Understanding the distinct roles within the data domain is crucial. Two pivotal positions, data scientists and data engineers, are often confused due to their interconnected yet separate functions. While both are integral to harnessing the power of data, they serve different purposes within an organization.
A data engineer is responsible for building and maintaining the infrastructure that allows data to be collected and organized. They design, construct, and manage systems that handle large volumes of information, ensuring that data is accessible and reliable for analysis. On the other hand, a data scientist utilizes this well-structured data to perform analyses, develop models, and extract actionable insights that inform strategic decisions.
The demand for both roles is on the rise. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment for data scientists is projected to grow 36% from 2023 to 2033, much faster than the average for all occupations. Similarly, data engineers are increasingly vital, with their role being critical in managing and optimizing data infrastructure.
While data engineers focus on the architecture and systems that collect and organize data, scientists delve into it to uncover patterns and insights.
This blog explains the difference between data engineering and data analytics, which is essential for organizations aiming to leverage their data assets effectively.
What is Data Engineering?
Data engineering is the backbone of any data-driven organization. It involves designing, building, and maintaining systems that efficiently collect, store, and process data. Essentially, data engineers focus on creating the infrastructure and architecture that support the flow and availability of data for analysis.
Think of data engineering as the construction of a data pipeline. This pipeline moves raw data from various sources, such as customer interactions, financial transactions, or sensor data, into an organized and stored system. These systems often involve databases, cloud platforms, and other tools that make data easily accessible for those who need it.
One key component of data engineering is data management, which includes cleaning, transforming, and structuring data to ensure it’s ready for analysis. Without strong data engineering services, even the best data analysts or data scientists would struggle to access high-quality data, limiting the potential for meaningful insights.
What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics examines and interprets data to uncover patterns, trends, and insights that inform business decisions. Unlike data engineering, which focuses on organizing and managing data, data analytics involves extracting meaningful conclusions from the already structured and prepared data.
Data analysts use various techniques to explore data, from basic statistical methods to advanced machine learning algorithms. They work with the data provided by data engineers to answer specific business questions, identify opportunities for improvement, and help organizations make data-driven decisions.
Data analytics is about making sense of the data once it’s collected and cleaned. It involves tasks such as:
- Descriptive Analytics: Understanding what has happened in the past through data summaries and reports.
- Predictive Analytics: Using historical data to predict future trends and behaviors.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Recommending actions based on the insights gathered from data, often using optimization models.
Data analysts play a critical role in turning raw data into actionable insights. They work closely with business leaders, helping them understand data trends and guiding them in making informed decisions. Through this, data analytics helps organizations improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance their overall strategies.
Key Differences Between Data Engineering and Data Analytics
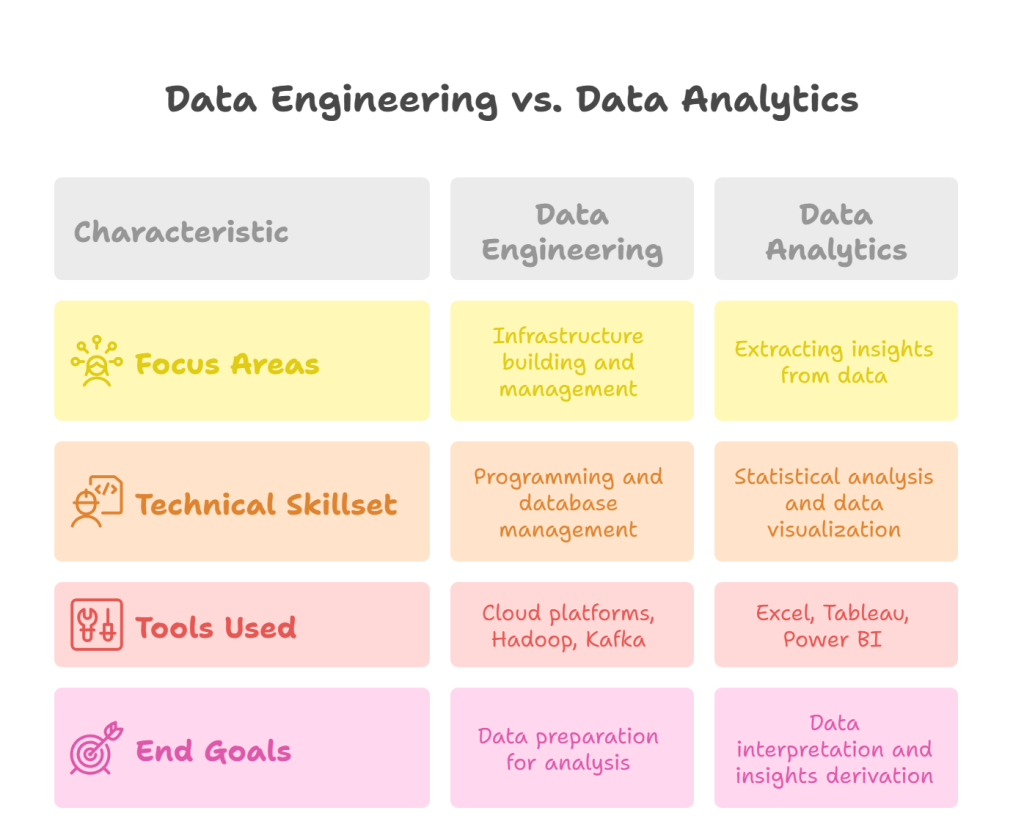
Data engineers’ and analysts’ roles differ significantly in focus, skillsets, tools, and end goals. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify their respective contributions to a data-driven organization.
