With its ever-increasing volume and complexity, data is the key to unlocking valuable insights, driving informed decision-making, and achieving a competitive edge. However, more than simply collecting data is required. Businesses need a strategic approach to harness their true potential.
Imagine your data landscape as a swirling current. Now, picture a roadmap that can transform this chaos into a source of actionable insights. This is where the concept of Enterprise Data Strategy comes into play. It’s the crucial roadmap that helps organizations navigate their data landscape.
A data strategy empowers organizations to break down data silos, mitigate shadow IT risks, and prioritize data security. It lays the foundation for using data as a strategic asset, driving better decision-making, optimizing operations, and achieving sustainable business growth.
So, keep reading this blog to understand all you need to know about Enterprise Data Strategy and why it’s become an essential tool for success in the information age.
What is an Enterprise Data Strategy?
An enterprise data strategy is a roadmap for managing and utilizing data effectively across an organization. It outlines how the company will collect, manage, and leverage its data resources to achieve business objectives, forming the backbone of an enterprise data management strategy.
Why is Data Strategy Important?
In today’s data-driven world, an enterprise data strategy framework is crucial for organizations aiming to unlock the full potential of data, generate profits, and gain a competitive edge. This approach goes beyond just data storage, emphasizing:
- Data Acquisition and Integration: Defining how data from various sources will be collected and integrated seamlessly, essential for effective management of enterprise data analytics.
- Data Quality Management: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency, providing a foundation for reliable analysis and decision-making.
- Data Accessibility and Utilization: Making data readily available to authorized personnel, fostering a data-driven culture.
Why Do Organizations Need a Data Strategy?
Enterprises today are inundated with information from multiple sources. A well-defined enterprise data strategy framework is vital to navigate this data deluge, particularly in areas like enterprise big data analytics.
Here’s why organizations prioritize a data strategy:
Enhancing Security and Risk Management: A strong data strategy establishes protocols that bolster data security, protecting sensitive information and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Combating Data Silo: A cohesive strategy prevents data compartmentalization and fosters collaboration across departments, enabling more accurate insights, such as understanding customer behavior and improving personalization.
Reducing Shadow IT: A clear data strategy minimizes the need for ad-hoc data solutions by providing centralized access, supporting data governance.
Benefits of an Enterprise Data Strategy?
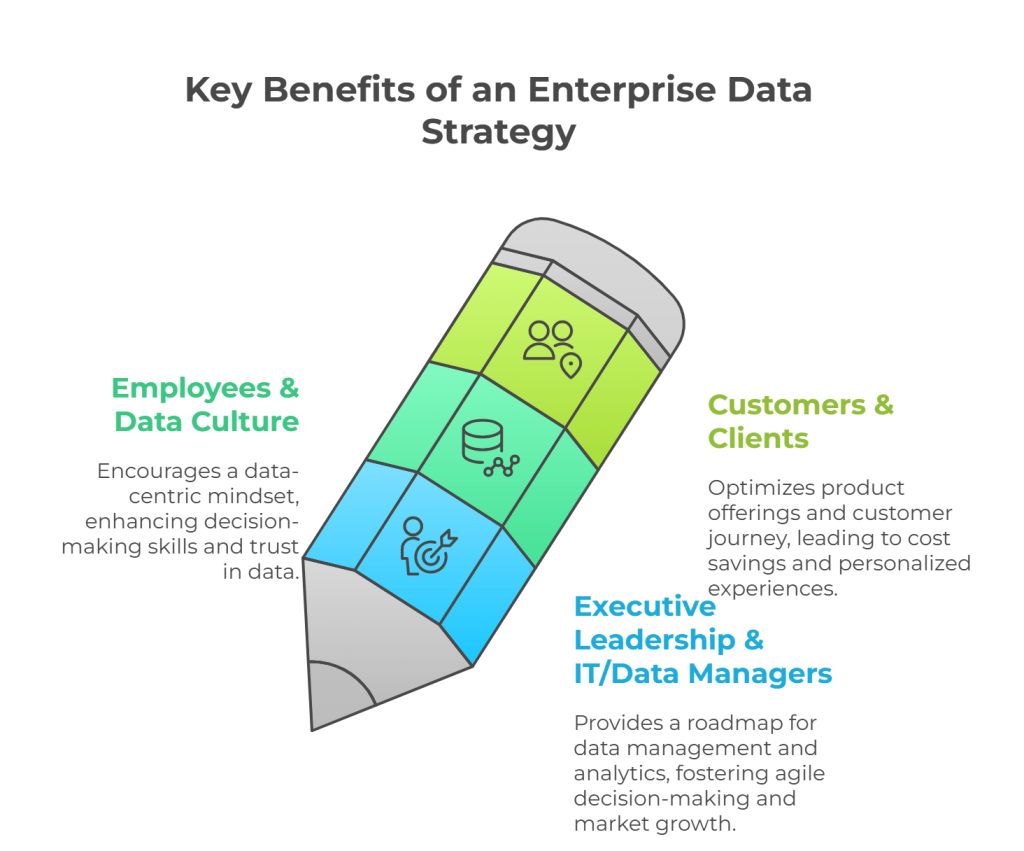
An enterprise data strategy isn’t just a fancy buzzword; it’s a powerful tool for transforming organizations and empowering people to make data-driven decisions that fuel positive business outcomes. This forms a core part of a comprehensive enterprise data strategy framework for the organization. Let’s explore the multifaceted benefits across various stakeholder groups:
Let’s explore the multifaceted benefits across various stakeholder groups:
1. Executive Leadership & IT/Data Managers
- Defined Roadmap & Agile Decision-Making: A data strategy outlines a clear path for data management and analytics initiatives, establishing expectations, timelines, and resources, which aids in the management of enterprise data analytics to foster agile decision-making.
