From ICU monitors to automated stock trading, real-time data powers decisions that can’t afford delays. As industries become increasingly interconnected, the need for accurate and immediate information has become essential, not optional.
In healthcare, real-time data monitoring enables the instant detection of patient risks. Finance relies on real-time fraud detection, retailers use real-time data collection tools for tracking sales and customer behavior, and manufacturers predict equipment failures with real-time analytics.
With global data creation expected to reach 181 zettabytes by 2025, efficiently managing this data is crucial. But what exactly is real-time data? What are the types of real-time information, and how do you collect real-time data reliably?
Whether through IoT, cloud APIs, or connected sensors, real-time data collection and processing systems are transforming how organizations operate. This article breaks down the importance, benefits, key components, and challenges of real-time data, as well as how real-time data collection and open delivery can support smarter decision-making in today’s digital economy.
Why Real-Time Data Collection Matters?
Unlike traditional batch processing, which gathers and processes data at scheduled intervals, a real-time data collection system captures and processes information the moment it is generated. This shift from delayed to instant access isn’t just a technical improvement it’s a necessity for many industries where timing directly impacts outcomes.
Benefits Over Traditional Batch Processing
Today’s consumers expect personalized experiences. Real-time data collection and open delivery—often guided by data strategy services—allow businesses to tailor content, offers, and service recommendations in the moment. Streaming platforms use viewing behavior to suggest what to watch next. E-commerce sites track clicks, scrolls, and cart activity to personalize promotions.
Faster Decision-Making and Responsiveness
Industries like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce rely on real-time data monitoring to make split-second decisions. In hospitals, continuous data from ICU monitors can flag critical changes in a patient’s vitals, enabling immediate medical intervention. In finance, real-time data processing helps detect fraudulent transactions within milliseconds before damage is done.
Retailers, too, are adopting real time data collection tools to track inventory levels, buying patterns, and customer interactions. The ability to act instantly on this information means fewer stockouts, dynamic pricing opportunities, and better allocation of marketing spend.
Competitive Advantage Through Agility
Speed isn’t just a luxury. It’s a competitive differentiator. A company with a strong data analytics strategy that uses real-time data management can identify supply chain issues, respond to market shifts, or reallocate resources hours or even days before a competitor relying on batch updates notices the same issue.
This kind of agility is particularly important in industries with thin margins or volatile markets. For example, ride-sharing apps use types of real time information like GPS data, weather conditions, and local demand to adjust pricing and route drivers more efficiently.
Enhanced Customer Experience and Personalization
Today’s consumers expect personalized experiences. Real-time data collection and open delivery allow businesses to tailor content, offers, and service recommendations in the moment. Streaming platforms use viewing behavior to suggest what to watch next. E-commerce sites track clicks, scrolls, and cart activity to personalize promotions.
Core Components of a Real-Time Data Collection System
Setting up a reliable real time data collection system involves more than just fast internet and connected devices. It requires a carefully designed pipeline that can handle data generation, ingestion, processing, and analysis all in real time. Here’s a breakdown of the essential components that make this possible:
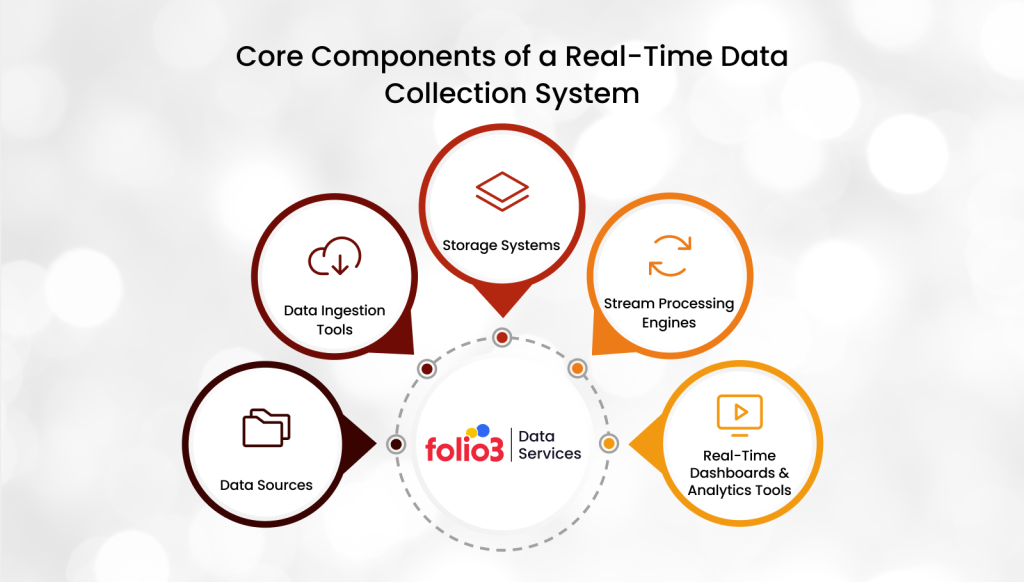
1. Data Sources
The process starts at the edge where data is generated. These sources can range from IoT devices, industrial sensors, and mobile applications to cloud APIs and user-facing platforms. For example, a smart greenhouse may use temperature and humidity sensors that continuously feed information into a central system. Understanding the types of real time information you’ll need is critical at this stage, whether it’s environmental data, user actions, machine telemetry, or financial transactions.
