Big data has transformed how organizations operate, but it comes with a steep learning curve. Organizations today struggle with data management maturity, with the ability to collect massive amounts of data meaning little if businesses can’t process, secure, and extract value from it. Companies face big data challenges that range from technical limitations to workforce gaps. Statista reports that global data creation is expected to grow to more than 180 zettabytes by 2025, making these challenges even more pressing.
This article explores the most significant big data challenges organizations encounter and provides actionable solutions to address them effectively.
What Is Big Data
Big data describes information collections exceeding the capacity of conventional processing systems to manage effectively. Three core attributes define it: volume (extensive data quantities), velocity (rapid data creation), and variety (diverse data formats from numerous origins). Businesses gather big data through customer engagements, connected devices, social platforms, monitoring equipment, financial transactions, and various other channels. The purpose is examining this information to reveal patterns, forecast developments, strengthen decision processes, and secure market advantages.
Why Big Data Is Difficult to Manage at Scale
Managing big data becomes exponentially harder as organizations grow because traditional infrastructure wasn’t built for modern data volumes. Legacy systems struggle with processing speed, storage costs multiply rapidly, and data silos prevent unified analysis across departments. The distributed nature of big data requires specialized architectures, different skill sets, and new approaches to security. As data sources multiply and regulations tighten, maintaining quality, governance, and compliance across petabytes of information creates operational headaches that conventional methods simply can’t solve efficiently.
Top 8 Big Data Challenges Organizations Face and How to Solve Them
Controlling big data grows increasingly challenging as businesses expand because conventional infrastructure lacks capability for contemporary data scales. Older systems face processing limitations, storage expenses escalate quickly, and fragmented data prevents integrated cross-departmental analysis. Big data’s dispersed characteristics demand specialized frameworks, distinct expertise, and alternative security strategies. With expanding data sources and stricter regulations, sustaining quality, oversight, and compliance across massive information volumes generates operational challenges that traditional approaches cannot address effectively.
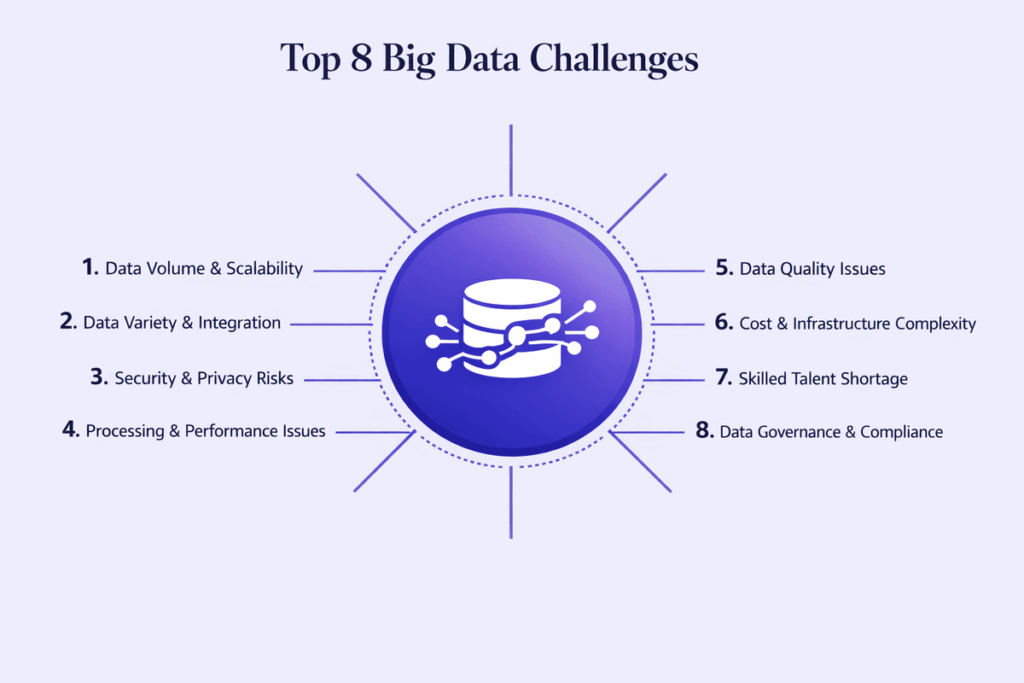
1. Data Volume & Scalability
Challenge
The sheer amount of data modern businesses generate creates storage and processing bottlenecks that overwhelm traditional systems. Organizations accumulate terabytes or petabytes of information daily from transactions, logs, sensors, and user activity. As datasets grow, query performance degrades, backup times extend, and infrastructure costs spiral upward. Many companies find their on-premise systems unable to keep pace with exponential data growth.