Focus Areas – Infrastructure vs. Insights
- Data Engineering: A data engineer’s primary focus is building and managing the infrastructure that supports data collection, storage, and processing. They create the “pipes” that carry data from its source to where it can be analyzed. This includes handling large-scale data systems, ensuring data quality, and optimizing workflows.
- Data Analytics: On the other hand, data analysts focus on extracting insights from data. They use tools and techniques to explore, analyze, and interpret data, turning it into valuable information that can guide business decisions. Their work is about understanding trends, patterns, and anomalies to provide actionable insights.
Technical Skillset Comparison
- Data Engineering: Data engineers must have strong programming and database management skills. They typically work with languages like Python, Java, or Scala and are skilled in handling databases, data lakes, and cloud technologies. They also need a solid understanding of ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes and big data tools like Hadoop, Spark, and Kafka.
- Data Analytics: While still tech-savvy, data analysts focus more on statistical analysis and data visualization. They often use SQL, Excel, R, or Python for data analysis. Their technical expertise centers around cleaning and transforming data to create meaningful reports and dashboards using tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Google Analytics.
Tools and Technologies Used
- Data Engineering: Data engineers work with robust data platforms and tools that support the ingestion, storage, and processing large datasets. These may include cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, tools like Apache Hadoop and Apache Kafka, and relational databases (SQL-based systems like MySQL or PostgreSQL).
- Data Analytics: Data analysts use tools and technologies that allow them to analyze and visualize data easily. This includes tools like Excel, Tableau, Power BI, Python (with libraries like Pandas and Matplotlib), and statistical software like R.
End Goals – Data Preparation vs. Data Interpretation
- Data Engineering: The ultimate goal for data engineers is to prepare data for analysis by ensuring that it’s organized, cleaned, and accessible. They focus on creating efficient data systems that prepare the data for analysts and scientists.
- Data Analytics: In contrast, data analysts interpret data and derive actionable insights. They answer specific business questions by exploring and analyzing data and presenting their findings so decision-makers can easily understand and act on them. For example, in the education sector, analysts often rely on education data solutions to interpret student performance data, learning outcomes, and engagement metrics—helping institutions make informed academic and administrative decisions.
Verdict: In summary, while both roles are crucial in a data-driven environment, data engineering vs data analytics revolves around different focuses: data engineers work on data infrastructure and systems, while data analysts interpret the data to drive business decisions.
How do Data Engineering and Data Analytics Work Together?
Although data engineering and data analytics have distinct roles, they are profoundly interconnected and rely on each other to turn raw data into valuable insights. The success of data-driven initiatives in an organization depends on seamless collaboration between the two functions.
The Collaboration Process
- Data Engineering Builds the Foundation: Data engineers lay the groundwork by designing and building the infrastructure that stores and processes data. This includes setting up data pipelines, managing databases, and ensuring data flows smoothly from various sources to centralized storage systems. Without a robust data infrastructure, the data would be complex to access, inconsistent, or unusable for analysis. Organizations often bring in data integration consultants at this stage to ensure different data sources connect seamlessly, avoiding silos that could hinder analysis.
- Data Analytics Unlocks the Value: Once the data engineers have organized and made the data accessible, data analysts can step in. They use the prepared data to run analyses, identify trends, and generate insights that help guide business decisions. For example, a data analyst might take sales data stored in a cloud-based system (set up by the data engineer) and analyze it to identify customer purchasing patterns or forecast future demand.
Supporting Each Other
- Data Engineering Supports Analytics: Data engineers make data analysts’ work easier by ensuring the data is cleaned, reliable, and properly structured. They optimize data storage and accessibility so that analysts don’t waste time dealing with poor-quality data or technical issues. They might even automate data transformation processes so analysts can access real-time or near-real-time data for their analyses. Many organizations also rely on Databricks consulting services to streamline these processes, ensuring their data pipelines are scalable and optimized for advanced analytics.
- Data Analytics Drives Data Engineering Improvements: Data analytics also informs data engineering. As data analysts uncover trends and insights, they might identify new data sources or changes needed in the data infrastructure. For example, if an analyst notices a data gap that limits analysis, they can work with the data engineering team to fill that gap or improve the data pipeline to collect additional information.
