Businesses are drowning in data. Every digital interaction—whether it’s a website visit, a social media comment, or a purchase at checkout—generates a new data point. For companies, especially in marketing, sales, and customer support, this surge isn’t just noise—it’s a goldmine of insights.
But here’s the challenge: customer data often sits in silos across multiple platforms—CRMs, email tools, eCommerce platforms, support desks—making it difficult to form a complete picture of the people they serve. Without a unified view, teams struggle to personalize campaigns, resolve issues efficiently, or identify cross-sell opportunities.
This is where customer data integration becomes essential. By combining data from various sources into a single, accurate, and up-to-date customer profile, companies can unlock smarter decision-making, boost customer satisfaction, and drive growth.
This blog breaks down what customer data integration is, how it works, and what businesses should know about the architecture and requirements needed to implement it successfully.
What is Customer Data Integration?
Customer data integration refers to the process of collecting customer information from various systems, cleaning it, and merging it into a single, consistent record. It’s not just a technical task—it’s a business necessity. Companies today interact with customers across multiple touchpoints: email, social media, websites, mobile apps, and call centers.
The projection that the global volume of data is expected to reach 175 zettabytes by 2025 originates from IDC’s “Data Age 2025” report. Each interaction generates data that tells a part of the customer’s story.
However, when data is scattered across disconnected systems, it becomes nearly impossible to understand customer behavior, preferences, or needs in real-time. According to Experian’s Global Data Management report, over 91% of companies believe bad data directly affects their revenue. That’s because fragmented or duplicate customer records result in missed opportunities, wasted marketing spend, and a subpar customer experience.
By integrating this information into a unified view, businesses can ensure that everyone, whether it’s a sales rep, support agent, or marketing manager, is working from the same, accurate customer profile. This unified view enables personalization of messages, anticipation of needs, and the development of stronger relationships. It also plays a crucial role in identifying trends and improving operational efficiency across departments.
Why Customer Data Integration Matters?
With the volume of global data growing at an unprecedented pace, businesses are under pressure to turn raw information into actionable insights. As mentioned earlier, 175 zettabytes of data are expected to be created worldwide by 2025, with a significant portion of that being customer-related. But having data isn’t enough—making sense of it across platforms is what drives results. That’s where customer data integration becomes a game-changer, especially when supported by expert data integration consulting to ensure a seamless and strategic approach.
1. Personalized Customer Experiences
Consumers expect personalized experiences—emails that address their needs, product recommendations tailored to their interests, and prompt responses to their queries. A unified customer view, enabled through customer data integration and customer experience analytics, helps brands deliver just that. According to McKinsey, companies that personalize customer experiences can increase revenue by 10% to 15% and significantly improve customer satisfaction.
2. Cross-Channel Consistency
When customer data lives in silos, it often leads to inconsistent messaging across email, ads, social media, and support. Integration ensures every platform reflects the same customer journey. Whether a customer contacts support or clicks on a sales email, the interaction feels connected and seamless. This alignment is only possible with a well-planned customer data integration architecture, often supported by expert data engineering services to ensure scalability and accuracy.
3. Real-Time Decision Making
Markets move fast—and so do customers. Businesses need access to real-time insights to act quickly. With integrated customer data and data visualization services, teams can identify trends, adjust campaigns, and respond to behavior in real time. According to Salesforce, 67% of consumers expect companies to understand their needs in real time. Integration makes this expectation achievable.
4. Enhanced Marketing and Sales Performance
Marketing teams utilize customer insights to segment audiences, target their efforts more effectively, and minimize wasted spending. Sales teams utilize these same insights to identify warm leads and close deals more efficiently. Without customer data integration, both functions are operating in the dark. With it, they’re operating with clarity. This kind of collaboration also supports customer data integration requirements, such as ensuring clean, updated, and usable data.
5. Regulatory Compliance and Data Governance
As privacy laws such as GDPR and CCPA continue to evolve, having clear visibility and control over customer data is crucial. Integration helps businesses meet compliance standards by maintaining accurate records, tracking consent, and controlling access. A well-structured customer data integration architecture plays a key role in supporting data governance across systems.