Solution
Cloud-based storage platforms like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Azure Blob Storage provide virtually unlimited scalability with pay-as-you-go pricing models. Implementing data lifecycle management policies helps archive or delete obsolete data automatically, reducing active storage requirements. Distributed processing frameworks such as Hadoop and Apache Spark enable parallel processing across multiple nodes, dramatically improving performance.
Designing systems around core big data architecture components such as scalable storage, distributed compute, and resource orchestration helps organizations handle growth efficiently. Organizations should also consider data compression techniques and tiered storage strategies that move infrequently accessed data to cheaper storage options while keeping hot data readily available.
2. Data Variety & Integration
Challenge
Modern organizations deal with structured data from databases, semi-structured data like JSON and XML, and unstructured data including emails, videos, and social media posts. Each data type requires different processing approaches, making integration difficult. Data arrives from countless sources using different formats, protocols, and schemas. Creating a unified view across these disparate systems while maintaining data integrity becomes a major technical hurdle.
Solution
Data lakes provide centralized repositories where organizations can store all data types in their raw format until needed for analysis. ETL tools like Apache NiFi, Talend, and Informatica automate data integration workflows, transforming and standardizing information from multiple sources. APIs and data connectors enable real-time synchronization between systems, reducing manual intervention. Schema-on-read approaches allow flexibility in data storage while deferring structure decisions until analysis time, accommodating various data formats without requiring upfront transformation.
3. Data Quality Issues
Challenge
Poor data quality undermines analytics accuracy and leads to flawed business decisions that can cost organizations millions. Duplicate records, missing values, inconsistent formatting, and outdated information plague big data environments. Data quality problems multiply when information flows from multiple sources without standardization. Manual data cleaning becomes impossible at scale, yet automated solutions often miss context-specific errors that humans would catch.
Solution
Automated data quality tools like Informatica Data Quality, Talend Data Quality, and Trifacta detect and fix common issues such as duplicates, null values, and format inconsistencies. Establishing data quality rules and validation checks at ingestion points prevents bad data from entering the system. Master data management practices ensure consistent definitions and standards across the organization. Regular data profiling helps identify quality trends and problem sources before they impact downstream analytics, while data stewardship programs assign accountability for maintaining quality in specific domains.
4. Security & Privacy Risks
Challenge
Big data environments expand the attack surface, creating more entry points for cybercriminals to exploit.According to IBM, the average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million in 2023, making big data security challenges extremely expensive. Distributed architectures complicate access control, encryption becomes resource-intensive at scale, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA requires meticulous tracking of data lineage and user consent, which is critical for effective big data storage and management.
Solution
Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure users only access data necessary for their roles. Encryption should protect data both at rest and in transit using industry-standard protocols like AES-256 and TLS. Data masking and tokenization techniques protect sensitive information during testing and analytics while maintaining data utility. Security information and event management (SIEM) systems monitor big data environments for suspicious activity in real time. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and employee training programs create multiple layers of defense against both external threats and insider risks.
5. Processing & Performance Issues
Challenge
Real-time analytics and complex queries on massive datasets can take hours or even days to complete using traditional processing methods. Performance bottlenecks occur when compute resources can’t keep up with data velocity, causing delays in insights that reduce their business value. Batch processing approaches create latency between data collection and analysis, making it difficult to respond quickly to changing conditions.
Solution
In-memory processing technologies like Apache Spark and Redis dramatically reduce query times by keeping frequently accessed data in RAM rather than reading from disk. Stream processing frameworks such as Apache Kafka and Apache Flink enable real-time data processing as information arrives, eliminating batch processing delays. Indexing strategies and partitioning schemes optimize query performance by reducing the amount of data scanned. Auto-scaling cloud infrastructure adjusts compute resources dynamically based on workload demands, ensuring performance remains consistent during peak usage periods without over-provisioning expensive resources during quiet times.
6. Cost & Infrastructure Complexity
Challenge
Building and maintaining big data infrastructure requires substantial capital investment in hardware, software licenses, and facility costs. On-premise solutions demand upfront spending before value realization, while ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and expansion add continuous expenses. Infrastructure complexity increases operational overhead as teams manage multiple interconnected systems, each requiring specialized knowledge. Organizations often overprovision resources to handle peak loads, wasting money during normal operations. Staying updated with big data trends helps organizations adopt more cost-effective architectures and modern tools that reduce operational strain.
