Modern supply chains generate massive amounts of data every second from procurement platforms and warehouse management systems to transportation networks and retail customer databases. Yet, for many enterprises, this wealth of information remains locked in isolated silos, creating blind spots that hinder efficiency, slow responses to disruptions, and increase operational costs.
Supply chain data integration addresses this challenge by strategically unifying disparate data sources into a single, connected ecosystem. Through data integration in supply chain operations, organizations gain end-to-end visibility across their supply chains, enabling real-time insights, accurate demand forecasting, and streamlined collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers.
Whether it’s achieving real-time supply chain integration for instant shipment tracking, implementing digital supply chain integration to automate procurement workflows, or using supply chain retail data integration to improve inventory planning, the benefits are transformative.
In this strategic guide, you’ll learn how to build integrated supply chain systems that break down data silos, strengthen decision-making, and unlock competitive advantage. We’ll explore core components, proven implementation steps, essential tools, and real-world case studies showing how global leaders leverage supply chain data management and integration to reduce costs, increase resilience, and accelerate growth.
What is Supply Chain Data Integration?
Supply chain data integration is the strategic process of connecting, standardizing, and synchronizing data from every system involved in moving products from suppliers to customers. This includes enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms, warehouse management systems (WMS), transportation management systems (TMS), and customer relationship management (CRM) tools, each a critical piece of the supply chain puzzle.
Organizations often apply proven data integration techniques to harmonize these diverse sources so information can flow seamlessly across the network.
Unlike basic data collection, data integration in supply chain operations creates a single source of truth that fuels end-to-end supply chain visibility. By harmonizing formats, definitions, and protocols, organizations enable smooth information sharing across procurement, manufacturing, logistics, and retail channels. This level of supply chain data interoperability ensures that stakeholders from planners to distribution managers can access accurate, real-time insights for faster, more coordinated decision-making.
Leading companies, such as Zara, have demonstrated the power of integrated supply chain systems by utilizing digital supply chain integration to link customer preferences to production and inventory allocation directly. This real-time connectivity allows them to cut time-to-market from months to weeks and respond instantly to shifting consumer demand.
Effective integration typically combines three core elements:
- Data harmonization: Standardizing formats and definitions across platforms for consistent interpretation.
- Real-time synchronization: Ensuring updates flow instantly across systems for real-time supply chain integration.
- Advanced analytics: Transforming raw data into actionable insights to drive predictive planning and proactive risk management.
Core Components of Supply Chain Data Integration
Building a scalable supply chain data integration framework requires five key components that work together to unify data flows and enable end-to-end supply chain visibility. Each element supports uninterrupted connectivity, a robust data governance strategy, and actionable insights across the supply chain ecosystem.
These components create a flexible, intelligent integration architecture that reduces costs, accelerates decisions, and empowers organizations to adapt quickly to changing market demands:
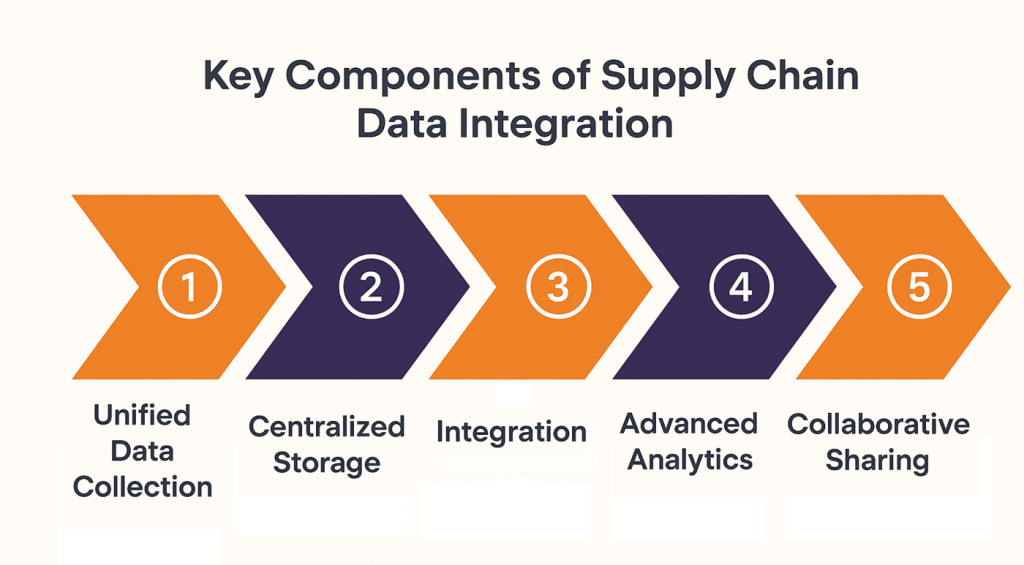
1. Unified Data Sources & Smart Collection
Integration begins by connecting all internal and external data sources, including ERP, WMS, TMS, supplier portals, logistics APIs, and IoT devices. Automated capture mechanisms reduce manual entry while enhancing data quality, enabling real-time integration of the supply chain from procurement to delivery.