Types of Customer Data Integration
Not every business has the exact data needs or resources. That’s why there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to customer data integration. From hands-on methods to fully automated platforms, the right integration type depends on your goals, tech stack, and customer engagement strategy. Here’s a look at the most common approaches:
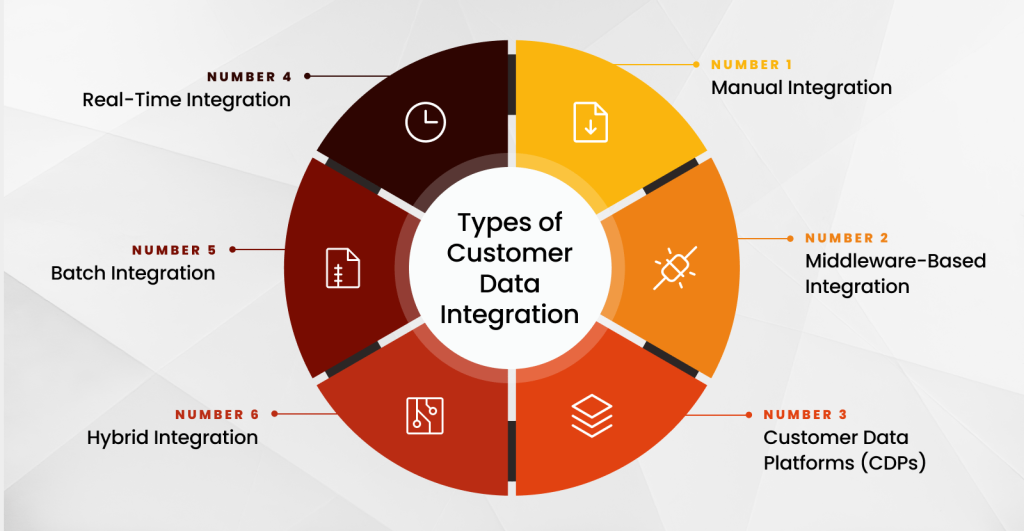
1. Manual Integration
This is the most basic form of customer data integration. It involves manually exporting and importing data between systems, like downloading a spreadsheet from a CRM and uploading it to an email platform. While it is low-cost and straightforward, it is also time-consuming and prone to errors. Manual integration might work for small businesses, but it doesn’t scale well.
2. Middleware-Based Integration
Middleware serves as a connector between systems, enabling them to exchange data without requiring direct links. Think of it as a translator that helps software “talk” to each other. This approach is flexible and works well when companies have multiple tools in play. A robust customer data integration architecture typically incorporates middleware to facilitate seamless syncing across CRM systems, support systems, and marketing tools.
3. Customer Data Platforms (CDPs)
CDPs are purpose-built platforms designed to unify and manage customer data. They automatically collect data from all touchpoints, clean it, and organize it into detailed customer profiles. This option supports real-time personalization and advanced analytics. CDPs are becoming increasingly popular as businesses seek to meet growing customer data integration requirements without building everything from scratch.
4. Real-Time Integration
Real-time integration ensures that customer data is updated instantly across all platforms. For example, if someone makes a purchase or opens a support ticket, that action is reflected across your CRM, marketing tool, and analytics dashboard immediately. This level of integration supports fast decision-making and consistent experiences, especially for customer-facing teams.
5. Batch Integration
With batch integration, data is collected and transferred at set intervals—hourly, daily, or weekly. While it’s not as immediate as real-time integration, it’s often more resource-efficient. Businesses that don’t require up-to-the-minute updates may opt for this option for tasks such as syncing email lists or updating purchase histories.
6. Hybrid Integration
Many companies use a combination of methods to meet their specific needs. A hybrid approach might include real-time integration for support systems, batch updates for marketing, and a Customer Data Platform (CDP) for centralized data storage and management. This customer data strategy enables flexibility while establishing a reliable customer data integration architecture.
Best Practices for Successful Customer Data Integration (CDI)
Building a strong foundation for customer data integration isn’t just about technology—it’s about strategy, collaboration, and long-term thinking. Even with the best tools in place, success depends on how well the data is managed and aligned with business goals.
When done right, customer data integration becomes more than just a tech project. It becomes a foundation for making smarter decisions, fostering stronger relationships, and driving faster growth. Below are some proven best practices to ensure your CDI efforts deliver real value.