Solution
Cloud platforms eliminate upfront hardware costs by offering infrastructure as a service with flexible pricing based on actual usage. Managed services like Amazon EMR, Google Dataproc, and Azure HDInsight reduce operational complexity by handling cluster management, patching, and scaling automatically. Implementing cost monitoring tools and setting budget alerts prevents unexpected spending while chargeback mechanisms help individual teams understand their resource consumption. Spot instances and reserved capacity options provide significant discounts for workloads with flexible timing or predictable usage patterns, reducing overall infrastructure expenses without sacrificing capabilities.
7. Skilled Talent Shortage
Challenge
The demand for big data professionals far exceeds supply, creating a critical skills gap that slows down initiatives and increases labor costs. Data engineers, data scientists, and big data architects require specialized expertise in distributed systems, advanced analytics, and modern tools that traditional IT staff often lack. High salaries and competitive recruiting make it difficult for many organizations to build capable teams.
Solution
Invest in training programs that upskill existing IT staff on big data technologies, reducing dependency on external hiring. Partnering with universities and bootcamps creates talent pipelines through internship and apprenticeship programs. Adopting user-friendly tools with graphical interfaces and automated features reduces the technical expertise required for common tasks. Outsourcing specialized functions to experienced consulting partners provides immediate access to expert knowledge while internal teams develop their capabilities. Creating clear career development paths and offering competitive compensation helps retain talent once acquired.
8. Data Governance & Compliance
Challenge
Regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA impose strict rules on data handling, storage, and processing that big data environments struggle to enforce. Without clear governance frameworks, organizations face regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Tracking data lineage across distributed systems becomes nearly impossible, making it difficult to respond to subject access requests or demonstrate compliance during audits.
Solution
Establish a data governance framework that defines policies, standards, and responsibilities for data management across the organization. Data cataloging tools like Collibra, Alation, and Apache Atlas provide visibility into what data exists, where it’s stored, and who has access to it. Automated compliance monitoring systems track data usage against regulatory requirements and flag potential violations before they become problems. Implementing data lineage tracking ensures transparency from data source to consumption, enabling quick responses to regulatory inquiries. Privacy by design principles should be embedded into data architecture from the beginning rather than added as an afterthought.
Folio3 helps organizations tackle the top 8 big data challenges—from scalability and integration to governance and talent shortages—delivering solutions that drive measurable business value.
Best Practices to Overcome Big Data Challenges
Adopting cloud platforms, enforcing governance, using AI analytics, monitoring performance, and upskilling teams are key practices to overcome big data challenges and turn data into actionable insights. Developing a clear big data strategy ensures that these efforts align with business goals and optimize both technology investments and team capabilities.

1. Adopt Cloud-Native Platforms
Cloud infrastructure provides the flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency that on-premise solutions can’t match for big data workloads. Modern cloud platforms offer managed services that handle infrastructure complexity, automatic scaling, and built-in redundancy. Organizations can start small and grow incrementally, paying only for resources consumed. Cloud providers continuously update their services with the latest capabilities, ensuring access to cutting-edge technology without requiring constant internal upgrades.
2. Implement Data Governance
Strong governance establishes the foundation for reliable, secure, and compliant big data operations across the entire organization. Clear policies define who can access what data, how information should be classified, and what security measures apply to different data types. Governance frameworks ensure consistency in data definitions, preventing confusion and errors when different teams analyze the same information. Regular audits and monitoring enforce compliance with both internal policies and external regulations.
3. Use AI-Driven Analytics
Artificial intelligence and machine learning automate complex analytical tasks that would be impossible for humans to perform manually at scale. AI algorithms can identify patterns, anomalies, and insights hidden in massive datasets far faster than traditional methods. Big data predictive analytics enables proactive decision-making based on future trend forecasts rather than reactive responses to past events. Natural language processing makes big data accessible to non-technical users through conversational interfaces.
4. Monitor Performance and Costs
Continuous monitoring provides visibility into system performance, resource utilization, and spending patterns that inform optimization decisions. Performance metrics help identify bottlenecks before they impact user experience or business operations. Cost tracking prevents budget overruns and reveals opportunities to reduce spending through resource right-sizing or architectural improvements. Automated alerting systems notify teams immediately when metrics exceed acceptable thresholds, enabling quick response to emerging issues.