2. Centralized Storage & Governance
Collected data must be stored in a secure, scalable architecture such as cloud-based data lakes or warehouses. A well-planned data warehouse strategy supports this approach, while strong governance ensures data consistency, ownership, and protection, forming the backbone of effective supply chain data management and integration.
3. Integration & Standardization Layer
This layer harmonizes formats and ensures supply chain data interoperability. Middleware platforms and APIs standardize communication between systems, forming the backbone of a scalable data integration architecture that enables real-time supply chain integration without complex point-to-point connections.
4. Advanced Processing & Analytics
Data cleansing, predictive analytics, and machine learning transform raw data into actionable insights. These capabilities drive accurate demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and risk mitigation across integrated supply chain systems.
Similar techniques are proving valuable in healthcare supply chain analytics, where real-time analysis of inventory and logistics helps hospitals anticipate shortages and maintain critical medical supplies.
5. Collaborative Sharing & Communication
Real-time dashboards, automated alerts, and secure partner portals provide stakeholders with the right information at the right time. Controlled visibility strengthens supplier collaboration and supports digital supply chain integration, ensuring every partner operates from a single, trusted source of truth.
7 Key Steps to Successful Supply Chain Data Integration
A successful supply chain data integration strategy requires a structured approach that balances technical execution with organizational readiness. Following these seven steps helps enterprises unify fragmented systems, enhance end-to-end supply chain visibility, and unlock real-time insights.
With these steps, enterprises can transform siloed data into a unified, analytics-ready infrastructure. Effective data integration in supply chain operations not only drives real-time decision-making but also strengthens resilience, efficiency, and customer satisfaction in a rapidly evolving market:
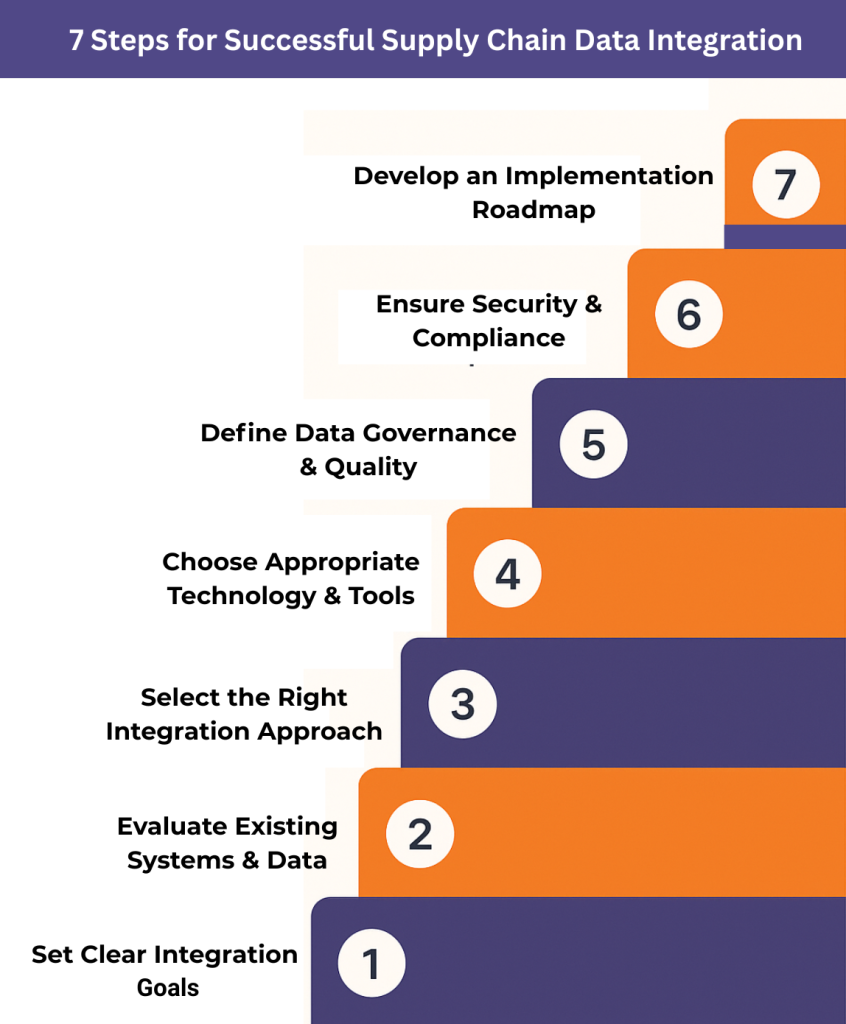
Step 1: Define Your Data Integration Goals
Begin by setting clear, measurable objectives that align with business priorities. Goals include improving on-time delivery, reducing inventory carrying costs, and enabling real-time shipment tracking. Define success metrics upfront to prevent scope creep and track progress effectively.
Step 2: Assess Current Systems and Data Sources
Audit all existing platforms ERP, WMS, TMS, CRM, supplier portals, and IoT sensors. Identify gaps, data silos, and quality issues that hinder supply chain integration. Pay special attention to legacy systems that may need custom APIs, middleware, or phased upgrades.
Step 3: Choose the Right Integration Approach and Solution
