Data-driven decision-making has become a necessity for modern businesses. With organizations generating massive amounts of information daily, turning that data into actionable insights is key to staying competitive. While terms like Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Analytics are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct yet interconnected practices.
Business Intelligence uses historical data to generate reports and dashboards, offering a clear view of past and present performance. On the other hand, Data Analytics dives deeper, using statistical models and algorithms to predict future trends and recommend actionable strategies. Understanding the difference between business intelligence and data analytics can help companies use their data to its full potential.
In this guide, we’ll explore how these two fields differ, how they complement each other, and how roles like data analyst vs. BI analyst contribute to driving business success.
What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence (BI) refers to collecting, analyzing, and visualizing historical data to provide actionable insights for businesses. It involves using tools, software, and methodologies to create comprehensive reports, dashboards, and visual presentations. Unlike predictive analytics, BI primarily focuses on understanding past and present performance to make informed decisions. These processes are often supported by business intelligence services that help organizations make sense of their data.
Companies use BI to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify operational inefficiencies, and monitor market trends. For example, a retail chain may use BI dashboards to analyze sales patterns across regions, while a manufacturing company might monitor production line data to optimize processes.
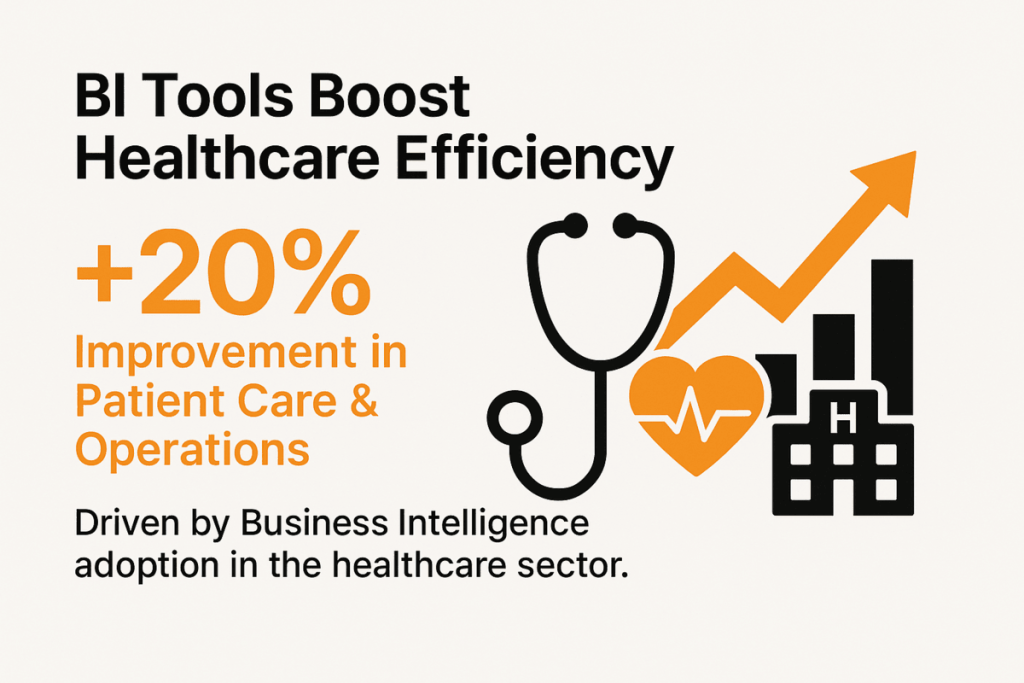
A study found a significant effect of BI tools in various sectors, including healthcare, banking, and manufacturing. Specifically, the healthcare sector reported a 20% improvement in patient care quality and operational efficiency due to the implementation of BI tools.
While both business intelligence vs data analytics play a role in decision-making, the difference between business intelligence and data analytics lies in their purpose. BI offers a retrospective view, helping organizations understand what happened and why. In contrast, data analytics often involves predictive modeling to anticipate future outcomes.
Professionals like data analyst vs BI analyst also have distinct roles. A BI analyst typically focuses on report generation, data visualization, and ensuring stakeholders receive clear insights. On the other hand, data analysts delve deeper into data sets to extract trends and create predictive models.
With a well-structured BI system, businesses can turn raw data into actionable intelligence, leading to smarter, faster decision-making.
What is Data Analytics?
Data Analytics involves examining raw data to uncover patterns, correlations, and actionable insights. Unlike Business Intelligence, which focuses on historical data to provide reports and dashboards, data analytics goes deeper by applying statistical models, algorithms, and machine learning techniques to predict future trends and recommend data-driven strategies. Many businesses rely on advanced data analytics services to gain a competitive edge.