- Market Growth & Improved Processes: With the help of data insights, businesses can identify new market opportunities, optimize internal processes, and gain a competitive edge. A data strategy helps streamline operations and improve scalability, effectively turning data into actionable insights.
- Measurable ROI & Future Project Approval: A well-defined data strategy facilitates the demonstration of return on investment (ROI) for data projects, allowing for buy-in and financial support for future initiatives, especially when showcasing the benefits of real-time analytics.
2. Employees & Data Culture
- From Data-Informed to Data-Driven: A data strategy fosters a culture where employees actively use data to guide decisions, supporting digital transformation data analytics by promoting a data-centric mindset.
- Self-Reliant Decision-Making & Skill Development: The data strategy emphasizes employee development in critical data skills, enabling them to work with and analyze data confidently. By providing access to relevant data and fostering a data-driven culture, the strategy helps employees become more self-reliant in decision-making.
- Regained Trust in Data: A robust data strategy ensures data quality and accessibility. This fosters trust among employees who rely on data for their work, leading to better decision-making and improved performance.
3. Customers & Clients
- Affordability & Improved Customer Journey: Data insights can reveal opportunities to optimize product offerings, pricing models, and marketing campaigns. This can lead to cost savings that benefit both the organization and the customer. Furthermore, by understanding customer preferences and behavior patterns, businesses can tailor the customer journey, resulting in a more personalized and satisfying experience.
- Brand Loyalty & Increased Customer Lifetime Value: Brand loyalty flourishes when customers feel valued and understood. A data strategy empowers businesses to use customer data to create a frictionless and engaging customer journey, increasing customer satisfaction and long-term brand loyalty.
Key Components of an Enterprise Data Strategy
An effective enterprise data strategy isn’t a one-time fix; it’s a dynamic roadmap that guides how an organization acquires, manages, utilizes, and ultimately uses its data for success. Here’s a breakdown of the key components that build this robust foundation:
1. Data Governance
It establishes the game’s rules by defining policies and procedures to ensure data quality, security, and regulation compliance. It also assigns clear roles and responsibilities for data stewardship and management, ensuring everyone understands their part in maintaining trustworthy information assets.
2. Data Architecture
Think of this as the blueprint for your data infrastructure. A well-designed data architecture is scalable and flexible, accommodating current and future data needs.
Crucially, it focuses on breaking down data silos by integrating data across different systems and departments. This unified view allows for seamless information flow and analysis.
3. Data Management
This component delves into the practicalities of handling data. Best data collection, storage, processing, and analysis practices are implemented. Data management tools also automate and streamline data operations, ensuring efficiency and accuracy.
4. Analytics & Insights
Data is valuable, but actionable insights are priceless. The data strategy fosters the development of advanced analytics capabilities that extract meaningful insights from the data. These insights are then translated into actionable strategies that drive informed decision-making and propel business growth.
5. Cultural Transformation
A data strategy is more than technology; it’s about empowering people. This component focuses on fostering a data-driven culture within the organization. Employees are provided with training and support to use data for decision-making, promoting a data-centric mindset across all levels.