Select an integration model based on complexity, scalability needs, and compliance requirements. Options include point-to-point integrations for simple connections, enterprise data integration platforms for large, multi-system environments, cloud-based integration platforms (iPaaS) for agile, digital supply chain integration, or hybrid setups for regulated environments.
Step 4: Select the Right Technology and Tools
Adopt scalable tools such as cloud data lakes, ETL/ELT pipelines, and API management platforms. Modern integration platforms with pre-built connectors speed implementation and simplify supply chain data management and integration, ensuring real-time synchronization across global operations.
Careful planning of data lake implementation at this stage helps ensure that storage and analytics capabilities can scale with future business needs.
Step 5: Establish Data Governance and Quality Standards
Create a governance framework to define data ownership, access policies, and master data management (MDM) standards. Automate validation rules and cleansing routines to maintain high-quality data and consistent definitions across all integrated supply chain systems.
Step 6: Plan for Security and Compliance
Protect sensitive supplier, pricing, and shipment data with end-to-end encryption, role-based access controls, and continuous monitoring. Build compliance into every layer to meet GDPR, CCPA, or industry-specific requirements while enabling safe supply chain data interoperability.
Step 7: Create a Detailed Implementation Roadmap
Develop a phased plan that starts with high-value integrations to show early wins and build momentum. Include user training, change management, and rollback options to minimize disruptions and ensure smooth adoption of new integrated workflows.
Key Benefits of Supply Chain Data Integration
Effective supply chain data integration transforms fragmented systems into a connected ecosystem, delivering measurable gains in efficiency, accuracy, and strategic decision-making. From end-to-end visibility to cost savings, integration provides a foundation for resilient, high-performing supply chains.
End-to-End Visibility
Unified data flows enable complete visibility across sourcing, production, warehousing, and last-mile delivery. Real-time insights supported by strong customer data integration alongside supplier and logistics information help companies identify exceptions, predict disruptions, and manage bottlenecks before they impact customers. Integrated dashboards enable stakeholders such as suppliers, logistics partners, and retailers to work from the same information, ensuring faster responses and enhanced supply chain interoperability.
Streamlined Processes
Data integration automates manual tasks, such as data entry, purchase order creation, and shipment updates, thereby reducing errors and freeing teams to focus on strategic work. Automated triggers for example, reordering inventory when stock levels drop eliminate delays and improve accuracy, enabling smoother supply chain operations across procurement, production, and distribution.