Organizations across industries use data analytics to solve complex problems. For example, Netflix uses advanced analytics to recommend content, while Amazon applies predictive analytics to suggest products based on user behavior. Using data analytics, they are five times more likely to make faster decisions than their competitors. Additionally, research conducted by Forrester indicates that customer-obsessed firms grew 2.5 times faster than non-obsessed ones
The difference between business intelligence and data analytics becomes evident when considering their goals. While BI helps businesses understand past performance, data analytics predicts what may happen next. This predictive capability is particularly valuable in finance, healthcare, and supply chain management sectors.
When it comes to roles, the data analyst vs BI analyst distinction is precise. A data analyst uses complex algorithms to generate predictive models, identify trends, and support future decision-making. In contrast, a BI analyst focuses on designing dashboards, creating reports, and ensuring stakeholders have an accurate view of current and historical data.
By applying data analytics, companies gain a competitive edge, reduce operational risks, and enhance customer experiences. Whether predicting market demand or identifying inefficiencies, data analytics transforms how organizations operate in a data-driven world.
BI vs Data Analytics: Comparison Table
| Aspect | Business Intelligence (BI) | Data Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Purpose & Focus | Understand past performance and monitor current operations | Predict future trends and recommend proactive actions |
| 2. Key Questions Answered | What happened? Why did it happen? | What will happen next? What should be done? |
| 3. Time Orientation | Retrospective (past and present) | Predictive and prescriptive (future-oriented) |
| 4. Tools & Techniques | Tools like Power BI, Tableau, Looker for reporting and dashboards | Tools like Python, R, SAS, Apache Spark, and ML algorithms for deep data modeling and forecasting |
| 5. User Base | Business executives, managers, and non-technical users | Data scientists, technical analysts, and engineering teams |
| 6. Output | Structured reports, dashboards, KPIs | Predictive models, simulations, actionable insights |
| 7. Ideal Use Cases | – Track KPIs – Generate historical reports – Ensure compliance – Make faster decisions | – Forecast demand – Detect patterns – Optimize operations – Personalize customer experience |
| 8. Strengths | Simplifies operational decision-making with visual insights | Drives innovation and competitive advantage through predictive and prescriptive analytics |
| 9. Example | Quarterly sales dashboard to monitor regional performance | Predicting next quarter’s top-selling products using purchase behavior trends |
| 10. Collaboration | Provides the data foundation and reporting | Builds on BI data to uncover trends and generate foresight |
Core Differences Between BI and Analytics
While both Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Analytics are essential for data-driven decision-making, they serve distinct purposes. So, companies need to assess their objectives when comparing business intelligence vs data analytics. BI is the right choice if the goal is to understand past performance and gain visibility into current operations.
Conversely, data analytics is more suitable if the focus is on forecasting trends and making proactive decisions. Many organizations implement both, using BI to monitor and analyze past data while employing analytics to plan future strategies. Understanding their differences helps businesses determine which approach best suits their goals—or when to combine both as part of a broader data strategy consulting initiative.
1. Purpose and Focus
Understanding the purpose and focus of business intelligence vs data analytics is key to determining which approach aligns with your business goals. While both rely on data, they serve different objectives. BI primarily focuses on past and present data to generate actionable insights, whereas analytics goes further to predict future outcomes and recommend actions. Let’s explore how these differences impact decision-making.
BI
Business Intelligence (BI) primarily focuses on providing insights from historical data. It analyzes past performance to answer questions like “What happened?” and “Why did it happen?” BI is often used for monitoring KPIs, generating reports, and making informed operational decisions.
Data Analytics
On the other hand, Data Analytics aims to predict future outcomes and recommend actions. It addresses questions like “What will happen next?” and “What actions should be taken?” Data analytics provides a forward-looking perspective by applying statistical models, predictive algorithms, and machine learning.
2. Time Orientation
The distinction between business intelligence vs data analytics also lies in how they handle time. While BI looks back to analyze historical data for insights, analytics takes a forward-looking approach to predict trends and make proactive decisions. Knowing which approach to apply can significantly enhance business outcomes.
BI
BI operates retrospectively. It provides insights into historical and current data, allowing businesses to evaluate their performance and identify trends. For instance, a BI dashboard might display last quarter’s regional sales.
Analytics
Data Analytics is future-oriented. It uses predictive and prescriptive analytics to forecast potential scenarios. Retailers, for example, often rely on data analytics to predict customer demand based on past purchasing behaviors.