6. Performance Monitoring
Data strategy effectiveness must be measured like any business initiative. This component establishes metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor the performance of data initiatives.
By continuously evaluating the data strategy’s impact, businesses can identify areas for improvement and demonstrate the tangible value of their data investments.
Steps to Create an Enterprise Data Strategy
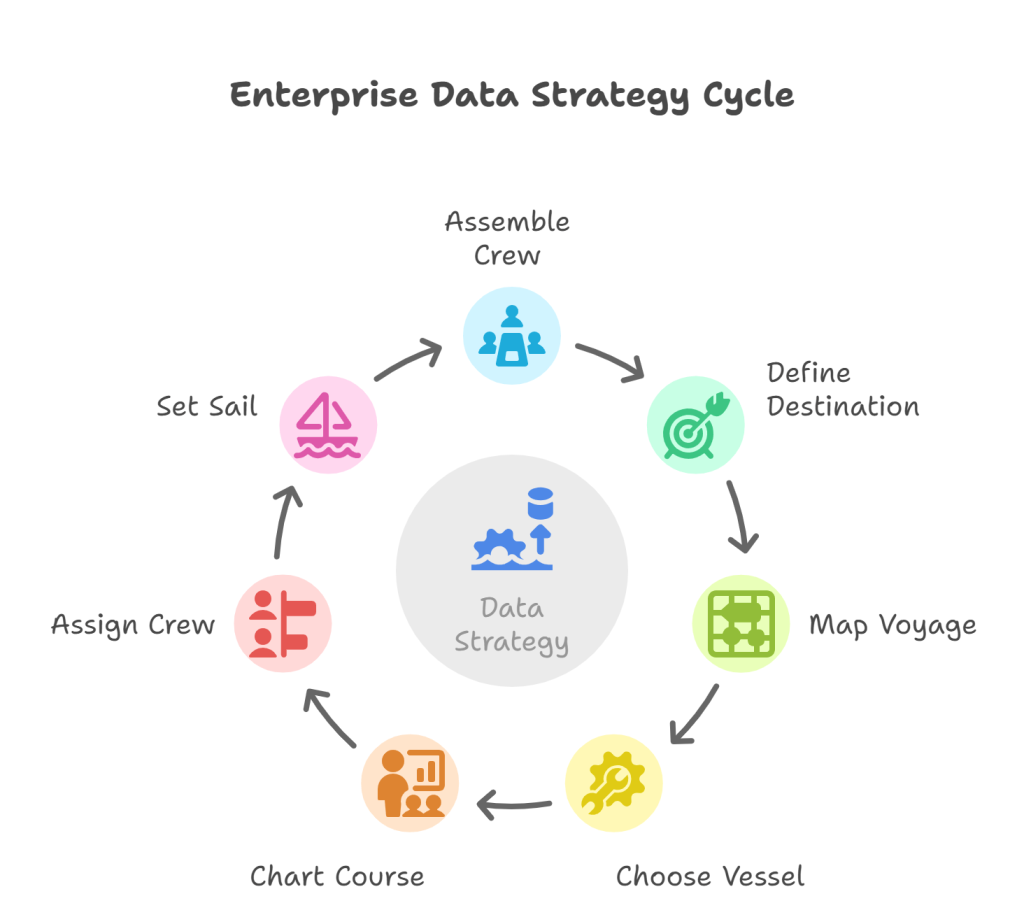
Building an effective data strategy is like embarking on a journey. You need a clear roadmap, engaged stakeholders, and a well-defined destination to navigate successfully. Here’s a breakdown of the critical steps:
Step 1: Assemble Your Crew (Identify Key Stakeholders)
- Who’s on the Ship? Identify vital organizational stakeholders – internal IT teams, business units, data consumers, project managers, executives, and finance. Their involvement is crucial for success.
- Charting the Course Together: Engage these stakeholders and identify key decision-makers. Consider their roles, influence, and interest in the data platform.
Step 2: Define Your Destination (Identify Company Goals & Objectives)
- Where Are We Headed? Ask crucial questions: Where will the data reside? What data will be collected? How will it be organized?
- Alignment is Key: Ensure your data strategy aligns with the business strategy. Review and update these goals regularly (quarterly/monthly) to maintain relevance.
Step 3: Map the Voyage (Outline Your Data Architecture)
- Laying the Groundwork: Develop a current state technical architecture snapshot. This includes an inventory of data resources like databases and content management systems.