5. Invest in Team Upskilling
Building internal expertise through training programs reduces dependency on expensive external consultants and accelerates project delivery. Upskilling creates career development opportunities that improve employee satisfaction and retention rates. Cross-training team members on multiple technologies increases flexibility and resilience when key personnel are unavailable. Hands-on learning through real projects with mentorship from experienced practitioners provides more effective skill development than theoretical classroom training alone.
Big Data Tools That Help Solve These Challenges
A range of these powerful tools helps organizations tackle big data challenges efficiently. Platforms like Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, Snowflake, and cloud services from AWS, Azure, and Google provide scalable storage, fast processing, real-time analytics, and simplified management to turn complex data into actionable insights.
1. Hadoop
Apache Hadoop pioneered distributed processing with its MapReduce programming model and HDFS storage system for handling massive datasets across clusters of commodity hardware. It excels at batch processing large volumes of structured and unstructured data. While newer technologies have emerged, Hadoop remains relevant for specific use cases and forms the foundation of many enterprise big data platforms.
2. Apache Spark
Spark delivers significantly faster processing than Hadoop by keeping data in memory rather than writing to disk between operations. Its unified engine supports batch processing, real-time streaming, machine learning, and graph processing within a single framework. Spark’s ease of use through high-level APIs in Python, Scala, and Java makes it accessible to developers while maintaining the performance needed for production workloads.
3. Apache Kafka
Kafka functions as a distributed event streaming platform that handles real-time data feeds from thousands of sources simultaneously. It provides reliable message delivery, fault tolerance through replication, and horizontal scalability to handle trillions of events per day. Kafka serves as the backbone for event-driven architectures and real-time analytics pipelines in many modern organizations.
4. Snowflake
Snowflake’s cloud-native data warehouse separates storage and compute, allowing independent scaling of each based on workload requirements. Its architecture eliminates infrastructure management while providing instant elasticity and strong performance for analytical queries. Features like automatic clustering, zero-copy cloning, and time travel simplify data operations and reduce costs compared to traditional data warehouses.
5. AWS Big Data Services
Amazon Web Services offers a comprehensive suite including S3 for storage, EMR for managed Hadoop and Spark, Kinesis for real-time streaming, and Redshift for data warehousing. These services integrate seamlessly with each other and the broader AWS ecosystem. Organizations can build complete big data pipelines using managed services that reduce operational complexity while maintaining flexibility for custom requirements.
6. Azure Synapse
Microsoft’s unified analytics platform combines data integration, enterprise data warehousing, and big data analytics in a single service. It provides both serverless and dedicated resource models to match different workload patterns and budgets. Deep integration with Power BI, Azure Machine Learning, and other Microsoft tools creates a cohesive environment for analytics workflows.
7. Google BigQuery
BigQuery’s serverless architecture eliminates infrastructure management while providing lightning-fast SQL queries on petabyte-scale datasets. Its columnar storage format and automatic optimization deliver strong performance without requiring manual tuning. Built-in machine learning capabilities enable advanced analytics without moving data to separate platforms, streamlining the path from data to insights.
Folio3’s Approach to Big Data Problems
Folio3 addresses big data challenges with tailored solutions that combine strategy, cloud architecture, AI integration, security, and industry-specific analytics. As a data analytics services company, Folio3 helps organizations translate complex data environments into scalable, insight-driven systems that support long-term growth. Let’s explore how these approaches help organizations overcome complex data problems effectively.
1. End-to-End Big Data Strategy
Folio3 begins every engagement by understanding business objectives, current data landscape, and specific pain points before recommending solutions. Our strategic planning process identifies quick wins alongside long-term architectural improvements that align technology decisions with business value. We help organizations prioritize initiatives based on ROI potential and resource constraints, ensuring focused execution rather than scattered efforts that dilute impact.
2. Cloud-Native Architecture Deployment
Our team designs and implements cloud-based big data solutions using platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud that provide scalability and flexibility. We leverage managed services wherever possible to reduce operational overhead while maintaining control over critical components. Reference architectures and proven patterns accelerate deployment timelines while ensuring reliability, security, and performance meet enterprise requirements from day one.
3. AI-Driven Data Integration
Folio3 employs machine learning algorithms to automate data mapping, transformation, and quality validation across heterogeneous sources. As experienced data integration consultants, the team builds AI-powered integration pipelines that adapt to schema changes and data drift automatically, reducing maintenance burden. Intelligent data profiling identifies relationships and patterns that inform better integration strategies, while automated anomaly detection catches quality issues before they impact downstream analytics.