Accurate Demand Forecasting
Integrated platforms combine diverse signals, sales data, market trends, weather forecasts, and social sentiment to create more precise demand forecasts. Companies can align production schedules with real-time market changes, reducing stockouts and overproduction.
Partnering with expert data engineering services can further enhance these forecasting models by ensuring clean, well-structured data pipelines. Better forecasting also improves promotion planning, enabling businesses to balance inventory levels with marketing campaigns effectively.
Supplier Collaboration
Integrated supply chain data fosters stronger supplier relationships by sharing real-time demand, capacity, and quality information. Vendors can proactively adjust their production, while buyers gain insight into supplier performance metrics, such as on-time delivery and cost efficiency. This transparency strengthens partnerships and reduces the risks associated with sudden disruptions.
Compliance & Risk Management
With consolidated data, companies can maintain accurate audit trails and comply with regulatory requirements across different regions. Integration supports product traceability, environmental reporting, and ethical sourcing by capturing every step of the supply chain. For industries such as pharmaceuticals and food, this visibility enables rapid responses to recalls or quality issues, while also supporting sustainability initiatives.
Operational Cost Savings
Integrated supply chain planning reduces inventory carrying costs, optimizes transportation routes, and minimizes redundant processes. Organizations with fully integrated systems typically achieve 20–25% lower operational costs through better load consolidation, reduced safety stock, and efficient resource utilization, key drivers of a leaner, more profitable supply chain.
Faster Time-to-Market
Smooth data sharing between design, sourcing, and production accelerates the launch of new products. Teams can evaluate supplier capabilities in real time, enabling quick adjustments to designs or sourcing strategies. In industries with short product lifecycles, such as fashion or consumer electronics, faster time-to-market can be a decisive competitive advantage.
Challenges in Implementing Supply Chain Data Integration (and Their Solutions)
Implementing supply chain data integration can transform operations, but it also brings technical, organizational, and regulatory hurdles. Addressing these challenges early ensures a smoother rollout and long-term success.
1. Data Silos and Fragmented Systems
- Challenge: Disconnected ERPs, WMS, TMS, and supplier platforms often create isolated data pools. Without standardized formats or interoperability, achieving cross-departmental visibility becomes challenging, which in turn slows decision-making.
- Solutions: Begin with a comprehensive data audit to identify sources, dependencies, and integration gaps. Use middleware or an integration platform (iPaaS) to connect disparate systems and unify data flows. Establish a single source of truth by utilizing a centralized data lake or warehouse, which eliminates silos and enables real-time collaboration.
2. Poor Data Quality and Inconsistent Standards
- Challenge: Inaccurate, duplicate, or outdated data leads to unreliable analytics, while suppliers may use inconsistent naming conventions, measurement units, or codes. Similar data lake challenges can arise when large volumes of raw information are ingested without proper validation.
- Solutions: Deploy automated data-cleansing tools and validation rules to standardize inputs at the source. Implement a master data management (MDM) framework to enforce company-wide standards for key entities like products, suppliers, and customers. Schedule regular quality checks and exception reporting to maintain accuracy over time.
3. Integration with Legacy Infrastructure
- Challenge: Older on-premise systems often lack APIs or modern connectivity, and upgrading them can involve high costs, downtime risks, and resistance from internal teams.
- Solutions: Use a hybrid integration model that blends cloud and on-premise systems to modernize gradually. Employ API gateways, custom adapters, or ETL/ELT tools to bridge gaps and enable secure data exchange. Plan phased upgrades with rollback contingencies to minimize operational disruptions while ensuring business continuity.
4. Security and Compliance Risks
- Challenge: Integrating shipment, pricing, and supplier data increases the attack surface and raises regulatory concerns under GDPR, CCPA, or industry-specific standards.
- Solutions: Enforce role-based access controls, end-to-end encryption, and continuous security monitoring. Conduct regular penetration testing and compliance audits to identify vulnerabilities. Partner with technology providers offering certifications such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001 to ensure strong data governance and regulatory adherence.
Folio3 helps businesses unify systems, standardize data, and maintain compliance for seamless, real-time supply chain insights.
