabilities rather than manually crafting every implementation detail.
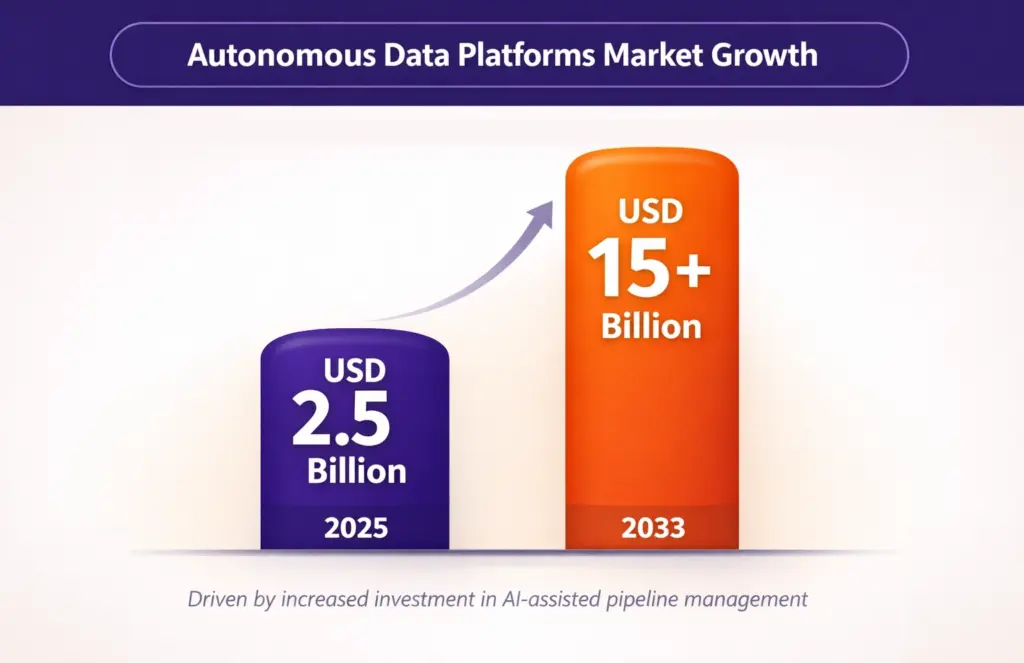
Autonomous data platforms market projected to grow from approximately USD 2.5 billion in 2025 to over USD 15 billion by 2033 as companies invest in AI-assisted pipeline management. These platforms monitor data quality, predict pipeline failures, and implement self-healing mechanisms. However, autonomous systems require robust testing, validation, and rollback capabilities to prevent cascading failures.
2. DataOps and Platform Engineering Maturation
DataOps methodologies gain widespread adoption as organizations apply DevOps principles to data pipelines. Continuous integration and deployment for data, automated testing frameworks, and infrastructure as code become standard practices. These approaches reduce deployment time, improve reliability, and enable rapid iteration on data products.
Platform engineering emerges as organizational model, with dedicated teams treating data systems as internal products. Rather than every squad maintaining separate infrastructure, platform teams provide standardized building blocks including ingestion frameworks, transformation templates, and deployment patterns. This reduces duplication and allows engineers to focus on data modeling and business logic rather than infrastructure plumbing.
Data contracts move from theoretical concept to everyday practice, defining dataset promises including schema, freshness, volume, and semantic meaning. Producers validate data against contracts before delivery, with violations failing fast rather than propagating downstream. This practice significantly reduces data quality incidents and enables confident data consumption.
3. Unified Data Platforms and Architecture Consolidation
The era of assembling dozen specialized data tools ends as complexity catches up with decentralized approaches. Organizations consolidate around unified platforms from Databricks, Snowflake, and Microsoft rather than maintaining fragile stacks of point solutions. The lakehouse architecture emerges as standard, providing a single platform for structured and unstructured data management, analytics, machine learning, and AI training.
Native governance capabilities including Unity Catalog, Snowflake Horizon, and AWS Glue Catalog build data quality, access control, and lineage tracking into platform foundations. This shift away from bolt-on governance tools reduces friction and delivers more reliable end-to-end coverage. Data quality checks, anomaly alerts, and usage monitoring run continuously in background.
