Data powers today’s business operations. It influences decision-making, fuels innovation, and enables companies to create tailored experiences for their customers. In large organizations, the importance of data grows even further.
It covers everything from customer records and financial data to research insights and operational processes—critical components for maintaining a competitive edge in a fast-evolving marketplace. Protecting this data isn’t just about meeting legal obligations; it’s about maintaining trust, staying competitive, and ensuring business continuity.
A strong data protection strategy doesn’t just guard against cyber threats—it helps enterprises manage complex systems, stay compliant with evolving global regulations, and build confidence among customers and partners. By taking a proactive approach, businesses can secure their most valuable asset: their data.
This blog will delve into the critical components of an adequate data privacy strategy and best practices for implementation.
What is a Data Protection Strategy?
A data protection strategy is a comprehensive plan to safeguard an organization’s sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
It outlines the policies, procedures, and technologies used to protect data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to disposal. A robust data security strategy is essential for maintaining business continuity, protecting reputation, and complying with data privacy regulations.
- Lowers the chances of data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Keeps sensitive information secure and ensures only authorized people can access it.
- Shields the organization from hefty fines by meeting data regulation requirements.
- Builds customer trust and boosts the company’s reputation.
- Offers a clear plan for recovering quickly and keeping operations running during unexpected events.
- Makes it easier to safely adopt new technologies like cloud computing and AI-driven tools.
Why Data Protection Strategy is Important?
Data fuels today’s businesses, driving innovation, guiding decisions, and strengthening customer relationships. But as companies rely more heavily on data, it has become a prime target for cybercriminals.
Breaches and cyber threats are on the rise, and the impact can be devastating—data breaches in 2024 cost organizations an average of $4.88 million per incident, creating significant financial and operational challenges. Beyond monetary losses, companies face reputational damage, loss of customer trust, and legal penalties for non-compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
A robust data protection strategy goes beyond compliance; it ensures the safety of sensitive information, minimizes business disruption, and safeguards an organization’s reputation. It’s not just about protecting data—it’s about securing the future of your business.
10 Key Components of a Successful Data Protection Strategy
Creating an effective data protection strategy involves several critical components. For organizations looking to integrate these components seamlessly, data strategy consulting can provide expert guidance on aligning data management practices with business objectives.
Here are ten essential components:
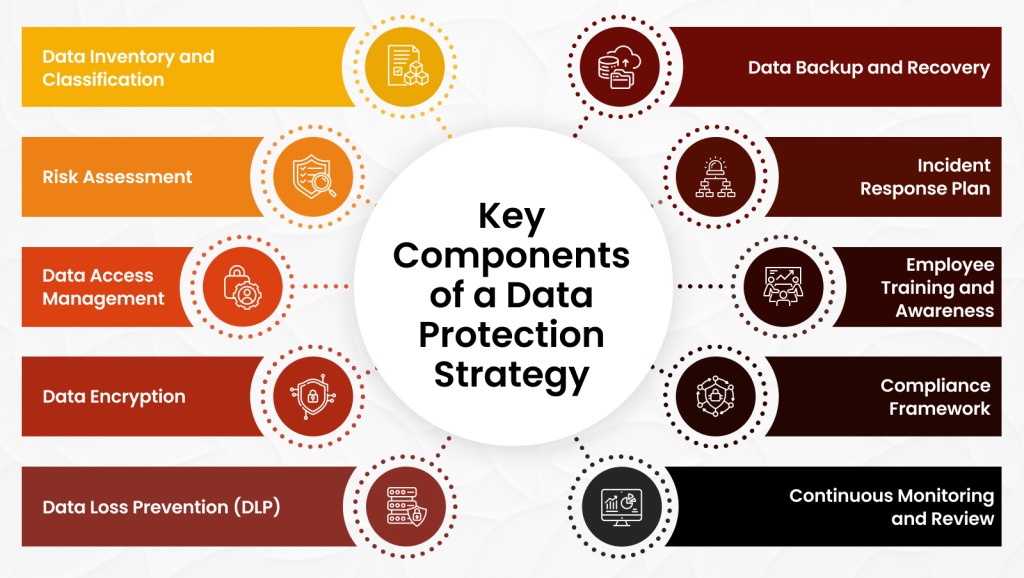
1. Data Inventory and Classification
A comprehensive catalog of data assets is fundamental. Data should be classified based on its sensitivity (e.g., public, internal, confidential, highly confidential) to determine the appropriate protection levels. This helps in prioritizing security measures and ensuring that sensitive data receives the highest level of protection.
2. Risk Assessment
Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities is crucial. This involves analyzing both internal and external factors that could compromise data integrity, confidentiality, or availability. Regular risk assessments help in understanding the potential impact of different threats and in developing strategies to mitigate them.
3. Data Access Management
Implementing strict controls over who can access and modify data is paramount. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and the principle of least privilege should be enforced.
This ensures that individuals only have access to the data necessary for their roles, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
4. Data Encryption
Protecting data with strong encryption algorithms is essential to render it useless if compromised. Encryption should be applied both at rest (when stored) and in transit (when transmitted over networks). This protects data from being intercepted and read by unauthorized parties.