Supply Chain Data Integration Approaches – Side-by-Side Comparisons
Selecting the optimal supply chain data integration approach depends on business requirements, technical complexity, and long-term scalability. Below is a concise comparison of the most common methods to help guide decision-making.
| Approach | Best For | Implementation Time | Cost | Scalability | Maintenance |
| Point-to-Point Integration | Simple, two-system connections that require only limited data exchange. | 2–6 weeks | Low | Limited | High (each new system requires custom connections). |
| Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) | Medium-complexity projects with an on-premise focus and moderate real-time needs. | 3–6 months | Medium | Good | Medium (centralized management reduces complexity). |
| Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) | Cloud-first organizations seeking rapid deployment and pre-built connectors for ERP, WMS, or TMS. | 1–3 months | Medium | Excellent (scales easily with business growth). | Low (vendor-managed updates). |
| API Management Platforms | Companies are adopting an API-first architecture to enable flexible, developer-driven integrations. | 2–4 months | Medium–High | Excellent | Medium (ongoing API monitoring required). |
| Data Virtualization | Businesses need real-time supply chain integration without physically moving data across systems. | 1–2 months | Medium | Good | Medium (depends on source system performance). |
| Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) | Batch processing and historical data aggregation in data warehouses or lakes. | 2–4 months | Medium | Good | Medium (requires regular data pipeline updates). |
| Event-Driven Architecture | Large, complex ecosystems require digital supply chain integration with real-time responsiveness. | 4–8 months | High | Excellent | Medium–High (advanced monitoring and orchestration). |
Best Practices for Supply Chain Data Integration Success
Achieving effective supply chain data integration requires more than just connecting systems. It demands strategic planning and disciplined execution. The following best practices help ensure a smooth, scalable, and future-ready integration process:
Conduct a Comprehensive Data Audit
Begin by mapping all supply chain data sources ERP, WMS, TMS, CRM, supplier portals, and IoT sensors. Identify data overlaps, gaps, and quality issues to create a single source of truth. A thorough audit reveals hidden dependencies, enabling smoother integration and reducing costly rework.
Establish Data Governance & Standards
Strong supply chain data management and integration rely on transparent governance. Define ownership, set quality benchmarks, and standardize formats to enable supply chain data interoperability.
Partnering with experienced data integration consulting services can help design robust master data management (MDM) policies and ensure consistent definitions for products, suppliers, and customers across all integrated systems.
Choose Scalable, Interoperable Tools
Select technologies, such as iPaaS platforms, API management tools, or cloud-based integration layers, that support real-time supply chain integration and facilitate future growth.
Adding capabilities like an AI enterprise search solution can further simplify access to integrated data, helping teams quickly locate critical insights across multiple systems. Scalable, interoperable solutions reduce complexity, accommodate new data sources, and adapt easily to evolving business needs.
Align IT & Business Goals
Integration success depends on collaboration between IT teams and business stakeholders. Aligning technology decisions with operational priorities, such as demand forecasting, inventory optimization, or end-to-end supply chain visibility, ensures that integration delivers measurable business value and aligns with the organization’s overall data analytics framework.
Train Teams and Encourage Change Management
Even the best technology fails without user adoption. Provide comprehensive training, clear communication, and ongoing support to help teams embrace new workflows. Foster a culture of adaptability to ensure long-term success in digital supply chain integration.
Real-World Uses and Case Studies of Supply Chain Data Integration
Supply chain data integration is more than a technology upgrade, but it’s a strategic driver of efficiency, agility, and competitive advantage. Across industries, companies are utilizing integrated supply chain systems to break down silos, provide real-time visibility, and enhance decision-making.
The following real-world examples illustrate how data integration in supply chain operations has a measurable impact across various sectors.
Retail Industry: Smarter Forecasting and Inventory Control
Retailers face constant pressure to meet fluctuating consumer demands while avoiding costly stockouts or excess inventory. By integrating POS, supplier, and inventory data, companies can achieve end-to-end supply chain visibility and more accurate demand forecasting.
Example: A leading global retailer worked with retail analytics consulting services to integrate real-time sales and supplier data across its digital supply chain network, reducing stockouts by 25% and boosting customer satisfaction. This collaboration enabled automated replenishment decisions and faster response to market shifts.
Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance and Production Optimization
Manufacturers are increasingly relying on IoT sensors and digital supply chain integration to connect data from ERP, MES, and shop-floor equipment. This unified approach supports predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and enhances production planning while drawing on data analytics stats to guide improvements and benchmark performance.