2. Data Ingestion Tools
Once generated, the next step is ingestion—getting data from the source to a central processing system without delay. This is where data ingestion architecture comes into play, providing the framework for efficiently collecting and transferring data. Tools like Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, and Amazon Kinesis are widely used for this purpose. These systems are designed for fault tolerance, high throughput, and low-latency transmission of event streams, making them ideal for high-frequency real-time data collection and open delivery.
3. Storage Systems
Traditional relational databases often fall short when it comes to handling real-time workloads. Instead, time-series databases like InfluxDB or in-memory databases like Redis are used for real-time scenarios. They’re optimized to store and retrieve time-stamped data efficiently, which is key for applications such as real time data monitoring in healthcare or utilities.
4. Stream Processing Engines
Real-time data is only useful if it can be acted on immediately. This is where stream processing comes in. Tools like Apache Spark Streaming, Flink, and Google Cloud Dataflow process incoming data streams on the fly, applying logic, filtering, aggregating, and even triggering alerts or automation. This component is essential for true real-time data processing not just fast reporting.
5. Real-Time Dashboards and Analytics Tools
Finally, decision-makers need a way to interpret the data. Real-time analytics tools such as Grafana, Power BI, or Tableau (with live connectors) provide dashboards that update continuously as new data flows in. These tools not only visualize trends, flag anomalies, and support quick decisions, but they also highlight the benefits of real-time analytics, enabling faster, more informed decision-making without waiting for the next scheduled report.
Whether you’re tracking energy usage, monitoring machine health, or analyzing user behavior, a complete real-time system ensures every part of the pipeline from how to collect real time data to how it’s displayed is optimized for immediacy and reliability.
Use Cases Across Industries
Real-time data isn’t just a technical advantage it’s a strategic necessity across many sectors. Whether it’s reducing risk, improving efficiency, or responding instantly to market shifts, organizations are using real-time data collection systems to transform how they operate.
Here’s a closer look at how different industries apply this technology:
Healthcare
In critical care environments, seconds can make the difference between stability and crisis. Real-time data monitoring tools capture vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation in ICU patients. By integrating these systems with data analytics for healthcare, clinicians can identify trends, predict complications, and respond proactively to changes in patient conditions. These values are continuously streamed from bedside monitors, enabling automated alerts if they move out of range.
Retail
Retailers use real time data collection tools to monitor in-store inventory, track customer behavior, and adjust pricing strategies dynamically. For example, if a product is selling faster than expected, the system can trigger restocking or limit promotions to prevent stockouts. Personalized product recommendations are also driven by real time data processing based on recent browsing or purchase behavior.
Manufacturing
In industrial settings, unplanned equipment failure is expensive and disruptive. Manufacturers deploy real time data collection systems to monitor machine health indicators like vibration, temperature, or pressure.
When integrated with big data & predictive analytics, these systems help anticipate breakdowns before they occur, cutting downtime and maintenance costs. This kind of real-time data management supports lean operations and extends equipment life, especially in sectors like automotive and electronics, where precision is key.
Finance
Speed and accuracy are critical in financial transactions. Banks and fintech companies rely on real-time data processing for fraud detection analyzing spending patterns, login locations, and transaction histories in milliseconds to flag suspicious activity.
High-frequency trading firms also use real-time data collection and open delivery models to track stock prices, execute trades, and respond to market shifts ahead of competitors.
Logistics
For logistics and transportation, real time data benefits are both operational and customer-facing. Fleet tracking systems use GPS data to monitor vehicle location, fuel efficiency, and driver behavior. Delivery platforms update customers instantly with estimated arrival times and route changes.
Smart Cities
Urban centers use types of real time information like traffic flow, public transit usage, and energy consumption to optimize resource allocation. Smart traffic lights adjust signals based on live congestion data, while real-time electricity meters help manage grid loads during peak hours. These systems help cities respond faster to emergencies, reduce carbon footprints, and improve citizens’ quality of life.