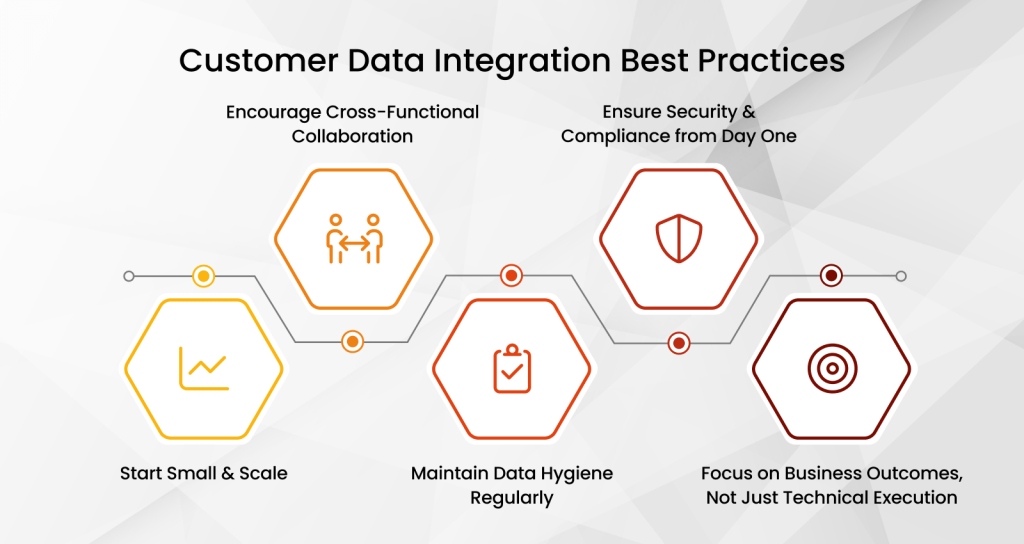
1. Start Small and Scale
It can be tempting to integrate every data source right away, but rushing in often leads to missed details and unnecessary complexity. Instead, identify a few high-impact systems, such as your CRM and email marketing platform, and begin there. This phased approach allows your team to learn, refine processes, and scale responsibly.
For example, integrating just marketing and sales data can already improve lead qualification and targeting. Once that’s working smoothly, you can expand to include customer support, website activity, and other touchpoints.
2. Encourage Cross-Functional Collaboration
Successful CDI isn’t the sole responsibility of IT. Marketing, sales, and customer service teams all utilize customer data differently, so they all require a voice in how it is integrated. Regular check-ins between departments help identify data gaps, eliminate duplicate efforts, and keep everyone aligned on goals.
Cross-functional collaboration is especially important when designing your customer data integration architecture, as each team brings insight into what data matters most and how it should be structured.
In industries like energy, oilfield data integration solutions play a similar role—bringing together exploration, drilling, and production data into one cohesive system so different teams can act on a unified, reliable view.
3. Maintain Data Hygiene Regularly
Integrating data is only helpful if the data is clean, accurate, and up-to-date. Outdated contact details, duplicate entries, or inconsistent formatting can lead to confusion and flawed insights. Establish routine checks to clean and validate your customer records. Leveraging an AI data extraction solution can further automate this process by standardizing inputs, reducing errors, and ensuring that only high-quality data flows into your systems.
According to Gartner, poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually. Addressing this early is essential to meet core customer data integration requirements and ensure a reliable customer view.
4. Ensure Security and Compliance from Day One
With regulations like GDPR and CCPA in full force, handling customer data responsibly is non-negotiable. That means protecting customer information through encryption, access controls, and regular audits. It also means maintaining consent records and ensuring transparency in how data is used.
Your integration strategy should be built with security in mind, not added as an afterthought. A secure customer data integration architecture helps prevent breaches and supports long-term compliance.
5. Focus on Business Outcomes, Not Just Technical Execution
It’s easy to get caught up in API connections and system compatibility, but the real goal of CDI is business impact. Whether it’s higher conversion rates, improved retention, or better customer service, integration efforts should be tied to measurable outcomes.
Before launching, define what success looks like—then choose the tools, teams, and tactics that support that vision. This outcome-first mindset keeps integration efforts grounded and aligned with what matters most: delivering value to the business and the customer.
FAQs
What is an example of customer integration?
Connecting a CRM system with an email marketing platform to sync customer details and communication history is a typical example of customer integration.
What is an example of data integration?
Merging sales, support, and website data into a single dashboard to get a unified view of performance is a typical example of data integration.
What is CDI in digital marketing?
CDI, or Customer Data Integration, in digital marketing refers to combining customer data from multiple touchpoints to enable personalized campaigns and better targeting.
What is meant by data integration?
Data integration is the process of combining data from different sources into a unified system for easier analysis, reporting, and decision-making.
What are the types of data integration?
Common types include manual, batch, real-time, middleware-based, CDP-driven, and hybrid integration approaches, each tailored to meet specific business needs.
What do you mean by data integrity?
Data integrity ensures that customer data is accurate, consistent, and reliable across all systems and over time.
Conclusion
Customer data integration isn’t just about connecting systems—it’s about creating a complete, accurate, and actionable view of your customers. When done right, it empowers personalized experiences, consistent communication, and smarter decision-making across marketing, sales, and support. But achieving this requires the right strategy, architecture, and ongoing maintenance.
If you’re looking to simplify the complexity of CDI and unlock the full potential of your data, Folio3’s data integration services are here to help. From planning and implementation to long-term support, we ensure your business builds a scalable, secure, and data-driven foundation that delivers insights. Let’s build better customer journeys—together.