- Building the Ship: Craft a strategy encompassing scope, ETL/ELT approach, querying, analytics, standards, security, etc.
- Future-Proofing: Create a future state architecture map for the deployment plan.
- Bridging the Gap: Map your data infrastructure, architecture, and tools. Data catalogs will help users locate datasets, and a single platform can centralize data storage.
- Setting Sail: Draft an initial architecture based on the information gathered and sequenced strategic initiatives, ensuring each deployment supports your data vision.
Step 4: Choose Your Vessel (Assess the Technology Options)
- A Fleet of Options: Explore various data management solutions like data warehouses (centralized structured data storage), data lakes (storage for both structured and unstructured data in raw format), cloud-based solutions (scalable options), and data governance tools (ensuring data quality, security, and compliance).
- Weighing Anchor: Each option has limitations. Consider scalability challenges with data warehousing, security concerns with data lakes, and potential vendor lock-in with cloud solutions.
Step 5: Charting the Course (Conduct a Strategy Session)
- Navigating the Waters: Hold a strategy session to address critical questions: What are your organization’s data needs? What data is crucial for decision-making? What data is currently collected, and how is it used? What data management processes need improvement?
Step 6: Assign the Crew (Define Organizational Structure & Responsibilities)
- Man the Helm: Establish a cross-functional team led by a data or IT leader who deeply understands the data platform architecture.
- Shared Ownership: Assign clear ownership for each part of the data pipeline. Data producers should also have accountability for the data they generate.
Step 7: Set Sail (Implement the Data Platform Architecture)
- Choosing Your Course: Select a data platform architecture such as data warehousing, data lakes, or cloud-based solutions. Customize it to your needs, incorporating data governance and quality assessment.
Systems That Help in the Implementation of Enterprise Data Strategy
Your enterprise data strategy is like a complex mission. To succeed, you’ll need a well-equipped arsenal of systems to manage, analyze, and use your data.
Here’s a breakdown of key systems that will empower your journey:
Data Analytics Platforms (DAPs)
Data Analytics platform provide a comprehensive environment for data collection, management, and analysis. Popular options include AWS, Azure, Dataiku, Snowflake, and Tableau. Choosing the right DAP depends on your specific use cases and the needs of your analytics team.
Query Engines
These act as search engines for your data, allowing users to query multiple data sources with a single query. They simplify complex data analysis and provide business insights through various interfaces like reporting dashboards, advanced analytics systems, and ad-hoc data discovery tools.
Data Quality Management System (DQMS)
This system is your quality control unit, ensuring the accuracy and consistency of your data. It uses profiling techniques, active/passive data quality checks, and data cleansing strategies to maintain high data standards.
Information Architecture Systems
These systems form the bedrock of your data strategy. They encompass data analytics, modeling, visualization, transformation, and enrichment tools.
Marketing dashboards, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and supply chain management systems are all examples of information architecture systems.
Data Governance System
Think of this as the rulebook for your data. It defines who can access and modify data, establishes data ownership, and outlines policies and procedures for effective data management.
This system includes features like authentication, information architecture, data provisioning, and data lineage tracking.
Business Intelligence Systems (BI)
BI systems are your data visualization and analysis powerhouses. They facilitate the collection, analysis, and presentation of data in a way that’s easy to understand and use for informed decision-making.
BI systems can provide a centralized platform for data management and empower you to streamline data processes across departments.
Big Data Platforms
For organizations grappling with massive datasets, big data platforms like Amazon EMR, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer the tools and infrastructure to manage and analyze vast amounts of data efficiently.
Data Integration Process
This process acts like a bridge, seamlessly combining data from disparate sources into a unified view. A well-defined data integration plan ensures your analytics team has access to the relevant information they need for insightful analysis.
Data Science Tools
These specialized tools, like Dataiku and Tableau, empower data scientists to uncover hidden patterns and trends in data from various sources. They play a crucial role in extracting meaningful insights to inform strategic decision-making.
Information Collection Systems
These systems are the data gathering workhorses. They encompass databases, file systems, and marketing dashboards, collecting, storing, and analyzing data from various sources. By transforming raw data into actionable information, they fuel your data strategy.
Conclusion
In today’s data-rich world, an Enterprise Data Strategy is your roadmap to success. It unlocks the true potential of your information, empowering informed decisions, optimized processes, and a thriving data-driven culture. So, use this strategy and take your organization towards a future fueled by valuable insights!