End-to-End Data Lifecycle
Together, data engineers and data analysts form a team that covers the full data lifecycle. Data engineering builds the data systems and infrastructure, while data analytics takes the data, interprets it, and turns it into actionable information. The process might look something like this:
- Data Collection: Data engineers set up pipelines to collect raw data from various sources.
- Data Preparation: Data engineers clean, organize, and structure the data to make it usable.
- Data Analysis: Data analysts use the prepared data to identify trends, create reports, and answer business questions.
- Actionable Insights: The business uses the insights generated by the data analysts to make informed decisions.
In this way, both roles complement each other, and their combined efforts enable businesses to make the most of their data resources.
Which One Should You Choose?
Whether to pursue a career in data engineering or data analytics depends mainly on your interests, strengths, and career goals. Both fields offer exciting opportunities but cater to different skill sets and responsibilities. Let’s break down what each role entails to help you decide which path might fit you.
Choose Data Engineering If You Enjoy Building Systems and Working with Technology
- Technical Challenges: Data engineering might be a good fit if you enjoy tackling complex technical challenges and working with large datasets. This role requires a deep understanding of how data flows within an organization and involves designing and building systems that efficiently handle and process data. For example, industries like veterinary healthcare are increasingly adopting pet care data engineering solutions to manage patient health records, sensor data from wearable devices, and appointment scheduling systems, ensuring reliable infrastructure that supports both care providers and pet owners.
- Programming and Infrastructure: Data engineering requires proficiency in programming languages like Python, Java, or Scala and working knowledge of database management systems, cloud platforms, and big data tools. This field will likely appeal to you if you’re more inclined toward infrastructure, software engineering, and creating robust systems.
- Long-Term Impact: Data engineers build the foundation for data analysis and scientific discovery. Their work ensures businesses have reliable, scalable data infrastructures that can handle growing data needs. If you enjoy seeing the impact of your work at a systems level, data engineering could be the right career path.
Choose Data Analytics If You Enjoy Interpreting Data and Making Insights Actionable
- Problem Solving and Decision Making: If you’re more interested in making sense of data to uncover insights, then data analytics might be your calling. This role interprets data to answer specific business questions, find trends, and provide actionable insights that inform decisions. Staying aware of current data analytics stats can also help you understand how rapidly the field is expanding and where the biggest opportunities lie.
- Analytical Thinking and Communication: Data analysts need strong analytical skills and the ability to communicate findings. If you enjoy working with data to create reports, visualizations, and dashboards and can convey complex insights easily, data analytics may be best for you.
- Business Impact: Data analysts directly influence business strategy and decision-making. Data analysts help companies optimize operations, improve customer experiences, and maximize profits by finding trends and patterns. Analytics is the way to go if you’re motivated by driving tangible change through data insights.
Which Role Offers Better Career Prospects?
Both data engineering and data analytics are in high demand. However, the two roles differ in the type of opportunities they offer:
- Data Engineering: According to recent reports, data engineers are among the highest-paid professionals in the tech industry. There is a strong demand for data engineers due to the increasing need for big data management and infrastructure. Data engineering is a great choice if you’re looking for a role with a technical focus and the opportunity to work on cutting-edge technologies.
- Data Analytics: On the other hand, data analysts are also in demand as companies rely on data to drive business decisions. While the salary range may be lower than data engineering, data analytics offers a path into strategic decision-making roles and business leadership. It also allows for growth in data science, where you can further expand your skill set and career options.
Consider Your Interests and Strengths
Ultimately, the choice between data engineering and data analytics comes down to where your interests lie:
- Data engineering may be a better fit for you if you enjoy building, creating, and working with the backend of data systems.
- If you prefer to work with data to uncover insights, make decisions, and communicate findings to stakeholders, data analytics might be your role.
FAQs
Are data engineers paid more than data analysts?
Yes, data engineers generally earn higher salaries than data analysts due to the technical skills and responsibilities required.
Which is better, data engineering or data analytics?
It depends on your interest. Data engineering focuses on building data infrastructure, while data analytics involves interpreting data to drive insights.
Which is better, data analytics or data engineering?
Both roles are valuable, but your choice should depend on whether you prefer working on data infrastructure (engineering) or interpreting and analyzing data (analytics).
Are data engineers paid more than data analysts?
Data engineers typically earn more than data analysts due to their specialized technical skills and responsibilities.
Should I learn data analysis before data engineering?
Learning data analysis first is unnecessary, as data engineering can be pursued independently, but understanding data analysis can complement your engineering skills.
Which is higher, an engineer or an analyst?
Data engineers generally have higher salaries and more technical responsibilities than data analysts.
Conclusion
While data engineers and data analysts play distinct yet complementary roles, both are essential to a data-driven organization. Data engineers build the infrastructure, while data analysts unlock insights that guide business decisions.
Organizations looking to optimize their data processes can rely on Folio3 data analytics services, ensuring seamless integration, scalable infrastructure, and actionable insights. With expert guidance, you can harness the full potential of data engineering and analytics for long-term business success.