Example: A global manufacturer reduced equipment downtime by 18% and optimized raw material usage through supply chain data management and integration, which combined IoT sensor inputs with production data for real-time decision-making.
Logistics & Transportation: Real-Time Shipment Visibility
For logistics providers, real-time supply chain integration is essential for tracking shipments and improving delivery performance. Integrating WMS, TMS, and GPS systems provides continuous visibility across transport networks.
Example: A 3PL provider reduced delivery delays by 15% and improved on-time performance by implementing an integrated supply chain system that enabled dynamic routing and predictive arrival alerts.
Healthcare & Pharma: Cold Chain Compliance and Risk Reduction
In healthcare and pharmaceuticals, supply chain data interoperability ensures regulatory compliance and safeguards product quality. By incorporating healthcare data integration into these processes, organizations can merge supplier, distribution, and compliance information to create a transparent, traceable chain of custody.
Example: A major pharmaceutical company partnered with a firm specializing in healthcare data analytics consulting to streamline cold-chain monitoring and reduce spoilage by 12% through digital supply chain integration that tracks temperature-sensitive shipments in real time.
E-Commerce: Faster Fulfillment and Customer Satisfaction
In e-commerce, where speed is critical, supply chain retail data integration enables online retailers to synchronize order, warehouse, and shipping data, thereby accelerating fulfillment. Leveraging advanced predictive analytics techniques, these retailers can forecast demand spikes and optimize inventory positioning to keep pace with rapid market changes.
Example: An online retailer achieved 20% faster delivery times during peak demand by integrating customer order data with predictive analytics and logistics systems, ensuring rapid response to surging volumes.
From ERP to logistics and warehouse systems, Folio3 provides end-to-end integration that drives efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports growth.
Must-Have Tools & Technologies for Supply Chain Data Integration
Implementing supply chain data integration requires more than strategy. It demands the right technology stack to unify disparate systems, enable real-time data exchange, and ensure long-term scalability. From integration platforms to advanced analytics, these core tools form the backbone of integrated supply chain systems, driving actionable insights across the entire network.
Integration Platforms (iPaaS & Middleware)
Integration platforms as a service (iPaaS) and middleware solutions are the foundation of supply chain integration, connecting ERP, WMS, TMS, and CRM systems into a smooth data ecosystem. These platforms eliminate the need for complex point-to-point connections by offering pre-built connectors, automated workflows, and real-time data integration capabilities.
iPaaS solutions, such as MuleSoft, Dell Boomi, and Informatica, enable real-time supply chain integration, supporting cloud-to-cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments. Middleware serves a similar role for organizations that need on-premise control, ensuring smooth communication between legacy systems and modern applications.
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
APIs are crucial to achieving supply chain data interoperability, as they enable systems to exchange data securely and efficiently. RESTful APIs and API management platforms simplify connections between internal applications and external partners such as suppliers, logistics providers, and customers.
Well-structured APIs support digital supply chain integration by enabling real-time order tracking, inventory updates, and shipment notifications, which are essential for maintaining end-to-end visibility.
Cloud Data Warehouses or Data Lakes
Centralized data storage is crucial for managing the vast volumes of structured and unstructured supply chain data. Modern cloud data integration with platforms such as Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, or Azure Data Lake provides scalable and cost-effective solutions for supply chain data management.
These systems consolidate ERP transactions, IoT sensor data, supplier metrics, and customer information into a single repository, enabling advanced analytics, machine learning, and predictive modeling for smarter decision-making.
ETL/ELT & Data Pipeline Tools
ETL and ELT tools automate the process of collecting, cleaning, and standardizing data from multiple sources before it is stored or analyzed in analytics platforms.
Tools like Talend, Apache NiFi, and Fivetran ensure that supply chain data is accurate, timely, and ready for real-time processing. These pipelines are especially valuable for integrating data from retail, manufacturing, and logistics into a unified format, feeding retail data warehouses to support end-to-end supply chain visibility.
Master Data Management (MDM) Solutions
Consistency and accuracy are critical in large, complex supply chains. Master Data Management (MDM) solutions provide a single source of truth for key entities, including suppliers, products, customers, and locations.