Technologies Powering Real-Time Data Collection
Behind every effective real time data collection system is a combination of technologies designed to move, process, and act on data instantly. These tools not only support speed, but also scalability and reliability critical factors as global data volumes continue to rise. Here’s a breakdown of the key technologies enabling real-time operations across industries:
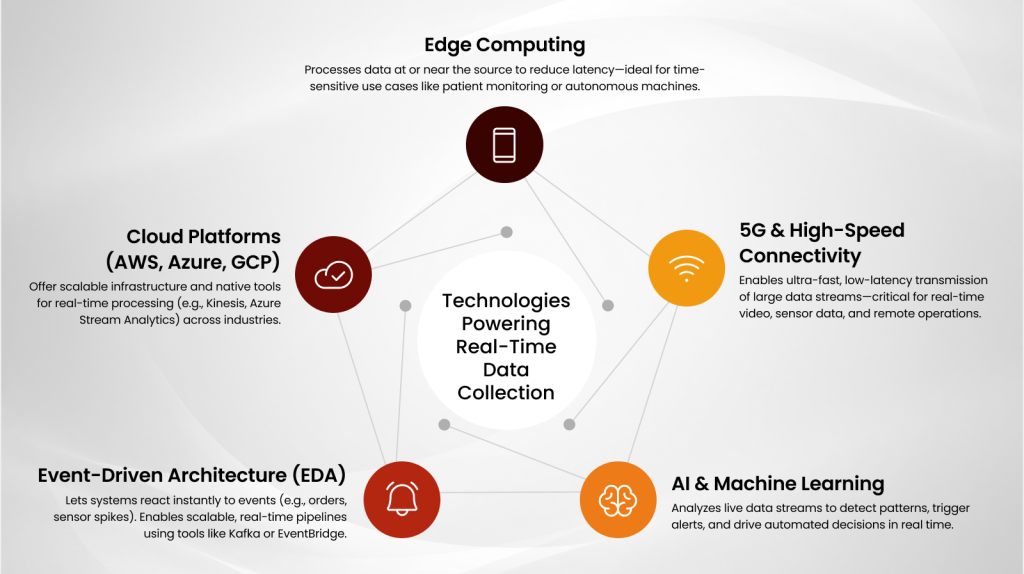
Edge Computing
Edge computing allows data to be processed closer to its source on the device itself or nearby servers rather than being sent to a centralized cloud for analysis. This reduces latency and ensures faster response times, especially for applications where delays are costly or dangerous, such as patient monitoring or autonomous machinery. In many real time data collection tools, edge devices also filter and prioritize data before sending it onward, reducing bandwidth usage and enhancing efficiency.
5G and High-Speed Connectivity
The rollout of 5G networks is a game-changer for real-time data processing. With speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G and ultra-low latency, 5G supports uninterrupted transmission of high-volume data streams. This is especially valuable in industries like manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture, where real-time video, telemetry, or sensor data needs to be acted upon immediately.
AI & Machine Learning for Stream Analytics
While AI is often linked to predictive modeling, it also plays a vital role in analyzing data streams in real time. As part of modern data analytics, machine learning algorithms can detect patterns or anomalies in financial transactions, patient vitals, or supply chain movements as they happen. When integrated into real-time data monitoring systems, AI models can trigger alerts, flag risks, or recommend actions without human intervention.
Event-Driven Architecture (EDA)
EDA is a design approach where systems respond to “events” any change in state, such as a new customer order or a machine temperature spike. Unlike traditional batch systems, event-driven models react instantly to new inputs. This makes them essential for building scalable real-time data collection and open delivery pipelines. Event brokers like Apache Kafka or AWS EventBridge enable microservices to communicate efficiently and stay updated as data changes.
Cloud-Based Data Platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP)
Cloud services provide the infrastructure and tools needed to manage the growing demands of real time data management. Platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer serverless compute, scalable storage, and native integration with streaming tools. These ecosystems make it easier to collect, process, and visualize real-time data across locations, devices, and applications.
For example, AWS Kinesis and Azure Stream Analytics are commonly used to support high-speed data pipelines across industries ranging from e-commerce to logistics.
Challenges in Implementing Real-Time Data Collection
While the benefits of real-time data are substantial, putting a real time data collection system into practice comes with its share of challenges. Organizations need to carefully address these obstacles to make sure their real-time initiatives succeed and deliver meaningful results.