Apache Iceberg adoption accelerates as standard for open table formats, enabling multi-engine data access without duplication. This interoperability breakthrough allows organizations to future-proof data without rewriting infrastructure each time ecosystem shifts. Cloud providers and data platforms increasingly standardize on Iceberg for lakehouse implementations.
4. Real-Time and Event-Driven Architecture Proliferation
Real-time data processing transitions from specialized capability to baseline expectation across digital products, analytics platforms, and AI systems. Organizations design pipelines handling events continuously rather than batch schedules. Streaming infrastructure including Kafka, Kinesis, and Pub/Sub becomes standard components of data architecture.
Event-driven architectures enable systems responding instantly to changes rather than waiting for scheduled refreshes. This capability proves especially valuable for operational use cases including fraud detection, supply chain optimization, predictive maintenance, and personalized customer experiences requiring immediate action.
Edge computing adoption grows as organizations process data closer to generation sources, reducing latency and bandwidth costs. Twenty-nine percent of enterprises deploy edge computing for latency-sensitive workloads. Integration between edge processing and centralized data platforms creates hybrid architectures balancing performance and analytical depth.
5. Sustainability and Cost-Aware Engineering
Environmental sustainability emerges as consideration in data engineering decisions as data volumes and processing requirements grow. Organizations optimize data retention policies, reduce redundant processing, and design energy-efficient architectures. Cloud cost optimization and FinOps practices support both financial accountability and environmental responsibility.
Engineers gain visibility into financial and environmental impacts of architectural choices, changing behavior patterns. Cost awareness moves from abstraction to first-class concern, with spending attributed to specific pipelines and teams. Storage tiering, query optimization, and compute scheduling become standard practices balancing performance with efficiency.
Data centers consume approximately 1.5 percent of global electricity and account for one percent of energy-related carbon emissions. Organizations with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance using cloud infrastructure demonstrate 4.7 times higher operating margins, indicating business value beyond environmental benefits.
Conclusion
The data engineering landscape in 2026 reflects both rapid growth and rising expectations. Expanding market size, widespread cloud adoption, and higher compensation levels underscore how critical data engineering has become to analytics, AI, and business performance. At the same time, the statistics highlight a clear shift toward cloud-native platforms, real-time pipelines, stronger governance, and cost-aware engineering practices, as organizations demand faster insights with greater reliability and control.
For business leaders and practitioners alike, these trends point to a clear takeaway: investing in modern data engineering capabilities is essential.
Folio3 Data Services helps organizations translate these market trends into action by designing and operating scalable, cloud-native data platforms across Snowflake, Databricks, and BigQuery. With a focus on governance, performance, and measurable ROI, Folio3 enables teams to modernize faster, attract top data talent, and turn growing data volumes into sustained competitive advantage in 2026 and beyond.
References
- 2026 Data Engineering Facts — Jobs, Skills, Tools & Demand: https://suggestron.com/data-engineering-statistics-facts-adoption-salaries-trends/
- Mordor Intelligence. (2025). Big Data Engineering Services Market Size, Share & Companies: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/big-data-engineering-services-market
- Market Data Forecast. (2025). Big Data and Data Engineering Services Market Size, 2033: https://www.marketdataforecast.com/market-reports/big-data-engineering-services-market
- Gartner Peer Community Survey: https://www.gartner.com/peer-community/poll/types-data-pipelines-org-using