4. Security & Compliance Frameworks
We implement defense-in-depth security architectures that protect data through multiple layers including network isolation, encryption, access controls, and activity monitoring. Our compliance frameworks map regulatory requirements to technical controls with automated validation and documentation. Data governance programs establish policies, procedures, and accountability mechanisms that ensure ongoing adherence to security and privacy standards.
5. Industry-Specific Analytics Solutions
Folio3 brings deep domain expertise in healthcare, agriculture, and other industries to deliver analytics solutions tailored to sector-specific challenges. Our pre-built accelerators for common use cases reduce development time while incorporating industry best practices and regulatory requirements. We understand the unique data types, workflows, and compliance considerations that general-purpose tools often overlook, delivering more relevant and impactful results.
FAQs
What Are the Biggest Challenges of Big Data?
The biggest challenges include managing massive data volumes, integrating diverse data types, ensuring data quality, securing sensitive information, achieving acceptable performance, controlling costs, finding skilled talent, and maintaining compliance with regulations.
Why Is Big Data So Hard to Manage?
Big data is difficult to manage because traditional tools weren’t designed for the volume, velocity, and variety of modern data. Distributed architectures introduce complexity, quality issues multiply at scale, and security becomes harder across numerous systems.
How Do Companies Solve Big Data Challenges?
Companies solve big data challenges by adopting cloud platforms for scalability, implementing strong governance frameworks, using specialized tools like Spark and Kafka, investing in security measures, and building or acquiring necessary skills through training and partnerships.
What Tools Are Used to Handle Big Data Problems?
Common tools include Hadoop for distributed storage, Apache Spark for fast processing, Kafka for streaming, Snowflake for cloud warehousing, and cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud that provide managed big data services.
Is Cloud Computing Necessary for Big Data?
While not absolutely necessary, cloud computing provides significant advantages for big data including elastic scalability, reduced upfront costs, access to managed services, and ability to quickly adopt new technologies without major infrastructure investments.
What Are the Most Common Big Data Security Challenges?
Common security challenges include protecting data across distributed systems, managing access controls at scale, encrypting massive datasets without performance degradation, detecting threats in high-velocity data streams, and meeting regulatory compliance requirements.
How Can Data Quality Issues Be Fixed in Big Data Projects?
Data quality improves through automated validation at ingestion, data profiling to identify issues, cleansing tools that standardize formats, master data management for consistency, and governance programs that establish quality standards and accountability.
What Industries Face the Toughest Big Data Challenges?
Healthcare faces strict HIPAA compliance and patient privacy requirements, financial services must meet regulatory reporting standards, retail handles massive transaction volumes with real-time demands, and manufacturing manages complex IoT sensor data from production equipment.
How Does Real-Time Processing Affect Big Data Management?
Real-time processing adds complexity by requiring low-latency infrastructure, stream processing capabilities, immediate data validation, and continuous monitoring. It eliminates batch processing windows, demanding systems that handle sustained high-velocity data ingestion and analysis simultaneously.
What Skills Are Needed to Manage Big Data Effectively?
Essential skills include distributed systems architecture, programming languages like Python and Scala, SQL and NoSQL databases, cloud platform expertise, data modeling, statistics, machine learning basics, and understanding of security and governance principles.
How Can Companies Reduce the Cost of Big Data Infrastructure?
Cost reduction strategies include using cloud services with pay-per-use pricing, implementing auto-scaling to match resources with demand, leveraging spot instances for flexible workloads, archiving cold data to cheaper storage, and continuously monitoring to eliminate waste.
Conclusion
Big data challenges are real and significant, but they’re not insurmountable with the right approach, tools, and expertise. Organizations that address these issues systematically position themselves to extract maximum value from their data assets while managing risks and controlling costs effectively. The solutions discussed in this article provide a roadmap for overcoming common obstacles that prevent many companies from realizing their big data ambitions.
Folio3 Data Services specializes in helping organizations navigate big data challenges through comprehensive solutions spanning strategy, architecture, implementation, and ongoing optimization. Our team brings deep technical expertise across cloud platforms, data engineering, AI/ML, and industry-specific requirements to deliver results that drive measurable business impact. Whether you’re just beginning your big data journey or looking to optimize existing investments, Folio3 provides the knowledge and experience to turn data challenges into competitive advantages.