1. Scalability and Performance Issues
As the volume of data grows, maintaining low latency and high throughput becomes difficult. Handling thousands or millions of data points per second requires infrastructure that can scale efficiently. Without proper design, systems may slow down or even fail during peak loads, compromising the effectiveness of real-time data processing.
2. Data Quality and Validation
Collecting data quickly doesn’t guarantee that the data is accurate or reliable. Inconsistent or noisy data from sensors, devices, or applications can lead to incorrect insights or false alerts. Ensuring data quality in real-time demands robust validation and cleaning processes integrated into the pipeline. Data Integration Techniques play a key role here, helping to harmonize disparate data sources and ensure that only high-quality, reliable data is passed through the system, though implementing these techniques can be complex.
3. Security and Privacy Concerns
Real-time data often includes sensitive information, such as patient health records or financial transactions. Protecting this data requires strong encryption, access controls, and compliance with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR. Additionally, real-time systems must be resilient against cyberattacks that could disrupt continuous data flows.
4. Integration with Legacy Systems
Many organizations operate legacy IT environments that weren’t built for real-time operations. Integrating new real-time data platforms with older databases, applications, or hardware can be challenging and may require custom connectors or middleware, adding to development time and costs.
5. Cost of Infrastructure and Tools
Building and maintaining a real-time data ecosystem covering hardware, software licenses, cloud services, and skilled personnel can be expensive. Balancing the cost against the expected real time data benefits requires careful planning and often phased implementation to ensure return on investment.
Best Practices and Strategies for Real-Time Data Collection
A successful real time data collection system isn’t built overnight it requires careful planning, the right tools, and clear objectives. Below are proven strategies organizations can follow to make real-time data work effectively and sustainably.
1. Start with Clear Business Objectives
Before investing in tools or platforms, it’s critical to define what you’re trying to achieve. Are you looking to reduce response times in emergency services? Improve fraud detection in finance? Clarifying goals helps teams choose the right types of real time information to capture and ensures the data collected serves a specific, measurable purpose.
2. Use Scalable, Cloud-Native Architectures
Modern real time data management thrives on cloud-native solutions. Platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer elastic infrastructure and integrated services for real-time data processing. This setup not only reduces deployment time but also supports seamless scaling as data volumes grow without the need for major infrastructure overhauls.
3. Prioritize Data Governance and Compliance
As real-time systems handle sensitive and often personal information, having strong governance policies in place is non-negotiable. This includes data ownership, retention policies, audit trails, and access controls. Compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific standards must be factored into every part of the real time data collection system.
4. Combine Real-Time and Historical Analytics
Real-time data offers immediate insights, but combining it with historical trends provides deeper context. For instance, a sudden spike in network traffic might be normal on certain days unless past data shows otherwise. By analyzing data analytics trends, teams can spot patterns over time, helping them avoid overreacting to anomalies and make more informed decisions.
5. Implement Monitoring and Failover Mechanisms
Real-time systems must be available 24/7. Downtime or data loss can have serious consequences, especially in sectors like healthcare or transportation. Monitoring tools should be used to track system health and detect issues early, while failover strategies (such as active-passive replication or load balancing) help maintain availability even during disruptions.
Real-Time Analytics Made Easy with Folio3
Real-time data is only as powerful as the tools and expertise used to process it. Folio3’s analytics solutions help businesses capture, manage, and interpret data as it happens, enabling faster decisions and actionable insights.
By combining robust data pipelines, real-time monitoring, and advanced analysis techniques, organizations can respond instantly to market changes, optimize operations, and improve customer experiences. With Folio3’s analytics solutions, companies gain the clarity and agility needed to turn continuous streams of data into meaningful business outcomes.
FAQs
What are examples of real-time data?
Real-time data includes patient vitals from ICU monitors, stock market price changes, GPS tracking of delivery vehicles, and live customer interactions on e-commerce platforms.
How is real-time data collected?
It’s collected using connected sensors, IoT devices, mobile apps, and APIs, which transmit data instantly to a real time data collection system for immediate use.
What is real-time data processing?
Real-time data processing refers to analyzing and acting on data as it’s generated, allowing organizations to respond to events and make decisions without delay.
Conclusion
Real-time data is no longer a luxury it’s a competitive necessity. From improving patient care and preventing financial fraud to optimizing inventory and predicting equipment failure, industries that harness real-time insights are better positioned to act fast, reduce risks, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
However, building a reliable and scalable real-time data ecosystem requires not just the right tools, but also the right expertise. At Folio3, we specialize in end-to-end data engineering services that empower organizations to seamlessly collect, process, and act on real-time information. Our experts are here to help you unlock the full potential of real-time data.
Partner with Folio3 for Exclusive Real-Time Data Solutions!