5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Implementing DLP solutions to prevent data leakage through various channels, such as email, cloud storage, and removable media, is critical.
DLP tools monitor data movement and use, enforcing policies to prevent unauthorized sharing or transfer of sensitive data.
6. Data Backup and Recovery
Regular data backups and a robust recovery plan are essential to restore data in case of loss, corruption, or disaster.
Backups should be tested regularly to ensure they can be relied upon in an emergency, and recovery plans should include clear steps for data restoration and business continuity. Data engineering services can design and manage effective backup solutions and recovery processes, ensuring data integrity and availability during disruptions.
7. Incident Response Plan
A well-defined incident response plan outlines the steps to be taken in case of a data breach. This includes procedures for containment, investigation, notification of affected parties and authorities, and recovery. An effective incident response plan helps minimize damage and facilitates a quick return to normal operations.
8. Employee Training and Awareness
Educating employees about data protection best practices is vital. Regular training sessions should cover topics such as phishing, social engineering, secure data handling procedures, and the importance of following data protection policies.
9. Compliance Framework
Adhering to relevant data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA is mandatory. Staying updated on legal requirements and ensuring that the organization’s data protection practices align with these regulations helps avoid legal penalties and fosters trust among customers and stakeholders.
10. Continuous Monitoring and Review
Regularly assessing the effectiveness of data protection measures is essential. This includes continuous monitoring for threats, vulnerabilities, and compliance gaps.
Regular reviews and audits help ensure that the data protection strategy remains effective and is updated to address new challenges and regulatory changes.
Data Protection Strategy Best Practices
A robust data privacy strategy is underpinned by a series of best practices that ensure the effective safeguarding of sensitive information.
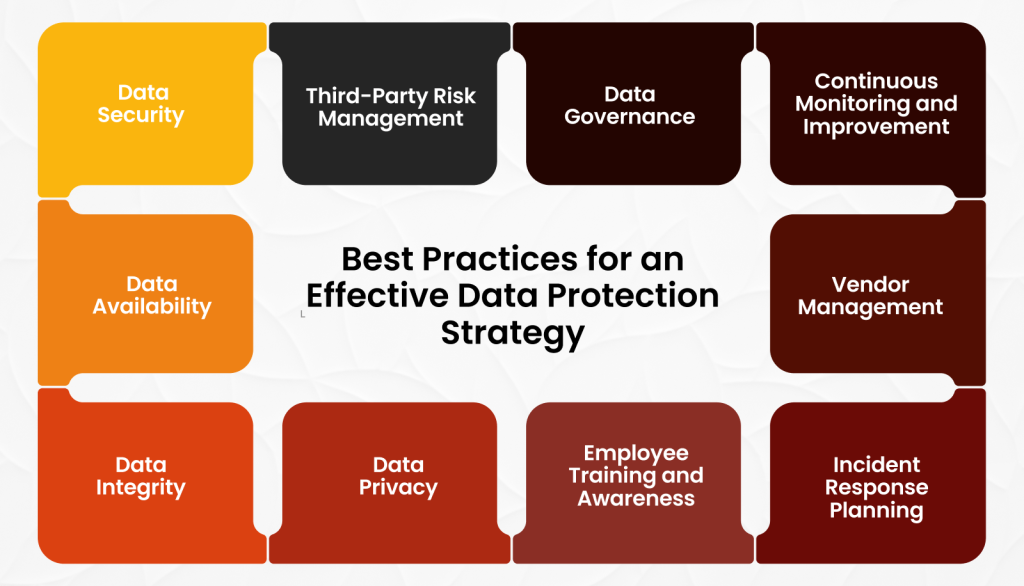
1. Data Security
- Encryption: Employing strong encryption algorithms for data at rest and in transit is paramount to protect information from unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Implementing robust access controls, such as role-based access control (RBAC) and least privilege principles, limits data exposure to authorized personnel.
- Network Security: Safeguarding the network infrastructure with firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and vulnerability management practices is essential.
2. Data Availability
- Data Backups: Regular data backups are crucial for business continuity. Implementing a comprehensive backup strategy, including off-site storage and disaster recovery plans, is vital.
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP): Developing a detailed BCP ensures minimal disruption to operations in case of data loss or system failures.
- Redundancy: Employing redundant systems and infrastructure can enhance data availability and resilience.
3. Data Integrity
- Data Validation: Implementing data validation checks to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Error Detection and Correction: Using techniques like checksums and parity checks to detect and correct data errors.
- Change Management: Controlling changes to data and systems to prevent unintended modifications.
4. Data Privacy
- Privacy by Design: Incorporating privacy principles into system and application development.
- Data Minimization: Collecting and retaining only the necessary data.
- Data Subject Rights: Implementing procedures to handle data subject requests, such as access, rectification, erasure, and data portability.
- Compliance Framework: Adhering to relevant data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA) and industry standards.
5. Employee Training and Awareness
- Security Awareness Programs: Conducting regular training to educate employees about data protection best practices, social engineering tactics, and phishing threats.