- Streamsets: Data Integration Problem Research Report: https://go.streamsets.com/rs/535-TEA-657/images/StreamSets_Research_Report-Lifting_the_Lid.pdf
- Reports and Data. (2021). Big Data and Data Engineering Services Market Size Projected to Reach USD 144.12 Billion by 2026: https://www.reportsanddata.com/report-detail/big-data-and-data-engineering-services-market
- Glassdoor. (2026). Data Engineer Average Salary & Pay Trends: https://www.glassdoor.com/Salaries/data-engineer-salary-SRCH_KO0,13.htm
- PayScale. (2026). Data Engineer Salary: https://www.payscale.com/research/US/Job=Data_Engineer/Salary
- Coursera. (2025). Data Engineering Salary: Your 2026 Guide: https://www.coursera.org/articles/data-engineer-salary
- Cloud Industry Statistics: ZipDo Education Reports 2025: https://zipdo.co/cloud-industry-statistics
- Rishabh Software. (2025). Latest Data Engineering Trends to Watch in 2026: https://www.rishabhsoft.com/blog/latest-trends-in-data-engineering
- Binariks. (2024). 10 Data Engineering Trends & Prospects for 2026-2028: https://binariks.com/blog/data-engineering-trends/
- Softjourn. (2026). 100+ Cloud Computing Statistics for 2026: https://softjourn.com/insights/cloud-computing-stats
- Spacelift. (2026). 55 Cloud Computing Statistics for 2026: https://spacelift.io/blog/cloud-computing-statistics
- DesignRush News Report: https://news.designrush.com/reliable-data-strategy
- Data Downtime Nearly Doubled Year Over Year | APMdigest: https://www.apmdigest.com/data-downtime
- Finout. (2025). 49 Cloud Computing Statistics You Need to Know in 2026: https://www.finout.io/blog/49-cloud-computing-statistics-in-2026
- Big Data and Data Engineering Services Market Size & Growth Report, 2035: https://www.globalgrowthinsights.com/market-reports/big-data-and-data-engineering-services-market-113626
- Big Data and Data Engineering Services Market Share | Industry Size & CAGR of 18.79%: https://www.industryresearch.biz/market-reports/big-data-and-data-engineering-services-market-114114
- Data Engineering Platform Market Research Report 2033: https://dataintelo.com/report/data-engineering-platform-market
- Data Governance Market Size | Growth & CAGR of 28.41%: https://www.industryresearch.biz/market-reports/data-governance-market-102846
- Sovereign Cloud Market Research Report 2033: https://marketintelo.com/report/sovereign-cloud-market/amp
- DTP Group. (2026). Cloud Computing Statistics 2026: https://dtpgroup.co.uk/insight/50-cloud-computing-statistics/
- Holori. (2025). Cloud Market share 2026: Top cloud providers and trends: https://holori.com/cloud-market-share-2026-top-cloud-vendors-in-2026/
- Database Trends and Applications. (2025). 9 Predictions for Cloud in 2026: https://www.dbta.com/Editorial/News-Flashes/9-Predictions-for-Cloud-in-2026-172808.aspx
- Integrate.io. (2026). Data Transformation Challenge Statistics: https://www.integrate.io/blog/data-transformation-challenge-statistics/
- KDnuggets. (2026). 5 Emerging Trends in Data Engineering for 2026: https://www.kdnuggets.com/5-emerging-trends-in-data-engineering-for-2026
- Refonte Learning. Data Engineering in 2026: Trends, Tools, and How to Thrive: https://www.refontelearning.com/blog/data-engineering-in-2026-trends-tools-and-how-to-thrive
- Trigyn. Data Engineering Trends 2026 for AI-Driven Enterprises: https://www.trigyn.com/insights/data-engineering-trends-2026-building-foundation-ai-driven-enterprises
- Alibaba Cloud. AI Trends Reshaping Data Engineering in 2026: https://www.alibabacloud.com/blog/ai-trends-reshaping-data-engineering-in-2026_602816
- Qrvey. (2026). 2026 Databricks vs Snowflake Comparison: https://qrvey.com/blog/databricks-vs-snowflake/
- Integrate.io. (2026). Databricks vs. Snowflake: A Comparative Analysis: https://www.integrate.io/blog/databricks-vs-snowflake-a-comparative-analysis/
- CIO. (2026). What’s in, and what’s out: Data management in 2026 has a new attitude: https://www.cio.com/article/4117488/whats-in-and-whats-out-data-management-in-2026-has-a-new-attitude.html
- EuroAmerican Education. (2026). Top 20 Popular Big Data Tools and Technologies to Master in 2026: https://www.euroamerican.eu/top-20-popular-big-data-tools-and-technologies-to-master-in-2026
- Gradient Flow. (2025). Data Engineering in 2026: What Changes? https://gradientflow.substack.com/p/data-engineering-for-machine-users