By maintaining standardized definitions and hierarchies, MDM systems prevent duplication, reduce errors, and enhance the quality of data integration in supply chain operations. This ensures that every department from procurement to logistics operates with the same reliable data set.
Future Trends in Supply Chain Data Integration
As supply chains become more complex and data-driven, supply chain data integration is evolving to deliver smarter, faster, and more sustainable operations. Key trends are shaping the next generation of digital supply chain strategies.
AI-Driven Predictive Insights
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are enabling predictive analytics that anticipate disruptions before they occur. By combining historical data with real-time signals, AI-powered platforms can even apply AI data extraction techniques to capture and process critical information, improving demand forecasting, optimizing inventory, and recommending proactive actions. This capability turns integrated data into actionable insights, enhancing decision-making across global supply networks.
Edge Computing & 5G Connectivity
Edge computing and 5G are redefining real-time supply chain integration. By processing data near its source, such as IoT sensors in warehouses or transport hubs, companies can reduce latency and respond instantly to changes in demand, production, or shipping conditions. Faster, more reliable data flow strengthens end-to-end supply chain visibility and responsiveness.
Organizations can further optimize these real-time data streams by engaging experts in Snowflake consulting to design scalable cloud architectures that complement edge deployments.
Sustainable & Green Supply Chain Metrics
Sustainability is now a key driver of integration strategies. Advanced data platforms track carbon emissions, energy usage, and waste across suppliers and logistics partners. By aligning with emerging data analytics trends, companies gain deeper insights that help meet ESG reporting requirements and reduce environmental impact through optimized transportation, sourcing, and production.
Growing Cybersecurity Demands
As cloud platforms, APIs, and IoT devices expand, cybersecurity becomes critical. Future-ready integration solutions will embed zero-trust frameworks, end-to-end encryption, and AI-based threat detection to protect sensitive supplier, shipment, and customer data.
FAQs
What is supply chain data integration, and why is it important?
Supply chain data integration connects data from ERP, WMS, TMS, and other systems into a unified platform, enabling smooth information flow. This improves visibility, decision-making, and overall supply chain performance.
How does real-time supply chain data integration improve operational efficiency?
Real-time integration provides instant updates on inventory, shipments, and production, allowing faster responses to disruptions. This reduces delays, minimizes costs, and enhances customer service.
What are the biggest challenges in integrating supply chain data?
Key challenges include data silos, inconsistent standards, legacy system limitations, and cybersecurity risks. Overcoming these requires scalable integration platforms and strong data governance.
What technologies enable modern supply chain integration?
Technologies such as iPaaS, APIs, cloud data warehouses, ETL/ELT tools, and master data management (MDM) solutions power efficient supply chain data integration. These tools ensure scalability and interoperability.
What steps are involved in a successful supply chain data integration strategy?
A strong strategy includes a comprehensive data audit, establishing governance standards, selecting scalable tools, aligning IT and business goals, and ongoing monitoring for continuous improvement.
What is the ROI of supply chain data integration?
Supply chain integration delivers ROI through cost savings, improved forecasting accuracy, reduced inventory levels, and enhanced customer satisfaction, often lowering operational costs by 20–25%.
How does cloud-based supply chain data integration differ from on-premise solutions?
Cloud-based integration offers faster deployment, better scalability, and lower maintenance than on-premise systems while supporting real-time analytics and global collaboration.
How does AI enhance supply chain data integration and analytics?
AI enables predictive insights by analyzing integrated data for demand trends, risk detection, and process optimization, transforming raw data into actionable strategies.
What is the difference between ETL and real-time data integration in supply chains?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes batch data for analytics, while real-time integration streams live data for immediate visibility and faster decision-making.
Conclusion
Supply chain data integration is no longer optional, it’s the backbone of real-time decision-making, cost optimization, and end-to-end visibility. By unifying fragmented systems into a single, intelligent network, enterprises can improve forecasting, streamline operations, and build resilience against disruptions.
To accelerate this transformation, Folio3 Data Services offers tailored integration solutions, including iPaaS implementation, cloud data management, and advanced analytics, helping businesses achieve smooth supply chain connectivity and measurable ROI. Partner with Folio3 to unlock smarter, more agile, and future-ready supply chains.