- Incident Reporting: Establishing clear procedures for employees to report suspicious activities or data breaches.
6. Incident Response Planning
- Incident Response Team: Forming a dedicated incident response team to handle security incidents effectively.
- Incident Response Plan: Developing a detailed plan outlining steps to be taken in case of a data breach, including containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned.
- Testing and Rehearsal: Regularly testing the incident response plan through simulations and tabletop exercises.
7. Vendor Management
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the security practices of third-party vendors and assessing potential risks.
- Contractual Obligations: Including data protection clauses in vendor contracts.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Regularly monitoring vendor performance and compliance.
8. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
- Threat Intelligence: Staying informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Management: Identifying and addressing system weaknesses.
- Performance Metrics: Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) related to data protection.
- Regular Reviews: Conducting periodic assessments of the data security strategy to identify areas for improvement.
9. Data Governance
- Data Ownership: Clearly defining data ownership and responsibilities within the organization.
- Data Retention Policies: Establishing guidelines for data retention and deletion to prevent data hoarding.
- Data Quality Management: Implementing processes to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
10. Third-Party Risk Management
- Vendor Assessment: Conducting thorough assessments of third-party providers to evaluate their data protection practices.
- Contractual Obligations: Including strong data protection clauses in contracts with third-party vendors.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Regularly monitoring third-party performance and compliance.
Principles of Data Protection
Data protection principles are the cornerstone of a comprehensive data protection strategy. These principles are designed to ensure that personal data is handled responsibly, securely, and in accordance with the law.
Each principle outlines specific requirements that organizations must follow to protect the privacy and rights of individuals.
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
Organizations must process personal data lawfully, fairly, and in a transparent manner. This means that data processing activities should have a clear legal basis.
Such as the consent of the data subject, the necessity for the performance of a contract, compliance with a legal obligation, protection of vital interests, the performance of a task carried out in the public interest, or legitimate interests pursued by the data controller or a third party.
Furthermore, individuals should be provided with clear, accessible information about how their data will be used, ensuring that they are aware of the data processing activities and their rights.
Purpose Limitation
Data should be collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes and not further processed in a manner incompatible with those purposes. This principle ensures that data is collected with a clear objective in mind and that its use is restricted to those purposes.
For instance, data collected for marketing purposes should not be used for research without the consent of the data subject. Organizations must clearly define and document the purposes for which data is collected.
Data Minimization
Only the minimum amount of personal data necessary for the fulfillment of the specified purpose should be collected and processed.
This principle aims to limit the collection of data to what is relevant and adequate, avoiding the collection of excessive or unnecessary information. Organizations should regularly review the data they hold to ensure it remains necessary and relevant to their operational needs.
Accuracy
Personal data must be accurate and kept up-to-date. Organizations have a responsibility to ensure that any inaccuracies in data are corrected without delay.
This may involve implementing procedures to verify the accuracy of data at the point of collection and maintaining mechanisms for individuals to update their information. Data cleansing processes should be in place to identify and rectify any inaccuracies.
Storage Limitation
Personal data should be retained only for as long as necessary to fulfill the purposes for which it was collected. Once the data is no longer needed, it should be securely deleted or anonymized.
Organizations must establish clear data retention policies and schedules, taking into account legal, regulatory, and operational requirements. This principle helps minimize the risk of data breaches and ensures that individuals’ data is not kept longer than necessary.
Integrity and Confidentiality
Personal data must be processed in a manner that ensures its security, including protection against unauthorized or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction, or damage.
This requires the implementation of appropriate technical and organizational measures to safeguard data. These measures may include encryption, access controls, regular security assessments, and employee training on data protection practices.
Accountability
Organizations are responsible for and must be able to demonstrate compliance with the data protection principles. This principle emphasizes the need for a proactive approach to data protection, where organizations implement and maintain policies, procedures, and controls to ensure compliance.
Organizations should document their data protection practices, conduct regular audits, and maintain records of data processing activities to demonstrate their adherence to the principles.
Frequently Asked Questions – Data Security Strategy
What are the 4 Key Areas of Data Protection?
Data protection centers on four areas: integrity (keeping data accurate), confidentiality (securing data from unauthorized access), availability (ensuring data is accessible), and compliance (meeting legal standards like GDPR).
What are the 4 Pillars of Data Privacy?
Data privacy relies on transparency (clear data usage communication), control (user data management), security (protecting data from breaches), and accountability (ensuring compliance with privacy laws).
Conclusion
A data protection strategy is essential for organizations seeking to safeguard sensitive information, maintain customer trust, and ensure business continuity in today’s digital landscape.
By understanding the core components, implementing best practices, and staying informed about evolving threats, businesses can create a resilient data protection framework. To effectively manage and protect your data, consider partnering with Folio3 Data Services.
Our expertise in data management can help your enterprise to implement a data protection strategy tailored to your specific needs.
With Folio3 Cloud and Data services, you can focus on your core business operations while we handle the complexities of data security.
Remember, data protection is an ongoing process. So, invest in a robust strategy and use expert support to safeguard your organization’s valuable assets and build a strong foundation for long-term success.