3. Tools and Techniques
Choosing the right tools and techniques is crucial when comparing business intelligence vs data analytics. While BI tools are designed for visualization and reporting, analytics tools delve deeper with predictive modeling and advanced algorithms. Let’s explore how each set of tools contributes to effective decision-making.
BI
BI systems use tools like Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and Looker to visualize and present data. Organizations often engage in Tableau consulting to optimize their dashboards and reporting processes, ensuring that visualizations deliver actionable insights efficiently. These platforms generate easy-to-read reports and dashboards that enable stakeholders to make quick decisions.
Analytics
Data analytics relies on advanced tools like Python, R, SAS, and Apache Spark. These tools are designed for data modeling, statistical analysis, and predictive forecasting. Additionally, machine learning algorithms are commonly used in analytics for deeper insights.
4. User Base
BI and analytics solutions users often have distinct roles within an organization. BI systems cater to business leaders and managers who need quick insights, while technical professionals predominantly use data analytics to solve complex problems. Understanding this difference helps organizations align tools with user expertise.
BI
Business Intelligence is typically used by business executives, department managers, and non-technical users who need to monitor operational performance. The reports generated by BI analysts often provide a clear and visual overview of key business metrics.
Analytics
Data scientists, analysts, and technical experts commonly use Data Analytics. These professionals apply advanced analytical models to solve complex business problems, often working closely with IT and engineering teams.
5. Output
The output is a significant factor when considering the difference between business intelligence and data analytics. BI typically generates structured reports and dashboards that visualize past performance, while analytics provides predictive insights and actionable recommendations. Knowing what type of output you need can help determine the right solution for your business.
BI
The primary output of BI systems is structured reports, dashboards, and visualizations. Examples of business intelligence reports might include sales reports, operational summaries, and inventory management dashboards. These outputs help organizations track progress and make data-backed decisions.
Analytics
Data Analytics delivers predictive models, actionable insights, and simulations. For instance, a predictive model may forecast which products will see increased demand in the next quarter. Based on these insights, analysts recommend pricing strategies or inventory adjustments.
When to Use BI vs. When to Use Analytics?
Whether to rely on business intelligence or data analytics depends on your organization’s specific goals and the insights you seek. While both play a crucial role in data-driven decision-making, they serve different purposes. Here’s how to determine the right fit for your needs:
When to Use Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business intelligence is ideal when you need to:
- Monitor and Track Performance: Use BI dashboards to visualize KPIs and ensure your business is on track. For instance, companies using BI systems experience up to a 23% increase in operational efficiency by identifying bottlenecks quickly.
- Generate Historical Reports: BI tools consolidate past data to create reports for performance analysis. Executives often use BI reports to track sales trends, customer satisfaction, or production output.
- Support Data-Driven Decisions: BI reporting systems provide intuitive visuals and summaries when stakeholders need clear and actionable insights. Businesses using BI for reporting are five times more likely to make faster decisions.
- Ensure Compliance and Auditing: Industries with strict regulations, like finance and healthcare, rely on business intelligence reports examples to meet compliance standards and generate audit trails.
When to Use Data Analytics?
Data analytics is more appropriate when you need to:
- Predict Future Outcomes: Analytics leverages machine learning and predictive models to forecast market trends, sales, or operational risks. Many organizations look at recent data analytics stats on market adoption and revenue impact to justify investing in these predictive capabilities, ensuring the effort aligns with industry growth.
- Identify Hidden Patterns: Unlike BI’s historical focus, analytics digs deeper into data to uncover correlations and root causes. Data analysts excel at answering “why” specific trends are occurring.
- Conduct Experimentation and Optimization: Businesses looking to optimize marketing campaigns or product performance use data analytics to run A/B tests and measure results.
- Enhance Personalization: E-commerce platforms use data analytics to recommend products based on customer behavior, leading to 40% higher sales conversion rates.
Collaboration Between BI and Analytics
It’s important to note that BI and data analytics are not mutually exclusive. The best results come from using both. While a BI analyst may generate reports to assess past performance, a data analyst can further interpret that data to predict future trends. Integrating both approaches empowers organizations to stay competitive by making well-informed decisions.
Ultimately, knowing the difference between business intelligence and data analytics enables companies to apply the right tools at the right time. Whether visualizing data to track KPIs or using algorithms to forecast future outcomes, Folio3 data analytics solutions help organizations integrate BI and analytics for a comprehensive and actionable data strategy.